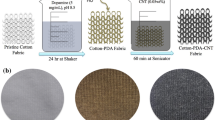
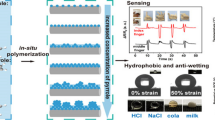
Abstract
Highly conductive polypyrrole (PPy)/single-walled carbon nanotube (SWCNT)/polydopamine (PDA)/cotton composite fabrics were developed for wearable sensing and joule heating applications. The PDA templated pristine knitted cotton fabric was dip-coated with SWCNT prior to the chemical polymerization of PPy. The different composites were characterized by employing scanning electron microscopy, energy-dispersive X-ray spectroscopy, X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy, and Fourier transform infrared spectroscopy. The PDA-induced surface modification of the cotton fabric ensured optimum absorption of the SWCNT molecules present in the coating media and provided an active substrate surface for PPy deposition. The presence of PPy significantly improved the electrical conductance of the SWCNT/PDA/cotton fabric and exhibited a superior conductivity of 8 Ω/sq. The composites showed improved electromechanical performance and excellent wearable sensing profile while monitoring different human motions such as finger bending, handwriting, drinking, etc. in real-time. In addition, the uniform heat distribution of the composite fabric attached to the hand gloves confirmed its suitability for a wearable thermal device that could reach 144.6 °C within 100 s after heating at 5 V. The fabrication of PPy/SWCNT/PDA/cotton composite fabric offers a facile but effective approach to develop durable electronic textiles for wearable applications.











Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
The data supporting the findings of this study are openly available as a DOI to an electronic repository.
References
Afzal A, Abuilaiwi FA, Habib A et al (2017) Polypyrrole/carbon nanotube supercapacitors: technological advances and challenges. J Power Sources 352:174–186. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jpowsour.2017.03.128
Alamer FA, Alnefaie MA, Salam MA (2022) Preparation and characterization of multi-walled carbon nanotubes-filled cotton fabrics. Results Phys 33:105205. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.rinp.2022.105205
Allison L, Hoxie S, Andrew TL (2017) Towards seamlessly-integrated textile electronics: methods to coat fabrics and fibers with conducting polymers for electronic applications. Chem Commun 53:7182–7193. https://doi.org/10.1039/c7cc02592k
Barani H, Miri A, Sheibani H (2021) Comparative study of electrically conductive cotton fabric prepared through the in situ synthesis of different conductive materials. Cellulose 28:6629–6649. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10570-021-03928-1
Barman J, Tirkey A, Batra S et al (2022) The role of nanotechnology based wearable electronic textiles in biomedical and healthcare applications. Mater Today Commun 32:104055. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.mtcomm.2022.104055
Bhagia S, Ďurkovič J, Lagaňa R et al (2022) Nanoscale FTIR and mechanical mapping of plant cell walls for understanding biomass deconstruction. ACS Sustain Chem Eng 10:3016–3026. https://doi.org/10.1021/acssuschemeng.1c08163
Bo Y, Zhao Y, Cai Z et al (2018) Facile synthesis of flexible electrode based on cotton/polypyrrole/multi-walled carbon nanotube composite for supercapacitors. Cellulose 25:4079–4091. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10570-018-1845-9
Chaturvedi R, Tyagi P (2020) Epoxy–polypyrrole–cotton tertiary composite with electro-tunable stiffness. Macromol Mater Eng 305:2000310. https://doi.org/10.1002/mame.202000310
Chen Z, Yu W, Du Z (2019) Study of electrothermal properties of silver nanowire/polydopamine/cotton-based nanocomposites. Cellulose 26:5995–6007. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10570-019-02506-w
Choi HW, Shin DW, Yang J et al (2022a) Smart textile lighting/display system with multifunctional fibre devices for large scale smart home and IoT applications. Nat Commun 13:1–9. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41467-022-28459-6
Choi K, Son H, Park J et al (2022b) Demonstration of durable electronic textiles via mechanically assisted highly adhesive printing of carbon nanotube-polymer composites on commercial fabrics. J Ind Eng Chem 108:508–513. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jiec.2022.01.031
Ding Y, Xu W, Wang W et al (2017) Scalable and facile preparation of highly stretchable electrospun PEDOT:PSS@PU fibrous nonwovens toward wearable conductive textile applications. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces 9:30014–30023. https://doi.org/10.1021/acsami.7b06726
Dong K, Hu Y, Yang J et al (2021) Smart textile triboelectric nanogenerators: current status and perspectives. MRS Bull 46:512–521. https://doi.org/10.1557/s43577-021-00123-2
Du Z, Chen Z, Xu J et al (2022) A facile approach to prepare a flexible and durable electrically driven cotton fabric-based heater. J Ind Text 51:406S-419S. https://doi.org/10.1177/1528083720965678
Duan Q, Lan B, Lv Y (2022) Highly dispersed, adhesive carbon nanotube Ink for strain and pressure sensors. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces 14:1973–1982. https://doi.org/10.1021/acsami.1c20133
Eom J, Jaisutti R, Lee H et al (2017) Highly sensitive textile strain sensors and wireless user-interface devices using all-polymeric conducting fibers. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces 9:10190–10197. https://doi.org/10.1021/acsami.7b01771
French AD (2017) Glucose, not cellobiose, is the repeating unit of cellulose and why that is important. Cellulose 24:4605–4609. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10570-017-1450-3
Ge Q, Chu J, Cao W et al (2022) Graphene-based textiles for thermal management and flame retardancy. Adv Funct Mater 32:2205934. https://doi.org/10.1002/adfm.202205934
Grancarić AM, Jerković I, Koncar V et al (2018) Conductive polymers for smart textile applications. J Ind Text 48:612–642. https://doi.org/10.1177/1528083717699368
Guo Q, Chen J, Wang J et al (2020) Recent progress in synthesis and application of mussel-inspired adhesives. Nanoscale 12:1307–1324. https://doi.org/10.1039/c9nr09780e
Halder O, Layani-Tzadka ME, Ziv Sharabani S et al (2022) Metal nanowires grown in situ on polymeric fibres for electronic textiles. Nanoscale Adv 4:1368–1374. https://doi.org/10.1039/d1na00872b
Hao B, Deng Z, Bi S et al (2021) In situ polymerization of pyrrole on CNT/cotton multifunctional composite yarn for supercapacitors. Ionics (Kiel) 27:279–288. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11581-020-03784-2
He H, Liu J, Wang Y et al (2022a) An ultralight self-powered fire alarm e-textile based on conductive aerogel fiber with repeatable temperature monitoring performance used in firefighting clothing. ACS Nano 16:2953–2967. https://doi.org/10.1021/acsnano.1c10144
He Y, Zhou M, Mahmoud MHH et al (2022b) Multifunctional wearable strain/pressure sensor based on conductive carbon nanotubes/silk nonwoven fabric with high durability and low detection limit. Adv Compos Hybrid Mater 5:1939–1950. https://doi.org/10.1007/s42114-022-00525-z
He Z, Zhou G, Oh Y et al (2022c) Ultrafast, highly sensitive, flexible textile-based humidity sensors made of nanocomposite filaments. Mater Today Nano 18:100214. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.mtnano.2022.100214
Huang S, Chen P, Lin W et al (2016) Electrodeposition of polypyrrole on carbon nanotube-coated cotton fabrics for all-solid flexible supercapacitor electrodes. RSC Adv 6:13359–13364. https://doi.org/10.1039/c5ra24214b
Huang H, Chen B, Wu J et al (2022) Strong and multi-responsive composite coiled yarn based on electrospun polyamide-6 nanofiber and carbon nanotube. Mater Today Commun 30:103052. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.mtcomm.2021.103052
Huang CY, Yang G, Huang P et al (2023) Flexible pressure sensor with an excellent linear response in a broad detection range for human motion monitoring. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces 15:3476–3485. https://doi.org/10.1021/acsami.2c19465
Hussain N, Mehdi M, Siyal SH et al (2021) Conductive and antibacterial cellulose nanofibers decorated with copper nanoparticles for potential application in wearable devices. J Appl Polym Sci 138:51381. https://doi.org/10.1002/app.51381
Hwang YH, Noh B, Lee J et al (2022) High-performance and reliable white organic light-emitting fibers for truly wearable textile displays. Adv Sci 9:1–10. https://doi.org/10.1002/advs.202104855
Ilanchezhiyan P, Zakirov AS, Kumar GM et al (2015) Highly efficient CNT functionalized cotton fabrics for flexible/wearable heating applications. RSC Adv 5:10697–10702. https://doi.org/10.1039/c4ra10667a
Jang J, Kim S, Lee K et al (2021) Knitted strain sensor with carbon fiber and aluminum-coated yarn, for wearable electronics. J Mater Chem C 9:16440–16449. https://doi.org/10.1039/d1tc01899j
Jiang L, Hong H, Hu J, Yan X (2022) Development of flexible supercapacitors with coplanar integrated multi-walled carbon nanotubes/textile electrode and current collectors. J Mater Sci Mater Electron 33:5297–5310. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10854-022-07718-8
Jin Y, Ka D, Jang S et al (2021) Fabrication of graphene based durable intelligent personal protective clothing for conventional and non-conventional chemical threats. Nanomaterials 11:940. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano11040940
Jin F, Lv D, Shen W et al (2022) High performance flexible and wearable strain sensor based on rGO and PANI modified Lycra cotton e-textile. Sens Actuators Phys 337:113412. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.sna.2022.113412
Kim H, Lee S (2018) Characterization of carbon nanofiber (CNF)/polymer composite coated on cotton fabrics prepared with various circuit patterns. Fash Text 5:1–13. https://doi.org/10.1186/s40691-017-0120-2
Kong LB, Yan W, Huang Y et al (2016) Carbon nanomaterials based on carbon nanotubes (CNTs). In: Husain M, Khan ZH et al (eds) Advanced structured materials. Springer, New Delhi, pp 25–101
Lee SW, Jung HG, Kim I et al (2020) Highly conductive and flexible dopamine-graphene hybrid electronic textile yarn for sensitive and selective NO2 detection. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces 12:46629–46638. https://doi.org/10.1021/acsami.0c11435
Li L, Fan T, Hu R et al (2017) Surface micro-dissolution process for embedding carbon nanotubes on cotton fabric as a conductive textile. Cellulose 24:1121–1128. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10570-016-1160-2
Li H, Tang S, Chen W et al (2022) Robust multifunctional superhydrophobic, photocatalytic and conductive fabrics with electro-/photo-thermal self-healing ability. J Colloid Interface Sci 614:1–11. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jcis.2022.01.090
Lin R, Kim HJ, Achavananthadith S et al (2022) Digitally-embroidered liquid metal electronic textiles for wearable wireless systems. Nat Commun 13:1–10. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41467-022-29859-4
Liu L, Xu W, Ding Y et al (2020) A review of smart electrospun fibers toward textiles. Compos Commun 22:100506. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.coco.2020.100506
Liu X, Miao J, Fan Q et al (2022a) Recent progress on smart fiber and textile based wearable strain sensors: materials, fabrications and applications. Adv Fiber Mater 4:361–389. https://doi.org/10.1007/s42765-021-00126-3
Liu L, Wu M, Wu Q et al (2022b) Conductive, superhydrophobic, and microwave-absorbing cotton fabric by dip-coating of aqueous silk nanofibers stabilized MWCNTs and octadecanoyl chain bonding. Cellulose 29:4687–4701. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10570-022-04538-1
Liu L, Zhang X, Xiang D et al (2022c) Highly stretchable, sensitive and wide linear responsive fabric-based strain sensors with a self-segregated carbon nanotube (CNT)/polydimethylsiloxane (PDMS) coating. Prog Nat Sci Mater Int 32:34–42. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.pnsc.2021.10.012
Liu Z, Zhu T, Wang J et al (2022d) Functionalized fiber-based strain sensors: pathway to next-generation wearable electronics. Nano-Micro Lett 14:61. https://doi.org/10.1007/s40820-022-00806-8
Lund A, Wu Y, Fenech-Salerno B et al (2021) Conducting materials as building blocks for electronic textiles. MRS Bull 46:491–501. https://doi.org/10.1557/s43577-021-00117-0
Ma J, Zhao Q, Zhou Y et al (2021) Hydrophobic wrapped carbon nanotubes coated cotton fabric for electrical heating and electromagnetic interference shielding. Polym Test 100:107240. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.polymertesting.2021.107240
Maity D, Rajavel K, Rajendra Kumar RT (2021) MWCNT enabled smart textiles based flexible and wearable sensor for human motion and humidity monitoring. Cellulose 28:2505–2520. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10570-020-03617-5
Mattmann C, Clemens F, Tröster G (2008) Sensor for measuring strain in textile. Sensors 8:3719–3732. https://doi.org/10.3390/s8063719
Miao D, Cheng N, Wang X et al (2022) Sandwich-structured textiles with hierarchically nanofibrous network and Janus wettability for outdoor personal thermal and moisture management. Chem Eng J 450:138012. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cej.2022.138012
Newby S, Mirihanage W, Fernando A (2022) Recent advancements in thermoelectric generators for smart textile application. Mater Today Commun 33:104585. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.mtcomm.2022.104585
Peng X, Zhang X, Wang R et al (2022) Printing of carbon nanotube-based temperature and bending sensors for high-temperature-resistant intelligent textiles. ACS Appl Electron Mater 4:1949–1957. https://doi.org/10.1021/acsaelm.2c00133
Qu M, Li D, Qin T et al (2022) Carbon black nanoparticle/polydopamine-coated core-spun yarns for flexible strain sensors. ACS Appl Nano Mater 5:16996–17003. https://doi.org/10.1021/acsanm.2c03934
Ran J, Chen H, Bi S et al (2021) Polydopamine-induced in-situ growth of zeolitic imidazolate framework-8/TiO2 nanoparticles on cotton fabrics for photocatalytic performance. Prog Org Coatings 152:106123. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.porgcoat.2020.106123
Sadi MS, Pan J, Xu A et al (2019a) Direct dip-coating of carbon nanotubes onto polydopamine-templated cotton fabrics for wearable applications. Cellulose 26:7569–7579. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10570-019-02628-1
Sadi MS, Yang M, Luo L et al (2019b) Direct screen printing of single-faced conductive cotton fabrics for strain sensing, electrical heating and color changing. Cellulose 26:6179–6188. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10570-019-02526-6
Sahu M, Hajra S, Panda S et al (2022) Waste textiles as the versatile triboelectric energy-harvesting platform for self-powered applications in sports and athletics. Nano Energy 97:107208. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.nanoen.2022.107208
Seyedin S, Razal JM, Innis PC et al (2015) Knitted strain sensor textiles of highly conductive all-polymeric fibers. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces 7:21150–21158. https://doi.org/10.1021/acsami.5b04892
Shan Y, Li Z, Yu T et al (2022) Self-healing strain sensor based on silicone elastomer for human motion detection. Compos Sci Technol 218:109208. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.compscitech.2021.109208
Shin YE, Cho JY, Yeom J et al (2021) Electronic textiles based on highly conducting poly(vinyl alcohol)/carbon nanotube/silver nanobelt hybrid fibers. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces 13:31051–31058. https://doi.org/10.1021/acsami.1c08175
Tan J, Shao L, Lam NYK et al (2022) Intelligent textiles: designing a gesture-controlled illuminated textile based on computer vision. Text Res J 92:3034–3048. https://doi.org/10.1177/00405175211034245
Tang J, Wu Y, Ma S et al (2022) Flexible strain sensor based on CNT/TPU composite nanofiber yarn for smart sports bandage. Compos Part B Eng 232:109605. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.compositesb.2021.109605
Tangsirinaruenart O, Stylios G (2019) A novel textile stitch-based strain sensor for wearable end users. Mater (Basel) 12:1469. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma12091469
Tat T, Chen G, Zhao X et al (2022) Smart textiles for Healthcare and sustainability. ACS Nano 16:13301–13313. https://doi.org/10.1021/acsnano.2c06287
Trovato V, Teblum E, Kostikov Y et al (2020) Sol–gel approach to incorporate millimeter-long carbon nanotubes into fabrics for the development of electrical-conductive textiles. Mater Chem Phys 240:122218. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.matchemphys.2019.122218
ul Haque S, Nasar A, Duteanu N, Inamuddin (2022) Carbon based-nanomaterials used in biofuel cells: a review. Fuel 331:125634. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.fuel.2022.125634
Wang Z, Huang Y, Sun J et al (2016) Polyurethane/cotton/carbon nanotubes core-spun yarn as high reliability stretchable strain sensor for human motion detection. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces 8:24837–24843. https://doi.org/10.1021/acsami.6b08207
Wang H, Li S, Wang Y et al (2020) Bioinspired fluffy fabric with in situ grown carbon nanotubes for ultrasensitive wearable airflow sensor. Adv Mater 32:1–8. https://doi.org/10.1002/adma.201908214
Wang S, Huang H, Liu C et al (2022a) Waterproof and breathable graphene-based electronic fabric for wearable sensors. Adv Mater Technol 2200149:1–8. https://doi.org/10.1002/admt.202200149
Wang C, Wang Y, Jiang H et al (2022b) Continuous in-situ growth of carbon nanotubes on carbon fibers at various temperatures for efficient electromagnetic wave absorption. Carbon N Y 200:94–107. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.carbon.2022.08.053
Wang R, Sun L, Zhu X et al (2023) Carbon nanotube-based strain sensors: structures, fabrication, and applications. Adv Mater Technol 8:2200855. https://doi.org/10.1002/admt.202200855
Wen J, Xu B, Gao Y et al (2021) Wearable technologies enable high-performance textile supercapacitors with flexible, breathable and wearable characteristics for future energy storage. Energy Storage Mater 37:94–122. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ensm.2021.02.002
Xu J, Wang D, Yuan Y et al (2015) Polypyrrole/reduced graphene oxide coated fabric electrodes for supercapacitor application. Org Electron 24:153–159. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.orgel.2015.05.037
Yang M, Pan J, Xu A et al (2018) Conductive cotton fabrics for motion sensing and heating applications. Polymer (Basel) 10:568. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym10060568
Yuan M, Luo F, Wang Z et al (2023) Smart wearable band-aid integrated with high-performance micro-supercapacitor, humidity and pressure sensor for multifunctional monitoring. Chem Eng J 453:139898. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cej.2022.139898
Zahid M, Papadopoulou EL, Athanassiou A, Bayer IS (2017) Strain-responsive mercerized conductive cotton fabrics based on PEDOT:PSS/graphene. Mater Des 135:213–222. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.matdes.2017.09.026
Zhang YJ, Xue JQ, Li F et al (2019) Preparation of polypyrrole/chitosan/carbon nanotube composite nano-electrode and application to capacitive deionization process for removing Cu2+. Chem Eng Process Process Intensif 139:121–129. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cep.2019.03.004
Zhang H, Ou J, Fang X et al (2022a) Robust superhydrophobic fabric via UV-accelerated atmospheric deposition of polydopamine and silver nanoparticles for solar evaporation and water/oil separation. Chem Eng J 429:132539. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cej.2021.132539
Zhang D, Yin R, Zheng Y et al (2022b) Multifunctional MXene/CNTs based flexible electronic textile with excellent strain sensing, electromagnetic interference shielding and Joule heating performances. Chem Eng J 438:135587. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cej.2022.135587
Zhang H, Zhang D, Guan J et al (2022c) A flexible wearable strain sensor for human-motion detection and a human–machine interface. J Mater Chem C 10:15554–15564. https://doi.org/10.1039/d2tc03147g
Zhao Z, Zhou J, Fan T et al (2018) An effective surface modification of polyester fabrics for improving the interfacial deposition of polypyrrole layer. Mater Chem Phys 203:89–96. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.matchemphys.2017.09.062
Zhao J, Wu G, Wang P et al (2019) Mussel-inspired construction of multifunctional cotton fabric with superhydrophobicity, conductivity and antibacterial activity. Cellulose 26:6979–6993. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10570-019-02553-3
Zhao Y, Ren M, Shang Y et al (2020) Ultra-sensitive and durable strain sensor with sandwich structure and excellent anti-interference ability for wearable electronic skins. Compos Sci Technol 200:108448. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.compscitech.2020.108448
Zheng X, Shen J, Hu Q et al (2021a) Vapor phase polymerized conducting polymer/MXene textiles for wearable electronics. Nanoscale 13:1832–1841. https://doi.org/10.1039/d0nr07433k
Zheng L, Zhu M, Wu B et al (2021b) Conductance-stable liquid metal sheath-core microfibers for stretchy smart fabrics and self-powered sensing. Sci Adv 7:1–11. https://doi.org/10.1126/sciadv.abg4041
Zhou Z, Zhang W, Zhang J et al (2023) Flexible and self-adhesive strain sensor based on GNSs/MWCNTs coated stretchable fabric for gesture monitoring and recognition. Sens Actuators Phys 349:114004. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.sna.2022.114004
Zhu H, Dai S, Cao J et al (2022) A high-performance textile pressure sensor based on carbon black/carbon nanotube-polyurethane coated fabrics with porous structure for monitoring human motion. Mater Today Commun 33:104541. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.mtcomm.2022.104541
Zuo X, Zhang X, Qu L, Miao J (2022) Smart fibers and textiles for personal thermal management in emerging wearable applications. Adv Mater Technol 2201137:1–32. https://doi.org/10.1002/admt.202201137
Funding
The authors declare that no funds, grants, or other support were received during the preparation of this manuscript.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
MSS performed material preparation, data collection, analysis, and writing—original draft. EK performed supervision and writing—review and editing. All authors reviewed and approved the final manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Ethics approval and consent to participate
Not applicable.
Consent for publication
All the authors have agreed and given full consent for publication of this manuscript.
Additional information
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Sadi, M.S., Kumpikaitė, E. Highly conductive composites using polypyrrole and carbon nanotubes on polydopamine functionalized cotton fabric for wearable sensing and heating applications. Cellulose 30, 7981–7999 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10570-023-05356-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10570-023-05356-9