Abstract
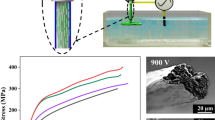
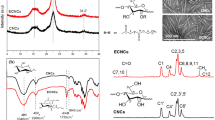
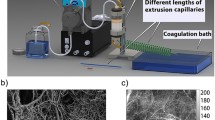
Cellulose nanocrystals (CNCs) with high crystallinity exhibit high mechanical stiffness and strength. However, the high dispersibility of CNCs results in limited spinnability and orientation. In this study, oxidized nanocellulose was selected to obtain regionally oxidized CNCs (RO-CNC) with carboxyl groups appended. For the formation of orientable and extensible RO-CNC filaments, chitosan was introduced as the sheath solution to induce orientation by electrostatic action. The chemical structures were analyzed by Fourier transform infrared spectroscopy. The morphology of the oriented CNCs filaments was characterized by scanning electron microscopy and wide-angle X-ray scattering. Analysis of the relationship between the mechanical strength and the CNCs directional arrangement revealed that the mechanical strength of the composite fibers increased with the injection speed ratio as a result of the orientation of the RO-CNC. The mechanical strength of the oriented reinforced composite filaments reached as high as 104 MPa with an orientation index of 0.73. The tensile strength and elastic modulus of the filaments increased by 33% and 20%, respectively, compared to the unmodified CNCs spun fiber.
Graphic abstract













Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
All data and materials support their published claims and comply with field standards.
References
Chen S, Schueneman G, Pipes RB, Youngblood J, Moon RJ (2014) Effects of crystal orientation on cellulose nanocrystals-cellulose acetate nanocomposite fibers prepared by dry spinning. Biomacromol 15:3827–3835
Geng L, Chen B, Peng X, Kuang T (2017) Strength and modulus improvement of wet-spun cellulose I filaments by sequential physical and chemical cross-linking. Mater Des 136:45–53
Geng S, Yao K, Zhou Q, Oksman K (2018) High-strength, high-toughness aligned polymer-based nanocomposite reinforced with ultralow weight fraction of functionalized nanocellulose. Biomacromol 19:4075–4083. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.biomac.8b01086
Hooshmand S, Aitomaki Y, Norberg N, Mathew AP, Oksman K (2015) Dry-spun single-filament fibers comprising solely cellulose nanofibers from bioresidue ACS applied materials. Interfaces 7:13022–13028. https://doi.org/10.1021/acsami.5b03091
Iwamoto S, Isogai A, Iwata T (2011) Structure and mechanical properties of wet-spun fibers made from natural cellulose nanofibers. Biomacromol 12:831–836. https://doi.org/10.1021/bm101510r
Jiang Y et al (2020) Rheology of regenerated cellulose suspension and influence of sodium alginate. Int J Biol Macromol 148:811–816. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2020.01.172
Kafy A, Kim HC, Zhai L, Kim JW, Hai LV, Kang TJ, Kim J (2017) Cellulose long fibers fabricated from cellulose nanofibers and its strong and tough characteristics. Sci Rep 7:17683. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-017-17713-3
Kim JH et al (2015) Review of nanocellulose for sustainable future materials. Int J Precis Eng Manuf Green Technol 2:197–213
Kim HC, Kim D, Lee JY, Zhai L, Kim J (2019) Effect of wet spinning and stretching to enhance mechanical properties of cellulose nanofiber filament. Int J Precis Eng Manuf Green Technol 6:567–575. https://doi.org/10.1007/s40684-019-00070-z
Konop AJ, Colby RH (1999) Polyelectrolyte charge effects on solution viscosity of Poly(acrylic acid). Macromolecules 32:2803–2805
Kou L et al (2014) Coaxial wet-spun yarn supercapacitors for high-energy density and safe wearable electronics. Nat Commun. https://doi.org/10.1038/ncomms4754
Lee WJ, Clancy AJ, Kontturi E, Bismarck A, Shaffer MS (2016) Strong and stiff: high-performance cellulose Nanocrystal/Poly(vinyl alcohol) composite fibers. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces 8:31500–31504. https://doi.org/10.1021/acsami.6b11578
Li P, Wu W, Xu J, Cao J, Zhang H (2020) Highly-ordered assembly sheath layers of graphene coaxial fibers for high-performance wearable devices. Sens Actuat A 303:111840. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.sna.2020.111840
Liu L, Yang X, Yu H, Ma C, Yao J (2014) Biomimicking the structure of silk fibers via cellulose nanocrystal as β-sheet crystallite. RSC Adv 4:14304–14313. https://doi.org/10.1039/c4ra01284d
Lundahl MJ, Cunha AG, Rojo E, Papageorgiou AC, Rautkari L, Arboleda JC, Rojas OJ (2016) Strength and water interactions of cellulose I filaments wet-spun from cellulose nanofibril hydrogels. Sci Rep 6:30695. https://doi.org/10.1038/srep30695
Lundahl MJ, Klar V, Ajdary R, Norberg N, Ago M, Cunha AG, Rojas OJ (2018) absorbent filaments from cellulose nanofibril hydrogels through continuous coaxial wet spinning. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces 10:27287–27296. https://doi.org/10.1021/acsami.8b08153
Mahadeva SK, Kim J, Jo C (2011) Effect of hydrophobic ionic liquid loading on characteristics and electromechanical performance of cellulose. Int J Precis Eng Manuf 12:47–52
Marais A, Erlandsson J, Söderberg LD, Wågberg L (2020) Coaxial spinning of oriented nanocellulose filaments and core-shell structures for interactive materials and fiber-reinforced composites. ACS Appl Nano Mater 3:10246–10251. https://doi.org/10.1021/acsanm.0c02192
Mirabedini A, Foroughi J, Thompson B, Wallace GG (2016) Fabrication of coaxial wet-spun graphene-chitosan biofibers. Adv Eng Mater 18:284–293. https://doi.org/10.1002/adem.201500201
Mittal N et al (2018) multiscale control of nanocellulose assembly: transferring remarkable nanoscale fibril mechanics to macroscale fibers. ACS Nano 12:6378–6388. https://doi.org/10.1021/acsnano.8b01084
Mredha MTI, Le HH, Tran VT, Trtik P, Cui J, Jeon I (2019) Anisotropic tough multilayer hydrogels with programmable orientation. Mater Horizons 6:1504–1511. https://doi.org/10.1039/c9mh00320g
Munier P, Gordeyeva K, Bergström L, Fall AB (2016) Directional freezing of nanocellulose dispersions aligns the rod-like particles and produces low-density and robust particle networks. Biomacromol 17:1875–1881
Peng J, Ellingham T, Sabo R, Turng LS, Clemons CM (2014) Short cellulose nanofibrils as reinforcement in polyvinyl alcohol fiber. Cellulose 21:4287–4298
Pullawan T, Wilkinson AN, Eichhorn SJ (2012) Influence of magnetic field alignment of cellulose whiskers on the mechanics of all-cellulose nanocomposites. Biomacromol 13:2528–2536. https://doi.org/10.1021/bm300746r
Reyes G, Borghei M, King AWT, Lahti J, Rojas OJ (2019) Solvent welding and imprinting cellulose nanofiber films using ionic liquids. Biomacromol 20:502–514
Reyes G, Lundahl MJ, Alejandro-Martin S, Arteaga-Perez LE, Oviedo C, King AWT, Rojas OJ (2020) Coaxial spinning of all-cellulose systems for enhanced toughness: filaments of oxidized nanofibrils sheathed in cellulose II regenerated from a protic ionic liquid. Biomacromol 21:878–891. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.biomac.9b01559
Sehaqui H, Ezekiel Mushi N, Morimune S, Salajkova M, Nishino T, Berglund LA (2012) Cellulose nanofiber orientation in nanopaper and nanocomposites by cold drawing. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces 4:1043–1049. https://doi.org/10.1021/am2016766
ShikhaShrestha F, Schueneman GT, Snyder JF, Youngblood JP (2018) Effects of aspect ratio and crystal orientation of cellulose nanocrystals on properties of poly(vinyl alcohol) composite fibers. Comp Sci Technol 167:482–488. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.compscitech.2018.08.032
Tanaka T, Fujita M, Takeuchi A, Suzuki Y, Iwata T (2006) Formation of highly ordered structure in Poly[(R)-3-hydroxybutyrate-co-(R)-3-hydroxyvalerate] high-strength fibers. Macromolecules 39:2940–2946
Torres-Rendon JG, Schacher FH, Ifuku S, Walther A (2014) Mechanical performance of macrofibers of cellulose and chitin nanofibrils aligned by wet-stretching: a critical comparison. Biomacromol 15:2709–2717. https://doi.org/10.1021/bm500566m
Wan Z, Chen C, Meng T, Mojtaba M, Teng Y, Feng Q, Li D (2019) Multifunctional wet-spun filaments through robust nanocellulose networks wrapping to single-walled carbon nanotubes. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces 11:42808–42817. https://doi.org/10.1021/acsami.9b15153
Wu C, Wang X, Zhuo Q, Sun J, Qin C, Wang J, Dai L (2018) A facile continuous wet-spinning of graphene oxide fibers from aqueous solutions at high pH with the introduction of ammonia. Carbon 138:292–299. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.carbon.2018.06.005
Xu S, Liu D, Zhang Q, Fu Q (2018) Electric field-induced alignment of nanofibrillated cellulose in thermoplastic polyurethane matrix. Compos Sci Technol 156:117–126. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.compscitech.2017.12.017
Yaari A, Schilt Y, Tamburu C, Raviv U, Shoseyov O (2016) Wet spinning and drawing of human recombinant collagen. ACS Biomateri Sci Eng 2:349–360. https://doi.org/10.1021/acsbiomaterials.5b00461
Yao J, Chen S, Chen Y, Wang B, Pei Q, Wang H (2017) Macrofibers with high mechanical performance based on aligned bacterial cellulose nanofibers. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces 9:20330–20339. https://doi.org/10.1021/acsami.6b14650
Yu JH, Fridrikh SV, Rutledge GC (2004) Production of submicrometer diameter fibers by two-fluid electrospinning. Adv Mater 16:1562–1566. https://doi.org/10.1002/adma.200306644
Zhou K, Chen C, Lei M, Gao Q, Nie S, Liu X, Wang S (2020) Reduced graphene oxide-based highly sensitive pressure sensor for wearable electronics via an ordered structure and enhanced interlayer interaction mechanism. Rsc Adv 10:2150–2159. https://doi.org/10.1039/c9ra08653f
Zong Y, Yue Z, Higgins MJ (2018) Nanocrystalline cellulose for anisotropic magnetoelectric composites. Macromol Mater Eng 303:1800099. https://doi.org/10.1002/mame.201800099
Acknowledgments
This study was financially supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (32060328), the Guangxi Natural Science Foundation (2018GXNSFAA294074), and the Scientific Research Foundation of Guangxi University (XJZ160945). we are thankful to Dr. Shangfei Wang for assistance with the AFM testing.
Funding
National Natural Science Foundation of China (32060328). Guangxi Natural Science Foundation (2018GXNSFAA294074). Scientific Research Foundation of Guangxi University (XJZ160945).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Conceptualization: Xinliang Liu; Methodology: Qian Gao; Formal analysis and investigation: Jiabao Wang and Jing Liu; Original draft preparation: Qian Gao; Review and editing: Qian Gao; Funding acquisition: Yuda Wang; Resources: Jinge Guo; Supervision: Ziyi Zhong.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare no potential conflicts of interest concerning the research, authorship, and/or publication of this article.
Consent to participate
All authors participated in this research.
Consent to publish
All authors consent to the publication of this manuscript.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Gao, Q., Wang, J., Liu, J. et al. High mechanical performance based on the alignment of cellulose nanocrystal/chitosan composite filaments through continuous coaxial wet spinning. Cellulose 28, 7995–8008 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10570-021-04009-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10570-021-04009-z