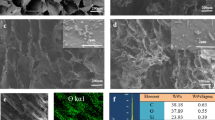
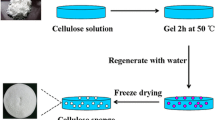
Abstract
Cellulose hydrogels are potential candidates to remove water from oil–water emulsions. However, their practical application has been limited by complex processing procedures and low separation rates limited by high water holding rates. Therefore, in this work, natural bacterial cellulose (BC) hydrogel with the characteristics of underwater superoleophobicity/underoil superhydrophilicity is introduced to remove water from oil-in-water and water-in-oil emulsions. Also, the influence of the treatment process of BC hydrogel on the separation rate was studied. The results showed that the separation rate of treated BC hydrogel was significantly higher than that of the original BC hydrogel, and the maximum separation flux could reach 180,000 ± 50 Lm−3 h−1 MPa−1. The mechanism has been investigated by the small-angle X-ray scattering and atomic force microscope, which was attributed to the decrease of the capability to confine water caused by the bundling of cellulose microfibrils during freezing or drying. The work might provide an alternative approach for improving the separation rate of cellulose materials for oil/water separation.








Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ashrafi Z, Lucia L, Krause W (2020) Underwater superoleophobic matrix-formatted liquid-infused porous biomembranes for extremely efficient deconstitution of nanoemulsions. ACS Appl Mater Inter 12:50996–51006. https://doi.org/10.1021/acsami.0c13718
Ashrafi Z, Hu Z, Lucia L, Krause W (2021) Bacterial superoleophobic fibrous matrices: a naturally occurring liquid-infused system for oil-water separation. Langmuir 37:2552–2562. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.langmuir.0c02717
Beaucage G (1995) Approximations leading to a unified exponential/power-law approach to small-angle scattering. J Appl Crystallogr 28:717–728. https://doi.org/10.1107/S0021889895005292
Beaucage G, Schaefer DW (1994) Structural studies of complex systems using small-angle scattering: a unified Guinier/power-law approach. J Non Cryst Solids 172–174:797–805. https://doi.org/10.1016/0022-3093(94)90581-9
Beaumont M, König J, Opietnik M, Potthast A, Rosenau T (2017) Drying of a cellulose II gel: effect of physical modification and redispersibility in water. Cellulose 24:1199–1209. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10570-016-1166-9
Beaumont M, Potthast A, Rosenau T (2018) Cellulose nanofibrils: from hydrogels to aerogels. In: Rosenau T, Potthast A, Hell J (eds) Cellulose science and technology. Wiley, Hoboken, pp 277–339
Beecroft LL, Ober CK (1997) Nanocomposite materials for optical applications. Chem Mater 9:1302–1317. https://doi.org/10.1021/cm960441a
Breßler I, Kohlbrecher J, Thünemann AF (2015) SASfit : a tool for small-angle scattering data analysis using a library of analytical expressions. J Appl Crystallogr 48:1587–1598. https://doi.org/10.1107/S1600576715016544
Ding Q, Zeng J, Wang B, Tang D, Chen K (2019) Effect of nanocellulose fiber hornification on water fraction characteristics and hydroxyl accessibility during dehydration. Carbohyd Polym 207:44–51. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.carbpol.2018.11.075
Dubansky B, Whitehead A, Miller JT, Rice CD, Galvez F (2013) Multitissue molecular, genomic, and developmental effects of the deepwater horizon oil spill on resident Gulf Killifish (Fundulus grandis). Environ Sci Technol 47:5074–5082. https://doi.org/10.1021/es400458p
Fakhru’l-Razi A, Pendashteh A, Abdullah LC, Biak DRA, Madaeni SS, Abidin ZZ (2009) Review of technologies for oil and gas produced water treatment. J Hazard Mater 170:530–551. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2009.05.044
Feng L, Gao Y, Dai Z, Dan H, Wang S (2021) Preparation of a rice straw-based green separation layer for efficient and persistent oil-in-water emulsion separation. J Hazard Mater 415:125594. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2021.125594
Glaser L (1958) The synthesis of cellulose in cell-free extracts of acetobacter xylinum. J Biol Chem 232:627–636. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0021-9258(19)77383-9
Haimer E, Liebner F, Rosenau T, Neouze MA, Wendland M (2008) Untersuchungen zur regeneration und trocknung bei der herstellung von cellulose-aerogelen. Chem Ing Tech 80:1385–1386. https://doi.org/10.1002/cite.200750497
Hou Y, Duan C, Zhu G, Luo H, Xu J (2019) Functional bacterial cellulose membranes with 3D porous architectures: Conventional drying, tunable wettability and water/oil separation. J Membr Sci 591:117312. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.memsci.2019.117312
Hu W, Chen G, Liu Y, Li B, Fang Z (2018) Transparent and hazy all-cellulose composite films with superior mechanical properties. ACS Sustain Chem Eng 6(5):6974–6980. https://doi.org/10.1021/acssuschemeng.8b00814
Jayme G (1944) Mikro-Quellungsmessungen an Zellstoffen. Wochenbl Papierfabr 6:187–194
Jiang J, Zhu J, Zhang Q, Zhan X, Chen F (2019) A shape recovery zwitterionic bacterial cellulose aerogel with superior performances for water remediation. Langmuir 35:11959–11967. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.langmuir.8b04180
Kang H, Liu R, Huang Y (2015) Graft modification of cellulose: methods, properties and applications. Polymer 70:A1–A16. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.polymer.2015.05.041
Koh JJ, Lim GJH, Zhou X, Zhang X, Ding J, He C (2019) 3D-printed anti-fouling cellulose mesh for highly efficient oil/water separation applications. ACS Appl Mater Inter 11:13787–13795. https://doi.org/10.1021/acsami.9b01753
Koizumi S, Yue Z, Tomita Y, Kondo T, Iwase H (2008) Bacterium organizes hierarchical amorphous structure in microbial cellulose. Eur Phys J E 26:137–142. https://doi.org/10.1140/epje/i2007-10259-3
Kollarigowda RH, Abraham S, Montemagno CD (2017) Antifouling cellulose hybrid biomembrane for effective oil/water separation. ACS Appl Mater Inter 9:29812–29819. https://doi.org/10.1021/acsami.7b09087
Li Z, Zhong L, Zhang T, Qiu F, Yang D (2019) Sustainable, flexible, and superhydrophobic functionalized cellulose aerogel for selective and versatile oil/water separation. ACS Sustain Chem Eng 7:9984–9994. https://doi.org/10.1021/acssuschemeng.9b01122
Li Z, Qiu F, Yue X, Tian Q, Yang D, Zhang T (2021) Eco-friendly self-crosslinking cellulose membrane with high mechanical properties from renewable resources for oil/water emulsion separation. J Environ Chem Eng 9:105857. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jece.2021.105857
Liu S, Zhang Q, Fan L, Wang R, Zhou Y (2020) 3D superhydrophobic sponge coated with magnesium hydroxide for effective oil/water mixture and emulsion separation. Ind Eng Chem Res 59(25):11713–11722. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.iecr.0c01276
Martínez-Sanz M, Lopez-Sanchez P, Gidley MJ, Gilbert EP (2015) Evidence for differential interaction mechanism of plant cell wall matrix polysaccharides in hierarchically-structured bacterial cellulose. Cellulose 22:1541–1563. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10570-015-0614-2
Medina-Sandoval CF, Valencia-Dávila JA, Combariza MY, Blanco-Tirado C (2018) Separation of asphaltene-stabilized water in oil emulsions and immiscible oil/water mixtures using a hydrophobic cellulosic membrane. Fuel 231:297–306. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.fuel.2018.05.066
Mo W, Li B, Chai X-S (2020) Impact of fiber initial water content on the water retention capacity of poplar APMP fibers during the thermal drying. Wood Sci Technol 54:227–235. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00226-019-01148-2
Nelson-Smith A (1971) The problem of oil pollution of the sea. In: Adv Mar Bio. Elsevier, pp 215–306. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0065-2881(08)60493-9
Sai H, Fu R, Xing L, Xiang J, Li Z, Li F, Zhang T (2015) Surface modification of bacterial cellulose aerogels’ web-like skeleton for oil/water separation. ACS Appl Mater Inter 7:7373–7381. https://doi.org/10.1021/acsami.5b00846
Sai H, Jin Z, Wang Y, Fu R, Wang Y, Ma L (2020) Facile and green route to fabricate bacterial cellulose membrane with superwettability for oil-water separation. Adv Sustain Syst 4:2000042. https://doi.org/10.1002/adsu.202000042
Saito T, Kimura S, Nishiyama Y, Isogai A (2007) Cellulose nanofibers prepared by TEMPO-mediated oxidation of native cellulose. Biomacromol 8:24852491
Salmén L, Stevanic JS (2018) Effect of drying conditions on cellulose microfibril aggregation and “hornification.” Cellulose 25:6333–6344. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10570-018-2039-1
Sanguanwong A, Pavasant P, Jarunglumlert T, Nakagawa K, Flood A, Prommuak C (2020) Hydrophobic cellulose aerogel from waste napkin paper for oil sorption applications. Nord Pulp Pap Res J 35:137–147. https://doi.org/10.1515/npprj-2018-0075
Sannino A, Demitri C, Madaghiele M (2009) Biodegradable cellulose-based hydrogels: design and applications. Materials 2:353–373. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma2020353
Seifert M, Hesse S, Kabrelian V, Klemm D (2004) Controlling the water content of never dried and reswollen bacterial cellulose by the addition of water-soluble polymers to the culture medium. J Polym Sci Polym Chem 42:463–470. https://doi.org/10.1002/pola.10862
Short J (2003) Long-term effects of crude oil on developing fish: lessons from the exxon valdez oil spill. Energy Sour Part A 25:509–517. https://doi.org/10.1080/00908310390195589
Song XL, Law KN, Daneault C (2007) Effects of freezing on fiber hornification. J Beijing for Univ 29(1):128–130
Teixeira J (1988) Small-angle scattering by fractal systems. J Appl Crystallogr 21:781–785. https://doi.org/10.1107/S0021889888000263
Wahid F, Zhao X-J, Duan Y-X, Zhao XQ, Zhong C (2021) Designing of bacterial cellulose-based superhydrophilic/underwater superoleophobic membrane for oil/water separation. Carbohyd Polym 257:117611. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.carbpol.2020.117611
Wang B, Yang D, Zhang H, Huang C, Xiong L, Luo J, Chen X (2016) Preparation of esterified bacterial cellulose for improved mechanical properties and the microstructure of isotactic polypropylene/bacterial cellulose composites. Polymers-Basel 8:129. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym8040129
Wang W, Lin J, Cheng J, Cui Z, Si J, Wang Q, Peng X, Turng LS (2020) Dual super-amphiphilic modified cellulose acetate nanofiber membranes with highly efficient oil/water separation and excellent antifouling properties. J Hazard Mater 385:121582. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2019.121582
Woo S, Cho H, Park J, Shin Y, Hwang W (2020) A novel approach to designing a biomimetic wettable patterned surface for highly efficient and continuous surfactant-free oil emulsion separation. Sep Purif Technol 248:116864. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.seppur.2020.116864
Yang X, Ma J, Ling J, Li N, Wang D, Yue F, Xu S (2018) Cellulose acetate-based SiO2/TiO2 hybrid microsphere composite aerogel films for water-in-oil emulsion separation. Appl Surf Sci 435:609–616. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apsusc.2017.11.123
Yang J, Cui J, Xie A, Dai J, Li C, Yan Y (2021) Facile preparation of superhydrophilic/underwater superoleophobic cellulose membrane with CaCO3 particles for oil/water separation. Coll Surf A 608:125583. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.colsurfa.2020.125583
Yuan J, Liu X, Akbulut O, Hu J, Suib SL, Kong J, Stellacci F (2008) Superwetting nanowire membranes for selective absorption. Nat Nanotechnol 3:332–336. https://doi.org/10.1038/nnano.2008.136
Zhang H, Lyu S, Zhou X, Gu H, Ma C, Wang C, Ding T, Shao Q, Liu H, Guo Z (2019) Super light 3D hierarchical nanocellulose aerogel foam with superior oil adsorption. J Coll Interface Sci 536:245–251. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jcis.2018.10.038
Zhang Y-R, Chen J-T, Hao B, Wang R, Ma P-C (2020) Preparation of cellulose-coated cotton fabric and its application for the separation of emulsified oil in water. Carbohyd Polym 240:116318. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.carbpol.2020.116318
Zhao X-Q, Wahid F, Cui J-X, Wang Y-Y, Zhong C (2021) Cellulose-based special wetting materials for oil/water separation: a review. Int J Biol Macromol 185:890–906. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2021.06.167
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by the Project of State Key Laboratory of Environment-friendly Energy Material, Southwest University of Science and Technology (No.20fksy18).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Supplementary file1 (AVI 187 KB)
Supplementary file2 (AVI 44830 KB)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Wang, M., Li, Z., Chen, A. et al. Influence of the freezing and lyophilization of bacterial cellulose hydrogel on water removal from both water-in-oil and oil-in-water emulsion. Cellulose 29, 5979–5990 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10570-022-04642-2
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10570-022-04642-2