Abstract
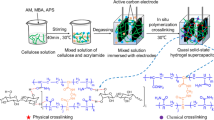
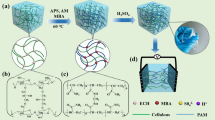
The PVA hydrogel electrolyte holds significant promise in flexible supercapacitors owing to its high conductivity and foldability. However, the poor mechanical properties and low capacitance of pure PVA hydrogel electrolytes need to be further solved. Herein, phosphoric acid was employed to dissolve cellulose, which solution was used to directly mix with PVA, and formed physical crosslinking point in composite hydrogel through a freeze-thawing cycle. The interaction between PVA and cellulose molecules plays a critical role in forming the PVA-Cellulose composite hydrogel. When the cellulose content in the hydrogel is 5%, the prepared composite hydrogel (P-CE 5%) exhibited impressive tensile strength of 306 kPa and elongation at break of 1106%. After adding 8 mol/L LiCl, the assembled supercapacitor with composite hydrogel (P-CE-L8) electrolyte exhibited a high area capacitance of 217 mF cm−2. Moreover, the incorporation of phosphoric acid and LiCl also conferred excellent frost resistance to the hydrogel electrolyte, as indicated by a capacitance retention rate of 92% after returning to room temperature from low temperature. Notably, the hydrogel exhibited remarkable self-healing capabilities, with its specific capacitance reaching 95% after wound healing. Therefore, this PVA-cellulose hydrogel electrolyte emerges as a promising candidate for the application in the energy storage device assembly.







Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
The authors confirm that the data supporting the findings of this study are available within the article.
References
Alves L, Medronho B, Filipe A, Romano A, Rasteiro MG, Lindman B, Topgaard D, Davidovich I, Talmon Y (2021) Revisiting the dissolution of cellulose in H3PO4(aq) through cryo-TEM. PTssNMR DWS Carbohydr Polym 252:117122. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.carbpol.2020.117122
Batisse N, Raymundo-Piñero E (2017) A self-standing hydrogel neutral electrolyte for high voltage and safe flexible supercapacitors. J Power Sources 348:168–174. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jpowsour.2017.03.005
Chang C, Lue A, Zhang L (2008) Effects of crosslinking methods on structure and properties of Cellulose/PVA hydrogels. Macromol Chem Physic 209:1266–1273. https://doi.org/10.1002/macp.200800161
Chen J, Shi X, Ren L, Wang Y (2017) Graphene oxide/PVA inorganic/organic interpenetrating hydrogels with excellent mechanical properties and biocompatibility. Carbon 111:18–27. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.carbon.2016.07.038
Chen G, Hong FF, Yuan J, Li L, Fang M, Wei W, Wang X, Wei Y (2022) Super solvent of cellulose with extra high solubility for tunable cellulose structure with versatile application. Carbohydr Polym 296:119917. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.carbpol.2022.119917
Conte P, Maccotta A, De Pasquale C, Bubici S, Alonzo G (2009) Dissolution mechanism of crystalline cellulose in H3PO4 as assessed by high-field NMR spectroscopy and fast field cycling NMR relaxometry. J Agr Food Chem 57:8748–8752. https://doi.org/10.1021/jf9022146
Das D, Bhattacharjee S, Bhaladhare S (2023) Preparation of cellulose hydrogels and hydrogel nanocomposites reinforced by crystalline cellulose nanofibers (CNFs) as a water reservoir for agriculture use. ACS Appl Polym Mater 5:2895–2904. https://doi.org/10.1021/acsapm.3c00109
Guo L, Ma W-B, Wang Y, Song X-Z, Ma J, Han X-D, Tao X-Y, Guo L-T, Fan H-L, Liu Z-S, Zhu Y-B, Wei X-Y (2020) A chemically crosslinked hydrogel electrolyte based all-in-one flexible supercapacitor with superior performance. J Alloy Compd 843:155895. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jallcom.2020.155895
He M, Chen H, Zhang X, Wang C, Xu C, Xue Y, Wang J, Zhou P, Zhao Q (2018) Construction of novel cellulose/chitosan composite hydrogels and films and their applications. Cellulose 25:1987–1996. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10570-018-1683-9
Heng Y, Xie T, Wang X, Chen D, Wen J, Chen X, Hu D, Wang N, Wu YA (2021) Raw cellulose/polyvinyl alcohol blending separators prepared by phase inversion for high-performance supercapacitors. Nanotechnology 32:095403. https://doi.org/10.1088/1361-6528/abcb62
Hou C, Huang T, Wang H, Yu H, Zhang Q, Li Y (2013) A strong and stretchable self-healing film with self-activated pressure sensitivity for potential artificial skin applications. Sci Rep 3:3138. https://doi.org/10.1038/srep03138
Hu M, Wang J, Liu J, Zhang J, Ma X, Huang Y (2018) An intrinsically compressible and stretchable all-in-one configured supercapacitor. ChemComm 54:6200–6203. https://doi.org/10.1039/c8cc03375g
Huang Y, Zhong M, Huang Y, Zhu M, Pei Z, Wang Z, Xue Q, Xie X, Zhi C (2015) A self-healable and highly stretchable supercapacitor based on a dual crosslinked polyelectrolyte. Nat Commun 6:10310. https://doi.org/10.1038/ncomms10310
Huang Y, Zhong M, Shi F, Liu X, Tang Z, Wang Y, Huang Y, Hou H, Xie X, Zhi C (2017) An intrinsically stretchable and compressible supercapacitor containing a polyacrylamide hydrogel electrolyte. Angew Chem Int Edit 56:9141–9145. https://doi.org/10.1002/anie.201705212
Irvin CW, Satam CC, Liao J, Russo PS, Breedveld V, Meredith JC, Shofner ML (2021) Synergistic reinforcement of composite hydrogels with nanofiber mixtures of cellulose nanocrystals and chitin nanofibers. Biomacromol 22:340–352. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.biomac.0c01198
Li L, Lu F, Wang C, Zhang F, Liang W, Kuga S, Dong Z, Zhao Y, Huang Y, Wu M (2018a) Flexible double-cross-linked cellulose-based hydrogel and aerogel membrane for supercapacitor separator. J Mater Chem A 6:24468–24478. https://doi.org/10.1039/c8ta07751g
Li Y, Deng Z, Peng J, Chen E, Yu Y, Li X, Luo J, Huang Y, Zhu J, Fang C, Li Q, Han J, Huang Y (2018b) A P2-Type layered superionic conductor Ga-doped Na2 Zn2TeO6 for all-solid-state sodium-ion batteries. Chem Eur J 24:1057–1061. https://doi.org/10.1002/chem.201705466
Li X, Zhang Y, Chen J, Wang Y, Cheng Z, Chen X, Guo M (2023) A cellulose-based interpenetrating network hydrogel electrolyte for flexible solid-state supercapacitors. Cellulose 30:2399–2412. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10570-023-05048-4
Liu Q, Qiu J, Yang C, Zang L, Zhang G, Sakai E (2020) High-performance PVA/PEDOT:PSS hydrogel electrode for all-gel-state flexible supercapacitors. Adv Mater Technol 6:2000919. https://doi.org/10.1002/admt.202000919
Lu N, Na R, Li L, Zhang C, Chen Z, Zhang S, Luan J, Wang G (2020) Rational design of antifreezing organohydrogel electrolytes for flexible supercapacitors. ACS Appl Energy Mater 3:1944–1951. https://doi.org/10.1021/acsaem.9b02379
Meng D, Wu C, Hu Y, Jing Y, Zhang X, Mahmud S, Su SP, Zhu J (2022) Ingenious synthesis of chitosan-based porous carbon supercapacitors with large specific area by a small amount of potassium hydroxide. J Energy Storage 51:104341. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.est.2022.104341
Moon WG, Kim GP, Lee M, Song HD, Yi J (2015) A biodegradable gel electrolyte for use in high-performance flexible supercapacitors. ACS Appl Mater Inter 7:3503–3511. https://doi.org/10.1021/am5070987
Peng X, Liu H, Yin Q, Wu J, Chen P, Zhang G, Liu G, Wu C, Xie Y (2016) A zwitterionic gel electrolyte for efficient solid-state supercapacitors. Nat Commun 7:11782. https://doi.org/10.1038/ncomms11782
Peng Z, Zou Y, Xu S, Zhong W, Yang W (2018) High-performance biomass-based flexible solid-state supercapacitor constructed of pressure-sensitive lignin-based and cellulose hydrogels. ACS Appl Mater Inter 10:22190–22200. https://doi.org/10.1021/acsami.8b05171
Rui-Hong X, Peng-Gang R, Jian H, Fang R, Lian-Zhen R, Zhen-Feng S (2016) Preparation and properties of graphene oxide-regenerated cellulose/polyvinyl alcohol hydrogel with pH-sensitive behavior. Carbohydr Polym 138:222–228. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.carbpol.2015.11.042
Saadiah MA, Samsudin AS (2018) Electrical study on carboxymethyl cellulose-polyvinyl alcohol based bio-polymer blend electrolytes. IOP Conf Ser: Mater Sci Eng 342:012045. https://doi.org/10.1088/1757-899x/342/1/012045
Saadiah MA, Nagao Y, Samsudin AS (2020) Proton (H+) transport properties of CMC–PVA blended polymer solid electrolyte doped with NH4NO3. Int J Hydrog Energy 45:14880–14896. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijhydene.2020.03.213
Wang C, Wallace GG (2015) Flexible electrodes and electrolytes for energy storage. Electrochim Acta 175:87–95. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.electacta.2015.04.067
Wang Y, Lv C, Ji G, Hu R, Zheng J (2020) An all-in-one supercapacitor with high stretchability via a facile strategy. J Mater Chem A 8:8255–8261. https://doi.org/10.1039/d0ta00757a
Wang J, Wu Y, Chen W, Wang H, Dong T, Bai F, Li X (2022) Cellulose nanofibrils with a three-dimensional interpenetrating network structure for recycled paper enhancement. Cellulose 29:3773–3785. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10570-022-04496-8
Wu X, Xie Y, Xue C, Chen K, Yang X, Xu L, Qi J, Zhang D (2019) Preparation of PVA-GO composite hydrogel and effect of ionic coordination on its properties. Mater Res Express 6:075306. https://doi.org/10.1088/2053-1591/ab11ee
Yin J, Wei K, Zhang J, Liu S, Wang X, Wang X, Zhang Q, Qin Z, Jiao T (2022) MXene-based film electrode and all-round hydrogel electrolyte for flexible all-solid supercapacitor with extremely low working temperature. Cell Rep Phys Sci 3:100893. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.xcrp.2022.100893
Zhang H, Xia H, Zhao Y (2012) Poly(vinyl alcohol) Hydrogel can autonomously self-heal. ACS Macro Lett 1:1233–1236. https://doi.org/10.1021/mz300451r
Zhang XF, Ma X, Hou T, Guo K, Yin J, Wang Z, Shu L, He M, Yao J (2019) Inorganic salts induce thermally reversible and anti-freezing cellulose hydrogels. Angew Chem Int Edit 58:7366–7370. https://doi.org/10.1002/anie.201902578
Zhang Y, Wu D, Huang F, Cai Y, Li Y, Ke H, Lv P, Wei Q (2022) “Water-in-salt” nonalkaline gel polymer electrolytes enable flexible zinc-air batteries with ultra-long operating time. Adv Funct Mater 32:2203204. https://doi.org/10.1002/adfm.202203204
Zhang M, Wang Y, Liu K, Liu Y, Xu T, Du H, Si C (2023) Strong, conductive, and freezing-tolerant polyacrylamide/PEDOT:PSS/cellulose nanofibrils hydrogels for wearable strain sensors. Carbohydr Polym 305:120567. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.carbpol.2023.120567
Zhong C, Deng Y, Hu W, Qiao J, Zhang L, Zhang J (2015) A review of electrolyte materials and compositions for electrochemical supercapacitors. Chem Soc Rev 44:7484–7539. https://doi.org/10.1039/c5cs00303b
Zhou G, Yang L, Li W, Chen C, Liu Q (2020) A regenerable hydrogel electrolyte for flexible supercapacitors. iScience 23:101502. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.isci.2020.101502
Zhu K-h, Han X-d, Ye S-f, Cui P-x, Dou L-y, Ma W-b, Heng S, Tao X-y, Wei X-y (2022a) Flexible all-in-one supercapacitors enabled by self-healing and anti-freezing polymer hydrogel electrolyte. J Energy Storage 53:105096. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.est.2022.105096
Zhu X, Ji C, Meng Q, Mi H, Yang Q, Li Z, Yang N, Qiu J (2022b) Freeze-tolerant hydrogel electrolyte with high strength for stable operation of flexible zinc-ion hybrid supercapacitors. Small 18:e2200055. https://doi.org/10.1002/smll.202200055
Funding
The authors are grateful for the support of the Large-scale instrument opening fund of Hunan Normal University (21CSZ076); Natural Science Foundation of Hunan Province of China (2023JJ30409); Changsha Natural Science Foundation (kq2202445); Opening Fund of Key Laboratory of Chemical Biology and Traditional Chinese Medicine Research, Hunan Normal University (KLCBTCM R201811); Key Scientific Research Projects of Hunan Provincial Department of Education (21A0062); Excellent Youth Project of Hunan Provincial Department of Education (22B0045).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
All authors contributed to the study conception and design. Material preparation, data collection and analysis were performed by Ru Zhang, Chunhuai Yao, Wenyan Yang, and Chengfeng Wu. The first draft of the manuscript was written by Ru Zhang and all authors commented on previous versions of the manuscript. All authors read and approved the final manuscript.
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing interests.
Conflicts of interest
The authors declare that they have no known competing financial interests or personal relationships that could have appeared to influence the work reported in this paper.
Ethics approval and consent to participate
All authors have consented to participate on the manuscript.
Consent for publication
All authors have approved the final version of the manuscript.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Zhang, R., Wu, C., Yao, C. et al. Preparation of PVA based multifunctional hydrogel electrolyte reinforced by phosphoric acid-dissolved-cellulose and its application in quasi-solid supercapacitors. Cellulose 31, 1071–1087 (2024). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10570-023-05661-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10570-023-05661-3