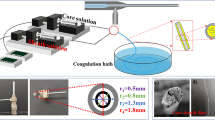
Abstract
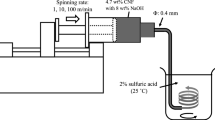
Continuous fabrication of nanocellulose long fibers (NCLFs) under an alternating current (AC) electric field was conducted by wet spinning cellulose nanofibers (CNF) suspension by adopting an environment-friendly coagulant. The alignment of CNFs in NCLFs under three different AC voltages was investigated at a constant spinning speed and an optimal electric field frequency. Upon application of AC voltage during the wet spinning process, Young’s modulus, tensile strength, yield strength, strain-at-break, and toughness of the NCLFs improved dramatically with increasing the applied AC voltage. The fabricated NCLFs at the AC voltage of 900 V exhibited remarkable mechanical properties: Young’s modulus of 28 GPa (48% increase), tensile strength of 395 MPa (33% increase), and toughness of 15 MJ/m3 (49% increase) in comparison to the no-electric field case. The CNF orientation increased with the applied electric voltage increase, as did their dense packing. The NCLFs fabricated using the proposed method are promising for fabricating strong and tough NCLF-reinforced polymer composites.
Graphical abstract








Similar content being viewed by others
References
Adusumalli R-B, Keckes J, Martinschitz KJ et al (2009) Comparison of molecular orientation and mechanical properties of lyocell fibre tow and staple fibres. Cellulose 16:765–772. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10570-009-9292-2
Biswas S, Ahsan Q, Cenna A et al (2013) Physical and mechanical properties of jute, bamboo and coir natural fiber. Fibers Polym 14:1762–1767. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12221-013-1762-3
Bordel D, Putaux J-L, Heux L (2006) Orientation of native cellulose in an electric field. Langmuir 22:4899–4901. https://doi.org/10.1021/la0600402
Cahyono TD, Syahidah (2019) Citric acid, an environmentally friendly adhesive and wood impregnation material-review of research. IOP Conf Ser Mater Sci Eng 593:012009. https://doi.org/10.1088/1757-899X/593/1/012009
Cheng G, Zhu P, Li J et al (2019) All-cellulose films with excellent strength and toughness via a facile approach of dissolution-regeneration. J Appl Polym Sci 136:46925. https://doi.org/10.1002/app.46925
Csoka L, Hoeger IC, Peralta P et al (2011) Dielectrophoresis of cellulose nanocrystals and alignment in ultrathin films by electric field-assisted shear assembly. J Colloid Interface Sci 363:206–212. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jcis.2011.07.045
George J, Ramana KV, Bawa AS, Siddaramaiah (2011) Bacterial cellulose nanocrystals exhibiting high thermal stability and their polymer nanocomposites. Int J Biol Macromol 48:50–57. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2010.09.013
Gindl W, Keckes J (2007) Drawing of self-reinforced cellulose films. J Appl Polym Sci 103:2703–2708. https://doi.org/10.1002/app.25434
Habibi Y, Heim T, Douillard R (2008) AC electric field-assisted assembly and alignment of cellulose nanocrystals. J Polym Sci Part B Polym Phys 46:1430–1436. https://doi.org/10.1002/polb.21479
Håkansson KMO, Fall AB, Lundell F et al (2014) Hydrodynamic alignment and assembly of nanofibrils resulting in strong cellulose filaments. Nat Commun 5:4018. https://doi.org/10.1038/ncomms5018
He X, Xiao Q, Lu C et al (2014) Uniaxially aligned electrospun all-cellulose nanocomposite nanofibers reinforced with cellulose nanocrystals: scaffold for tissue engineering. Biomacromolecules 15:618–627. https://doi.org/10.1021/bm401656a
Ilyas RA, Sapuan SM, Sanyang ML et al (2018) Nanocrystalline cellulose as reinforcement for polymeric matrix nanocomposites and its potential applications: a review. Curr Anal Chem 14:203–225. https://doi.org/10.2174/1573411013666171003155624
Kadimi A, Benhamou K, Ounaies Z et al (2014) Electric field alignment of nanofibrillated cellulose (NFC) in silicone oil: impact on electrical properties. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces 6:9418–9425. https://doi.org/10.1021/am501808h
Kafy A, Kim HC, Zhai L et al (2017) Cellulose long fibers fabricated from cellulose nanofibers and its strong and tough characteristics. Sci Rep 7:17683. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-017-17713-3
Kalidindi S, Ounaies Z, Kaddami H (2010) Toward the preparation of nanocomposites with oriented fillers: electric field-manipulation of cellulose whiskers in silicone oil. Smart Mater Struct 19:094002. https://doi.org/10.1088/0964-1726/19/9/094002
Kim HC, Kang J, Park JH et al (2017) Feasibility study of cellulose nanofiber alignment by high DC magnetic field. In: Varadan VK (ed) Nanosensors, biosensors, info-tech sensors and 3D systems 2017. International Society for Optics and Photonics, Bellingham
Kim HC, Kim D, Lee JY et al (2019) Effect of wet spinning and stretching to enhance mechanical properties of cellulose nanofiber filament. Int J Precis Eng Manuf Technol 6:567–575. https://doi.org/10.1007/s40684-019-00070-z
Kim HC, Kim JW, Zhai L, Kim J (2019b) Strong and tough long cellulose fibers made by aligning cellulose nanofibers under magnetic and electric fields. Cellulose 26:5821–5829. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10570-019-02496-9
Lee SH, Md Tahir P, Lum WC et al (2020) A review on citric acid as green modifying agent and binder for wood. Polym (Basel) 12:1692. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym12081692
Li J (2012) Synthesis and electric field-manipulation of high aspect ratio barium titanate. Doctoral dissertation. Texas A&M University
Lo Y, Lei U (2020) Measurement of the real part of the Clausius–Mossotti factor of dielectrophoresis for Brownian particles. Electrophoresis 41:137–147. https://doi.org/10.1002/elps.201900345
Lundén H, Liotta A, Chateau D et al (2015) Dispersion and self-orientation of gold nanoparticles in sol-gel hybrid silica – optical transmission properties. J Mater Chem C 3:1026–1034. https://doi.org/10.1039/C4TC02353F
Mittal N, Ansari F, Gowda VK et al (2018) Multiscale control of nanocellulose assembly: transferring remarkable nanoscale fibril mechanics to macroscale fibers. ACS Nano 12:6378–6388. https://doi.org/10.1021/acsnano.8b01084
Mondal S (2017) Preparation, properties and applications of nanocellulosic materials. Carbohydr Polym. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.carbpol.2016.12.050
Monti M, Natali M, Torre L, Kenny JM (2012) The alignment of single walled carbon nanotubes in an epoxy resin by applying a DC electric field. Carbon N Y 50:2453–2464. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.carbon.2012.01.067
Moscatello J, Kayastha V, Pandey A et al (2007) Dielectrophoretic deposition of carbon nanotubes with controllable density and alignment. MRS Proc. https://doi.org/10.1557/PROC-1057-II15-07
Pullawan T, Wilkinson AN, Eichhorn SJ (2012) Influence of magnetic field alignment of cellulose whiskers on the mechanics of all-cellulose nanocomposites. Biomacromolecules 13:2528–2536. https://doi.org/10.1021/bm300746r
Rosén T, Hsiao BS, Söderberg LD (2021) Elucidating the opportunities and challenges for nanocellulose spinning. Adv Mater 33:2001238. https://doi.org/10.1002/adma.202001238
Sehaqui H, Ezekiel Mushi N, Morimune S et al (2012) Cellulose nanofiber orientation in nanopaper and nanocomposites by cold drawing. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces 4:1043–1049. https://doi.org/10.1021/am2016766
Shahzad A (2013) A study in physical and mechanical properties of Hemp fibres. Adv Mater Sci Eng 2013:1–9. https://doi.org/10.1155/2013/325085
Tatsumi M, Kimura F, Kimura T et al (2014) Anisotropic polymer composites synthesized by immobilizing cellulose nanocrystal suspensions specifically oriented under magnetic fields. Biomacromolecules 15:4579–4589. https://doi.org/10.1021/bm501629g
Ten E, Jiang L, Wolcott MP (2013) Preparation and properties of aligned poly(3-hydroxybutyrate-co-3-hydroxyvalerate)/cellulose nanowhiskers composites. Carbohydr Polym 92:206–213. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.carbpol.2012.09.033
Uetani K, Yano H (2013) Self-organizing capacity of nanocelluloses via droplet evaporation. Soft Matter 9:3396. https://doi.org/10.1039/c3sm27822k
Ureña-Benavides EE, Kitchens CL (2011) Wide-angle X-ray diffraction of cellulose nanocrystal – Alginate nanocomposite fibers. Macromolecules 44:3478–3484. https://doi.org/10.1021/ma102731m
Van Hai L, Zhai L, Kim HC et al (2018) Cellulose nanofibers isolated by TEMPO-oxidation and aqueous counter collision methods. Carbohydr Polym 191:65–70. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.carbpol.2018.03.008
Velev OD, Gangwal S, Petsev DN (2009) Particle-localized AC and DC manipulation and electrokinetics. Annu Rep Sect C Phys Chem 105:213. https://doi.org/10.1039/b803015b
Wang L, Lundahl MJ, Greca LG et al (2019) Effects of non-solvents and electrolytes on the formation and properties of cellulose I filaments. Sci Rep 9:16691. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-019-53215-0
Wise HG, Takana H, Ohuchi F, Dichiara AB (2020) Field-assisted alignment of cellulose nanofibrils in a continuous flow-focusing system. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces 12:28568–28575. https://doi.org/10.1021/acsami.0c07272
Xu S, Liu D, Zhang Q, Fu Q (2018) Electric field-induced alignment of nanofibrillated cellulose in thermoplastic polyurethane matrix. Compos Sci Technol 156:117–126. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.compscitech.2017.12.017
Zander NE, Strawhecker KE, Orlicki JA et al (2011) Coaxial electrospun poly(methyl methacrylate)–polyacrylonitrile nanofibers: atomic force microscopy and compositional characterization. J Phys Chem B 115:12441–12447. https://doi.org/10.1021/jp205577r
Zhu H, Zhu S, Jia Z et al (2015) Anomalous scaling law of strength and toughness of cellulose nanopaper. Proc Natl Acad Sci 112:8971–8976. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.1502870112
Acknowledgments
National Research Foundation of Korea supported this research through the Creative Research Initiatives Program (NRF-2015R1A3A2066301).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Conceptualization, JK and PSP; Data curation and experiments, PSP and HCK; Writing—original draft preparation, PSP; Visualization, DOA, and RMM; Writing— review and editing, JK and HCK; Supervision, JK. All authors have approved the final version of the manuscript.
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Supplementary file2 (MP4 2949 KB)
Supplementary file3 (MP4 3544 KB)
Supplementary file4 (MP4 1776 KB)
Supplementary file5 (MP4 1768 KB)
Supplementary file6 (MP4 1172 KB)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Panicker, P.S., Kim, H.C., Agumba, D.O. et al. Electric field-assisted wet spinning to fabricate strong, tough, and continuous nanocellulose long fibers. Cellulose 29, 3499–3511 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10570-022-04492-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10570-022-04492-y