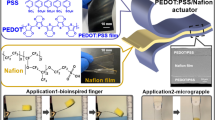
Abstract
Ionic electroactive polymer actuators with high performance and high durability for developing active components have attracted significant attention in micrototal analysis systems (μTAS) and microelectromechanical systems. Herein, we introduced a novel ionic actuator fabricated with a free-standing bacterial cellulose (BC) reinforced poly(diallyldimethylammonium chloride) (PDADMAC) polyelectrolyte membrane sandwiched between two free-standing conductive polymer membranes of poly(3,4-ethylenedioxythiophene) doped with poly(4-styrenesulfonate) (PEDOT/PSS) by hot pressing. Adding BC as reinforcement in the PDADMAC resulted in the preparation of a free-standing polyelectrolyte membrane with high mechanical properties. As a result, the hot-pressed BC-reinforced PDADMAC actuator exhibited excellent actuation performances with a large peak displacement of approx. 6 mm, a large bending strain of 0.16%, high reproducibility, high stability and durability up to 8 h. Simultaneously, we further verified the biomimetic applications of the actuators in microsystems including microgripper, bionic micro-finger, and micromixer in microfluidics.
Graphical abstract






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Chang L, Chen H, Zhu Z, Li B (2012) Manufacturing process and electrode properties of palladium-electroded ionic polymer–metal composite. Smart Mater Struct 21:065018. https://doi.org/10.1088/0964-1726/21/6/065018
Chang X, Chen L, Chen J, Zhu Y, Guo Z (2021) Advances in transparent and stretchable strain sensors. Adv Compos Hybrid Mater 4:435–450. https://doi.org/10.1007/s42114-021-00292-3
Chen I, Cottinet P, Tsai S, Foster B, Liang R, Wang B, Zhang C (2012) Improved performance of carbon nanotube bucky paper and ionic-liquid-in-Nafion actuators for rapid response and high durability in the open air. Sens Actuators B Chem 171–172:515–521. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.snb.2012.05.022
Chircov C, Grumezescu AM (2022) Microelectromechanical systems (MEMS) for biomedical applications. Micromachines 13:164. https://doi.org/10.3390/mi13020164
Chung CK, Fung PK, Hong YZ, Ju MS, Lin CCK, Wu TC (2006) A novel fabrication of ionic polymer-metal composites (IPMC) actuator with silver nano-powders. Sens Actuators B Chem 117:367–375. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.snb.2005.11.021
El-Gendi H, Taha TH, Ray JB, Saleh AK (2022) Recent advances in bacterial cellulose: a low-cost effective production media, optimization strategies and applications. Cellulose 29:7495–7533. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10570-022-04697-1
French AD (2014) Idealized powder diffraction patterns for cellulose polymorphs. Cellulose 21:885–896. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10570-013-0030-4
French AD (2017) Glucose, not cellobiose, is the repeating unit of cellulose and why that is important. Cellulose 24:4605–4609. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10570-017-1450-3
Hara Y, Yamaguchi Y (2014) Development of a paper actuator with PEDOT:PSS thin-films as an electrode. Actuators 3:285–292. https://doi.org/10.3390/act3040285
Iguchi M, Yamanaka S, Budhiono A (2000) Bacterial cellulose-a masterpiece of nature’s arts. J Mater Sci 35:261–270. https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1004775229149
Jeon JH, Oh IK, Kee CD, Kim SJ (2010) Bacterial cellulose actuator with electrically driven bending deformation in hydrated condition. Sens Actuators B Chem 146:307–313. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.snb.2010.02.046
Jung SY, Ko SY, Park JO, Park S (2016) Enhanced ionic polymer-metal composite actuator with pore size-controlled porous Nafion membrane using silica sol–gel process. J Intell Mater Syst Struct 28:1514–1523. https://doi.org/10.1177/1045389X1666755
Kikuchi K, Sakamoto T, Tsuchitani S, Asaka K (2011) Comparative study of bending characteristics of ionic polymer actuators containing ionic liquids for modeling actuation. J Appl Phys 109:073505–073515. https://doi.org/10.1063/1.3556434
Kim SS, Jeon JH, Kee CD, Oh IK (2013) Electro-active hybrid actuators based on freeze-dried bacterial cellulose and PEDOT:PSS. Smart Mater Struct 22:085026. https://doi.org/10.1088/0964-1726/22/8/085026
Kim SS, Jeon JH, Kim H, Kee CD, Oh IK (2015) High-fidelity bioelectronic muscular actuator based on graphene-mediated and TEMPO-oxidized bacterial cellulose. Adv Funct Mater 25:3560–3570. https://doi.org/10.1002/adfm.201500673
Lee JH, Jung JP, Jang E, Lee KB, Hwang YJ, Min BK, Kim JH (2016) PEDOT-PSS embedded comb copolymer membranes with improved CO2 capture. J Membr Sci 518:21–30. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.memsci.2016.06.025
Lu L, Liu J, Hu Y, Zhang Y, Randriamahazaka H, Chen W (2012) Highly stable air working bimorph actuator based on a graphene nanosheet/carbon nanotube hybrid electrode. Adv Mater 24:4317–4321. https://doi.org/10.1002/adma.201201320
Mohith S, Navin Karanth P, Kulkarni SM (2019) Recent trends in mechanical micropumps and their applications: a review. Mechatronics 60:34–55. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.mechatronics.2019.04.009
Nan M, Wang F, Kim S, Li H, Jin Z, Bang D, Kim C, Park J, Choi E (2019) Ecofriendly high-performance ionic soft actuators based on graphene-mediated cellulose acetate. Sens Actuators B Chem 301:127–127. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.snb.2019.127127
Onishi K, Sewa S, Asaka K, Fujiwara N, Oguro K (2001) Morphology of electrodes and bending response of the polymer electrolyte actuator. Electrochim Acta 46:737–743. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0013-4686(00)00656-3
Paratore F, Bacheva V, Bercovici M, Kaigala G (2022) Reconfigurable microfluidics. Nat Rev Chem 6:70–80. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41570-021-00343-9
Pei Q, Inganaes O (1992) Electrochemical applications of the bending beam method. 1. Mass transport and volume changes in polypyrrole during redox. J Phys Chem 96:10507–10514. https://doi.org/10.1021/j100204a071
Phisalaphong M, Jatupaiboon N (2008) Biosynthesis and characterization of bacteria cellulose-chitosan film. Carbohyd Polym 74(3):482–488. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.carbpol.2008.04.004
Qiu K, Netravali AN (2012) Bacterial cellulose-based membrane-like biodegradable composites using cross-linked and noncross-linked polyvinyl alcohol. J Mater Sci 47:6066–6075. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10853-012-6517-9
Shi M, Yeatman EM (2021) A comparative review of artificial muscles for microsystem applications. Microsyst Nanoeng 7:95. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41378-021-00323-5
Tamagawa H, Watanabe H, Sasaki M (2009) Bending direction change of IPMC by the electrode modification. Sens Actuators B Chem 140:542–548. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.snb.2009.04.054
Tiwari R, Garcia E (2011) The state of understanding of ionic polymer metal composite architecture: a review. Smart Mater Struct 20:083001. https://doi.org/10.1088/0964-1726/20/8/083001
Ullah H, Badshah M, Mäkilä E, Salonen J, Shahbazi M, Santos H, Khan T (2017) Fabrication, characterization and evaluation of bacterial cellulose-based capsule shells for oral drug delivery. Cellulose 24(3):1445–1454. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10570-017-1202-4
Wang F, Jeon JH, Park S, Kee CD, Kim SJ, Oh IK (2016a) A soft biomolecule actuator based on a highly functionalized bacterial cellulose nano-fiber network with carboxylic acid groups. Soft Matter 12:246–254. https://doi.org/10.1039/C5SM00707K
Wang F, Jeon JH, Kim SJ, Park JO, Park S (2016b) An eco-friendly ultra-high performance ionic artificial muscle based on poly (2-acrylamido-2-methyl-1-propanesulfonic acid) and carboxylated bacterial cellulose. J Mater Chem B 4:5015–5024. https://doi.org/10.1039/C6TB01084A
Wang D, Lu C, Zhao J, Han S, Wu M, Chen W (2017) High energy conversion efficiency conducting polymer actuators based on PEDOT:PSS/MWCNTs composite electrode. RSC Adv 7:31264. https://doi.org/10.1039/C7RA05469F
Wang S, Li T, Chen C, Kong W, Zhu S, Dai J, Diaz AJ, Hitz E, Solares SD, Li T, Hu L (2018) Transparent, anisotropic biofilm with aligned bacterial cellulose nanofibers. Adv Funct Mat 28:1707491. https://doi.org/10.1002/adfm.201707491
Wang F, Li Q, Park J, Zheng S, Choi E (2021a) Ultralow voltage high-performance bioartificial muscles based on ionically crosslinked polypyrrole-coated functional carboxylated bacterial cellulose for soft robots. Adv Funct Mater 31:2007749. https://doi.org/10.1002/adfm.202007749
Wang Y, Tang G, Zhao C, Wang K, Wang J, Ru J, Sheng J, Chang L, Li L (2021b) Experimental investigation on the physical parameters of ionic polymer metal composites sensors for humidity perception. Sens Actuators B Chem 345:130421. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.snb.2021.130421
Wang Y, Wang F, Kong Y, Wang L, Li Q (2022a) Novel ionic bioartificial muscles based on ionically crosslinked multi-walled carbon nanotubes-mediated bacterial cellulose membranes and PEDOT:PSS electrodes. Smart Mater Struct 31:025023. https://doi.org/10.1088/1361-665X/ac4576
Wang F, Kong Y, Shen F, Wang Y, Wang D, Li Q (2022b) High-performance microfibrillated cellulose-based low voltage electroactive ionic artificial muscles in bioinspired applications. Compos Part B 228:109436. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.compositesb.2021.109436
Wu Y, Minamikawa H, Nakazumi T, Hara Y (2020) Actuation properties of paper actuators fabricated using PEDOT/PSS electrode films. J Oleo Sci 69:1331–1337. https://doi.org/10.5650/jos.ess20113
Xu Y, Jia W, Zhang Y, Wang F, Zhao G, Zang D (2021) Mechanical properties analysis and surface composition research of Ag-IPMC. Sens Actuators A Phys 319:112565. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.sna.2021.112565
Zhang M, Du H, Liu K, Nie S, Xu T, Zhang X, Si C (2021) Fabrication and applications of cellulose-based nanogenerators. Adv Compos Hybrid Mater 4:865–884. https://doi.org/10.1007/s42114-021-00312-2
Zhao C, Wang Y, Tang G, Ru J, Zhu Z, Li B, Guo C, Li L, Zhu D (2022) Ionic flexible sensors: mechanisms, materials, structures, and applications. Adv Funct Mater 32:2110417. https://doi.org/10.1002/adfm.202110417
Zhou J, Anjum DH, Lubineau G, Li EQ, Thoroddsen ST (2015) Unraveling the order and disorder in poly(3,4-ethylenedioxythiophene)/poly (styrenesulfonate) nanofilms. Macromolecules 48:5688–5696. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.macromol.5b00851
Zhu Y, Chang T (2015) A review of microelectromechanical systems for nanoscale mechanical characterization. J Micromech Microeng 25:093001. https://doi.org/10.1088/0960-1317/25/9/093001
Acknowledgments
This research was supported by the Science Foundation of Zhejiang Sci-Tech University (Grant No. 21022315-Y) and the National Natural Science Foundation of China under Grant Nos. 51905487, 51525504, and 52175215.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Conceptualization: FW; Methodology: YW; Formal analysis and investigation: YW, BY; Data curation and writing-original draft preparation: YW; Writing—review and editing: FW, QL; Funding acquisition: FW, QL; Resources and Supervision: YW, BY, QL.
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare that they have no known competing financial interests or personal relationships that could have appeared to influence the work reported in this paper
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Wu, Y., Wang, F., Wu, Y. et al. Advanced ionic actuators with high-performance and high-reproducibility based on free-standing bacterial cellulose-reinforced poly(diallyldimethylammonium chloride) membranes and PEDOT/PSS electrodes. Cellulose 30, 7825–7837 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10570-023-05366-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10570-023-05366-7