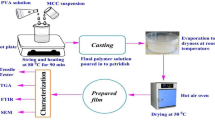
Abstract
Bacterial cellulose (BC) was reinforced via immersion in diluted skim natural rubber (SNR) latex and fresh natural rubber (FNR) latex to improve the mechanical, chemical and dielectric properties. The effects of the SNR and FNR latex concentrations (1–5% dry rubber content, DRC) and immersion temperatures (50–60 °C) on the composite film characteristics were investigated. The resulting mechanical properties of the SNR-BC and FNR-BC films were significantly enhanced compared to the neat BC film. Smaller size particles in SNR latex could extensively diffuse into the BC network, resulting in a much higher loading of SNR into BC film, as compared to that of FNR. The composite BC film with the highest elongation at break at 28% was obtained by immersion in a 5% SNR latex suspension at 60 °C, whereas the film with the highest tensile strength at 177 MPa was obtained by immersion in a 5% FNR latex suspension at 50 °C. The reinforcement strongly improved the structural stability of the composite films in water, and the composite films showed good chemical resistance in toluene. The composite films were biodegradable and could be degraded by 50–100% within 4–6 weeks in soil. The dielectric properties, in terms of dielectric constant and dielectric loss, of the BC film modified by a 5% SNR latex loading at immersion temperature of 60 °C were considerably enhanced to 170 (at 102 Hz) and 76 (at 102 Hz), respectively. With the reinforced mechanical and dielectric properties, SNR-BC composites offer potential for further development in electronic applications. FNR-BC films might also be applied as low dielectric materials for microelectronics.
Graphical abstract




modified by immersion in SNR and FNR latex suspension at various concentrations (0–5% DRC) at temperatures of 50 and 60 °C

modified by immersion in SNR and FNR latex suspension at various concentrations (0–5% DRC) at temperatures of 50 and 60 °C; the dry weight of BC ( ); the estimated dry weights of SNR and FNR (■)
); the estimated dry weights of SNR and FNR (■)



modified by immersion in SNR and FNR latex suspension at various concentrations (0–5% DRC) at temperatures of 50 and 60 °C




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ahmad MR, Ahmad NA, Suhaimi SA, Bakar NAA, Ahmad WYW, Salleh J. Tensile and tearing strength of uncoated and natural rubber latex coated high strength woven fabrics; 2012. IEEE. P. 541–545. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1109/SHUSER.2012.6268888
Amnuaypornsri S, Sakdapipanich J, Tanaka Y (2009) Green strength of natural rubber: the origin of the stress–strain behavior of natural rubber. J Appl Polym Sci 111(4):2127–2133. https://doi.org/10.1002/app.29226
Anju V, Narayanankutty SK (2016) Polyaniline coated cellulose fiber/polyvinyl alcohol composites with high dielectric permittivity and low percolation threshold. AIP Adv 6(1):015109. https://doi.org/10.1063/1.4940664
Azeredo H, Barud H, Farinas CS, Vasconcellos VM, Claro AM (2019) Bacterial cellulose as a raw material for food and food packaging applications. Front Sustain Food Syst 3:7. https://doi.org/10.3389/fsufs.2019.00007
Berthelot K, Lecomte S, Estevez Y, Zhendre V, Henry S, Thévenot J, Dufourc EJ, Alves ID, Peruch F (2014) Rubber particle proteins, HbREF and HbSRPP, show different interactions with model membranes. Biochim Biophys Acta 1:287–299. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bbamem.2013.08.025
Bhatt R, Shah D, Patel K, Trivedi U (2008) PHA–rubber blends: synthesis, characterization and biodegradation. Bioresour Technol 99(11):4615–4620. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biortech.2007.06.054
Bras J, Hassan ML, Bruzesse C, Hassan EA, El-Wakil NA, Dufresne A (2010) Mechanical, barrier, and biodegradability properties of bagasse cellulose whiskers reinforced natural rubber nanocomposites. Ind Crop Prod 32(3):627–633. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.indcrop.2010.07.018
Camargo MSA, Cercal AP, Silveira VF, Mancinelli KCB, Gern RMM, Garcia MCF, Apati GP, dos Santos Schneider AL, Pezzin APT (2020) Evaluation of wet bacterial cellulose degradation in different environmental conditions; 2020, Wiley Online Library. P. 2000149. Doi: https://doi.org/10.1002/masy.202000149
Cañas-Gutiérrez A, Osorio M, Molina-Ramírez C, Arboleda-Toro D, Castro-Herazo C (2020) Bacterial cellulose: a biomaterial with high potential in dental and oral applications. Cellulose. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10570-020-03456-4
Chen S-Q, Lopez-Sanchez P, Wang D, Mikkelsen D, Gidley MJ (2018) Mechanical properties of bacterial cellulose synthesised by diverse strains of the genus Komagataeibacter. Food Hydrocoll 81:87–95. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.foodhyd.2018.02.031
Danwanichakul P, Than-ardna B (2018) Permeation of salicylic acid through skim natural rubber films. Ind Crops Prod 122:166–173. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.indcrop.2018.05.066
Díez-Pascual AM (2019) Synthesis and applications of biopolymer composites. Int J Mol Sci 20(9):2321. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms20092321
Egbujuo WO, Anyanwu PI, Obasi HC (2020) Utilization of chitin powder as a filler in natural rubber vulcanizates: In comparison with carbon black filler. Int Rev Appl Sci Eng 11(1):43–51. https://doi.org/10.1556/1848.2020.00006
Gu R, Kokta BV, Frankenfeld K, Schlufter K (2010) Bacterial cellulose reinforced thermoplastic composites: preliminary evaluation of fabrication and performance. BioRes 5(4):2195–2207
Jayathilaka LP, Ariyadasa TU, Egodage SM (2020) Development of biodegradable natural rubber latex composites by employing corn derivative bio-fillers. J Appl Polym Sci 137(40):49205. https://doi.org/10.1002/app.49205
Kalapat N, Watthanachote L, Nipithakul T (2009) Extraction and characterization of proteins from skim rubber. Agric Nat Resour 43(5):319–325
Lai C-L, Liou R-M, Chen S-H, Shih C-Y, Chang J, Huang C-H, Hung M-Y, Lee K-R (2011) Dehydration of ethanol/water mixture by asymmetric ion-exchange membranes. Desalination 266(1–3):17–24. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.desal.2010.07.062
Lee HS, Lee AS, Baek K-Y, Hwang SS (2012) Low dielectric materials for microelectronics. In: Silaghi MA (ed) Dielectric Material. IntechOpen, Rijeka. https://doi.org/10.5772/51499
Li G, Nandgaonkar AG, Habibi Y, Krause WE, Wei Q, Lucia LA (2017) An environmentally benign approach to achieving vectorial alignment and high microporosity in bacterial cellulose/chitosan scaffolds. RSC Adv 7(23):13678–13688. https://doi.org/10.1039/C6RA26049G
Manaila E, Craciun G, Ighigeanu D (2020) Water absorption kinetics in natural rubber composites reinforced with natural fibers processed by electron beam irradiation. Polymers 12(11):2437
Mastalygina E, Varyan I, Kolesnikova N, Gonzalez MIC, Popov A (2020) Effect of natural rubber in polyethylene composites on morphology, mechanical properties and biodegradability. Polymers 12(2):437. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym12020437
Mh JA, Majid MA, Afendi M, Marzuki H, Hilmi EA, Fahmi I, Gibson A (2016) Effects of water absorption on Napier grass fibre/polyester composites. Compos Struct 144:138–146
Mohan S, Oluwafemi OS, Kalarikkal N, Thomas S, Songca SP (2016) Biopolymers–application in nanoscience and nanotechnology. Recent Adv Biopolym 1(1):47–66. https://doi.org/10.5772/62225
Nie S, Hao N, Zhang K, Xing C, Wang S (2020) Cellulose nanofibrils-based thermally conductive composites for flexible electronics: a mini review. Cellulose 27(8):4173–4187. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10570-020-03103-y
Nimpaiboon A, Amnuaypornsri S, Sakdapipanich J (2013) Influence of gel content on the physical properties of unfilled and carbon black filled natural rubber vulcanizates. Polym Test 32(6):1135–1144. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.polymertesting.2013.07.003
Nun-anan P, Wisunthorn S, Pichaiyut S, Nathaworn CD, Nakason C (2020) Influence of nonrubber components on properties of unvulcanized natural rubber. Polym Adv Technol 31(1):44–59. https://doi.org/10.1002/pat.4746
Panitchakarn P, Wikranvanich J, Phisalaphong M (2019) Synthesis and characterization of natural rubber/coal fly ash composites via latex aqueous microdispersion. J Mater Cycles Waste Manag 21(1):134–144. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10163-018-0774-x
Phomrak S, Phisalaphong M (2017) Reinforcement of natural rubber with bacterial cellulose via a latex aqueous microdispersion process. J Nanomater. https://doi.org/10.1155/2017/4739793
Phomrak S, Phisalaphong M (2020) Lactic acid modified natural rubber–bacterial cellulose composites. Appl 10(10):3583. https://doi.org/10.3390/app10103583
Portela R, Leal CR, Almeida PL, Sobral RG (2019) Bacterial cellulose: a versatile biopolymer for wound dressing applications. Microb Biotechnol 12(4):586–610. https://doi.org/10.1111/1751-7915.13392
Potivara K, Phisalaphong M (2019) Development and characterization of bacterial cellulose reinforced with natural rubber. Materials 12(14):2323. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma12142323
Rippel MM, Lee L-T, Leite CA, Galembeck F (2003) Skim and cream natural rubber particles: colloidal properties, coalescence and film formation. J Coll Interface Sci 268(2):330–340. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jcis.2003.07.046
Rosli NA, Ahmad I, Anuar FH, Abdullah I (2019) Effectiveness of cellulosic Agave angustifolia fibres on the performance of compatibilised poly (lactic acid)-natural rubber blends. Cellulose 26(5):3205–3218. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10570-019-02262-x
Sadasivuni KK, Cabibihan J-J, Ponnamma D, AlMaadeed MA, Kim J (2016) Biopolymer composites in electronics. Elsevier, Amsterdam
Schröpfer SB, Bottene MK, Bianchin L, Robinson LC, Lima Vd, Jahno VD, Barud HdS, Ribeiro SJL (2015) Biodegradation evaluation of bacterial cellulose, vegetable cellulose and poly (3-hydroxybutyrate) in soil. Polímeros 25(2):154–160. https://doi.org/10.1590/0104-1428.1712
Shakun A, Sarlin E, Vuorinen J (2021) Energy dissipation in natural rubber latex films: the effect of stabilizers, leaching and acetone-treatment. J Appl Polym Sci 138(1):49609. https://doi.org/10.1002/app.49609
Sintharm P, Phisalaphong M (2021) Green natural rubber composites reinforced with black/white rice husk ashes: effects of reinforcing agent on film’s mechanical and dielectric properties. Polymers 13(6):882. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym13060882
Sriring M, Nimpaiboon A, Kumarn S, Sirisinha C, Sakdapipanich J, Toki S (2018) Viscoelastic and mechanical properties of large-and small-particle natural rubber before and after vulcanization. Polym Test 70:127–134. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.polymertesting.2018.06.026
Sriring M, Nimpaiboon A, Dechnarong N, Kumarn S, Higaki Y, Kojio K, Takahara A, Ho CC, Sakdapipanich J (2019) Pre-vulcanization of large and small natural rubber latex particles: film-forming behavior and mechanical properties. Macromol Mater Eng 304(9):1900283. https://doi.org/10.1002/mame.201900283
Than-ardna B, Tamura H, Furuike T (2019) Improving deproteinized skim natural rubber latex with a further leaching process. Eng Appl Sci Res 46(1):64–71
Thekkedath J, Bipinbal P, Thomas T, Narayanankutty S (2020) Polythiophene coated cellulosic fibers from banana stem for improved electrical, mechanical, thermal and dielectric properties of polypropylene composites. J Sci Res 12(4):687–699
Urbina L, Alonso-Varona A, Saralegi A, Palomares T, Eceiza A, Corcuera MÁ, Retegi A (2019) Hybrid and biocompatible cellulose/polyurethane nanocomposites with water-activated shape memory properties. Carbohydr Polym 216:86–96. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.carbpol.2019.04.010
Wang J, Tavakoli J, Tang Y (2019) Bacterial cellulose production, properties and applications with different culture methods–a review. Carbohydr Polym 219:63–76. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.carbpol.2019.05.008
Wei Y, Zhang H, Longmei Wu, Jin L, Liao S (2017) A review on characterization of molecular structure of natural rubber. MOJ Poly Sci 1(6):197–199. https://doi.org/10.15406/mojps.2017.01.00032
Xiang Q, Xia K, Dai L, Kang G, Li Y, Nie Z, Duan C, Zeng R (2012) Proteome analysis of the large and the small rubber particles of Hevea brasiliensis using 2D-DIGE. Plant Physiol Biochem 60:207–213. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.plaphy.2012.08.010
Xu L, Huang C, Luo M, Qu W, Liu H, Gu Z, Jing L, Huang G, Zheng JJRA (2015) A rheological study on non-rubber component networks in natural rubber. J Rsc Adv 5(111):91742–91750. https://doi.org/10.1039/C5RA07428B
Zaborski M, Piotrowska M, Żakowska Z (2006) Hydrophilic-hydrophobic rubber composites with increased susceptibility to biodegradation. Polimery 51(7/8):534–538. https://doi.org/10.14314/polimery.2006.534
Zhou Y, Fan M, Chen L, Zhuang J (2015) Lignocellulosic fibre mediated rubber composites: an overview. Compos B Eng 76:180–191. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.compositesb.2015.02.028
Funding
This research is funded by Thailand Science Research and Innovation Fund Chulalongkorn University (CU_FRB65_bcg (24)_138_21_04). PS received support from the 90th Anniversary of Chulalongkorn University Fund (Ratchadaphiseksomphot Endowment Fund). YL received support from National Taiwan University (110L2033-58).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Ethical approval
This paper does not contain any studies with human participants or animals performed by any of the authors.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Sintharm, P., Nimpaiboon, A., Liao, YC. et al. Bacterial cellulose reinforced with skim/fresh natural rubber latex for improved mechanical, chemical and dielectric properties. Cellulose 29, 1739–1758 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10570-021-04366-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10570-021-04366-9