Abstract
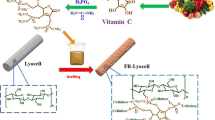
How to improve the flame retardancy of lyocell fibers has become an important issue in textile industry. Herein, lyocell fibers were firstly undergone etherification reaction between sodium chloroacetate and the hydroxyl groups of lyocell fibers to obtain carboxymethylated lyocell fibers (CM-lyocell), then the sodium ions of CM-lyocell were replaced by aluminum ions, and the flame retardant lyocell fibers (FR-lyocell) were prepared. Compared with lyocell fibers, the degradation temperature of FR-lyocell decreased by about 80 °C, and the char residue in nitrogen increased from 15.1 to 31.8 wt% at 800 °C. Importantly, the limiting oxygen index (LOI) value of FR-lyocell fabric was increased from 17.2 to 26.4%. Besides, the peak of heat release rate (PHRR) and total heat release (THR) of FR-lyocell had 77.4% and 76.3% reduction, respectively. The FR-lyocell can generate a highly graphitized char layer and release more water at high temperatures, which are beneficial to improving the flame retardancy of lyocell fibers. Moreover, the tensile test showed that the tensile strength of FR-lyocell decreased from 3.95 to 3.08 cN/dtex with a 22% reduction, showing good strength retention.
Graphic abstract
















Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abdelhameed RM, El-Zawahry M, Emam HE (2018) Efficient removal of organophosphorus pesticides from wastewater using polyethylenimine-modified fabrics. Polymer 155:225–234. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.polymer.2018.09.030
Ahmed HB, El-Hawary NS, Emam HE (2017) Self-assembled AuNPs for ingrain pigmentation of silk fabrics with antibacterial potency. Int J Biol Macromol 105:720–729. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2017.07.096
Ahmed HB, Emam HE, Mashaly HM, Rehan M (2018) Nanosilver leverage on reactive dyeing of cellulose fibers: Color shading, color fastness and biocidal potentials. Carbohyd Polym 186:310–320. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.carbpol.2018.01.074
Alongi J, Frache TA (2011) Hydrotalcite and nanometric silica as finishing additives to enhance the thermal stability and flame retardancy of cotton. Cellulose 18:179–190. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10570-010-9473-z
Alongi J, Malucelli G (2015) Cotton flame retardancy: state of the art and future perspectives. RSC Adv 5:24239–24263. https://doi.org/10.1039/c5ra01176k
Alongi J, Colleoni C, Rosace G, Malucelli G (2014) Sol-gel derived architectures for enhancing cotton flame retardancy: effect of pure and phosphorus-doped silica phases. Polym Degrad Stab 99:92–98. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.polymdegradstab.2013.11.020
Alongi J, Ferruti P, Manfredi A, Carosio F, Feng ZX, Hakkarainen M, Ranucci E (2019) Superior flame retardancy of cotton by synergetic effect of cellulose-derived nano-graphene oxide carbon dots and dilulphide-containing polyamidoamines. Polym Degrad Stab 169:108993. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.polymdegradstab.2019.108993
Azzaoui K, Mejdoubi E, Lamhamdi A, Jodeh S, Hamed O, Berrabah M, Jerdioui S, Salghi R, Akartasse N, Errich A, Ríos Á, Zougagh M (2017) Preparation and characterization of biodegradable nanocomposites derived from carboxymethyl cellulose and hydroxyapatite. Carbohyd Polym 167:59–69. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.carbpol.2017.02.092
Bai BC, Kim EA, Jeon YP, Lee CW, In SJ, Lee YS, Ji SI (2014) Improved flame retardant properties of lyocell fiber achieved by phosphorus compound. Mater Lett 135:226–228. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.matlet.2014.07.131
Bechtold T, Manian AP, Öztürk HB, Paul U, Široká B, Široký J, Soliman H, Vo LTT, Hai VM (2013) Ion-interactions as driving force in polysaccharide assembly. Carbohyd Polym 93:316–323. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.carbpol.2012.01.064
Carosio F, Fontaine G, Alongi J, Bourbigot S (2015) Starch-based layer by layer assembly: efficient and sustainable approach to cotton fire protection. ACS Appl Mater Interf 7:12158–12167. https://doi.org/10.1021/acsami.5b02507
Chen L, Wang YZ (2010) A review on flame retardant technology in China: part I—development of flame retardants. Polym Adv Technol 21:1–26. https://doi.org/10.1002/pat.1550
Chen Y, Wu XQ, Wei JF, Wu HL, Fang J (2020) Reuse polyester/cotton blend fabrics to prepare fiber reinforced composite: fabrication, characterization, and interfacial properties evaluation. Polym Compos 2020:1–12. https://doi.org/10.1002/pc.25814
Cheng XW, Liang CX, Guan JP, Yang XH, Tang RC (2018) Flame retardant and hydrophobic properties of novel sol-gel derived phytic acid/silica hybrid organic-inorganic coatings for silk fabric. Appl Surf Sci 427:69–80. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apsusc.2017.08.021
Dong CH, Lu Z, Zhang FJ, Zhu P, Wang P, Che Y, Sui SY (2016) Combustion behaviors of cotton fabrics treated by a novel nitrogen-and phosphorus-containing polysiloxane flame retardant. J Therm Anal Calorim 123:535–544. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10973-015-4914-4
El Oudiani A, Chaabouni Y, Msahli S, Sakli F (2011) Crystal transition from cellulose I to cellulose II in NaOH treated Agave americana L. fibre. Carbohyd Polym 86:1221–1229. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.carbpol.2011.06.037
Eltaweil AS, Elgarhy GS, El-Subruiti GM, Omer AM (2020) Carboxymethyl cellulose/carboxylated graphene oxide composite microbeads for efficient adsorption of cationic methylene blue dye. Int J Biol Macromol 154:307–318. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2020.03.122
Emam HE (2019) Antimicrobial cellulosic textiles based on organic compounds. 3Biotech 9:29. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13205-018-1562-y
Emam HE (2019) Generic strategies for functionalization of cellulosic textiles with metal salts. Cellulose 26:1431–1447. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10570-018-2185-5
Emam HE, Manian AP, Široká B, Bechtold T (2012) Copper inclusion in cellulose using sodium D-gluconate complexes. Carbohyd Polym 90:1345–1352. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.carbpol.2012.07.003
Emam HE, Abdellatif FHH, Abdelhameed RM (2018) Cationization of celluloisc fibers in respect of liquid fuel purification. J Clean Prod 178:457–467. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jclepro.2018.01.048
Emam HE, Darwesh OM, Abdelhameed RM (2020) Protective cotton textiles via amalgamation of cross-linked zeolitic imidazole frameworks. Ind Eng Chem Res 59:10931–10944. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.iecr.0c01384
Fang F, Xiao DZ, Zhang X, Meng YD, Cheng C, Bao C, Ding X, Cao H, Tian XY (2015) Construction of intumescent flame retardant and antimicrobial coating on cotton fabric via layer-by-layer assembly technology. Surf Coat Technol 276:726–734. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.surfcoat.2015.05.023
French AD (2014) Idealized powder diffraction patterns for cellulose Polymorphs. Cellulose 21:885–896. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10570-013-0030-4
Huang ST, Tao R, Ismail A, Wang YX (2020) Cellulose nanocrystals derived from textile waste through acid hydrolysis and oxidation as reinforcing agent of soy protein film. Polymers 12:985. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym12040958
Jóźwiak T, Filipkowska U, Brym S, Zyśk M (2020) The use of aminated cotton fibers as an unconventional sorbent to remove anionic dyes from aqueous solutions. Cellulose 27:3957–3969. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10570-020-03054-4
Kim HG, Bai BC, In SJ, Lee YS (2016) Effects of an inorganic ammonium salt treatment on the flame-retardant performance of lyocell fibers. Carbon Lett 17:74–78. https://doi.org/10.5714/CL.2016.17.1.074
Li SS, Song YL, Yang HR, An QD, Xiao ZY, Zhai SR (2020) Carboxymethyl cellulose-based cryogels for efficient heavy metal capture: Aluminum-mediated assembly process and sorption mechanism. Int J Biol Macromol 164:3275–3286. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2020.08.186
Li N, Ming J, Yuan RC, Fan S, Liu L, Li FX, Wang XL, Yu JY, Wu DQ (2020) Novel eco-friendly flame retardants based on nitrogen-silicone schiff base and application in cellulose. ACS Sustain Chem Eng 8:290–301. https://doi.org/10.1021/acssuschemeng.9b05338
Li MY, Liu J, Hu YM, Gao XP, Yuan QD, Zhao FG (2020) Investigation of the specularite/chlorite separation using chitosan as a novel depressant by direct flotation. Carbohyd Polym 240:116334. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.carbpol.2020.116334
Lin DM, Zeng XR, Li HQ, Lai XJ, Wu TY (2019) One-pot fabrication of superhydrophobic and flame-retardant coatings on cotton fabrics via sol-gel reaction. J Colloid Interf Sci 533:198–206. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jcis.2018.08.060
Liu Y, Wang JS, Zhao JC, Zhang CJ, Ran JH, Zhu P (2014) The flame retardancy and thermal degradation behaviors of trivalent metal-alginate films. Nanomater Energy 3:3–10. https://doi.org/10.1680/nme.13.00030
Liu Y, Zhao JC, Zhang CJ, Ji H, Zhu P (2014) The flame retardancy, thermal properties, and degradation mechanism of zinc alginate films. J Macromol Sci Part B-Phys 53:1074–1089. https://doi.org/10.1080/00222348.2014.891169
Liu Y, Li ZF, Wang JS, Zhu P, Zhao JC, Zhang CJ, Guo Y, Jin X (2015) Thermal degradation and pyrolysis behavior of aluminum alginate investigated by TG-FTIR-MS and Py-GC-MS. Polym Degrad Stab 118:59–68. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.polymdegradstab.2015.04.010
Liu Y, Zhang CJ, Zhao JC, Guo Y, Zhu P, Wang DY (2016) Bio-based barium alginate film: Preparation, flame retardancy and thermal degradation behavior. Carbohyd Polym 139:106–114. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.carbpol.2015.12.044
Liu Y, Zhao XR, Peng YL, Wang D, Yang LW, Peng H, Zhu P, Wang DY (2016) Effect of reactive time on flame retardancy and thermal degradation behavior of bio-based zinc alginate film. Polym Degrad Stab 127:20–31. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.polymdegradstab.2015.12.024
Liu XH, Zhang QY, Cheng BW, Ren YL, Zhang YG, Ding C (2017) Durable flame retardant cellulosic fibers modified with novel, facile and efficient phytic acid-based finishing agent. Cellulose 25:799–811. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10570-017-1550-0
Liu XH, Zhang YG, Cheng BW, Ren YL, Zhang QY, Ding C, Peng B (2018) Preparation of durable and flame retardant lyocell fibers by a one-pot chemical treatment. Cellulose 25:6745–6758. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10570-018-2005-y
Liu JX, Chen P, Qin DJ, Jia S, Jia C, Li L, Bian HL, Wei J, Shao ZQ (2020) Nanocomposites membranes from cellulose nanofibers, SiO2 and carboxymethyl cellulose with improved properties. Carbohyd Polym 233:115818. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.carbpol.2019.115818
Liu XH, Ding C, Peng B, Ren YL, Cheng BW, Lin SG, He J, Su XW (2020) Synthesis and application of a new, facile, and efficient sorbitol-based finishing agent for durable and flame retardant lyocell fibers. Cellulose 27:3427–3442. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10570-019-02894-z
Liu XH, Zhang QY, Peng B, Ren YL, Cheng BW, Ding C, Su XW, He J, Lin SG (2020) Flame retardant cellulosic fabrics via layer-by-layer self-assembly double coating with egg white protein and phytic acid. J Clean Prod 243:118641. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jclepro.2019.118641
Martínez-Rodríguez MD, Madla-Cruz E, Urrutia-Baca VH, de la Garza-Ramos MA, González-González VA, Garza-Navarro MA (2020) Influence of polysaccharides’ molecular structure on the antibacterial activity and cytotoxicity of green synthesized composites based on silver nanoparticles and carboxymethyl-cellulose. Nanomaterials 10:1164. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano10061164
Mengal N, Syed U, Malik SA, Ali SI, Jeong SH (2016) Citric acid based durable and sustainable flame retardant treatment for lyocell fabric. Carbohyd Polym 153:78–88. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.carbpol.2016.07.074
Michelin M, Marques AM, Pastrana LM, Teixeira JA, Cerqueira MA (2020) Carboxymethyl cellulose-based films: effect of organosolv lignin incorporation on physicochemical and antioxidant properties. J Food Eng 285:110107. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jfoodeng.2020.110107
Misra N, Rawat S, Goel NK, Shelkar SA, Kumar V (2020) Radiation grafted cellulose fabric as reusable anionic adsorbent: a novel strategy for potential large-scale dye wastewater remediation. Carbohyd Polym 249:116902. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.carbpol.2020.116902
Nabipour H, Wang X, Song L, Hu Y (2020) A fully bio-based coating made from alginate, chitosan and hydroxyapatite for protecting flexible polyurethane foam from fire. Carbohyd Polym 246:116641. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.carbpol.2020.116641
Peng HY, Wang D, Li M, Zhang LP, Liu MM, Fu SH (2019) Ultra-small SiO2 nanospheres self-pollinated on flower-like MoS2 for simultaneously reinforcing mechanical, thermal and flame-retardant properties of polyacrylonitrile fiber. Compos Part B-Eng 174:107037. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.compositesb.2019.107037
Rasali NMJ, Saadiah MA, Zainuddin NK, Nagao Y, Samsudin AS (2020) Ionic transport studies of solid bio-polymer electrolytes based on carboxymethyl cellulose doped with ammonium acetate and its potential application as an electrical double layer capacitor. Express Polym Lett 14:619–637. https://doi.org/10.3144/expresspolymlett.2020.51
Ren YL, Huo TG, Qin YW, Liu XH (2018) Preparation of flame retardant polyacrylonitrile fabric based on sol-gel and layer-by-layer assembly. Materials 11:483. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma11040483
Ren YL, Liu YS, Wang Y, Guo X, Liu XH (2020) Preparation of durable and flame retardant lyocell fabrics by using a biomass-based modifier derived from vitamin C. Cellulose 27:6677–6689. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10570-020-03218-2
Riaz T, Zeeshan R, Zarif F, Ilyas K, Muhammad N, Safi SZ, Rahim A, Rizvi SAA, Rehman IU (2018) FTIR analysis of natural and synthetic collagen. Appl Spectrosc Rev 53:703–746. https://doi.org/10.1080/05704928.2018.1426595
Rosace G, Colleoni C, Trovato V, Iacono G, Malucelli G (2017) Vinylphosphonic acid/methacrylamide system as a durable intumescent flame retardant for cotton fabric. Cellulose 24:3095–3108. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10570-017-1294-x
Sahito IA, Sun KC, Arbab AA, Qadir MB, Jeong SH (2015) Integrating high electrical conductivity and photocatalytic activity in cotton fabric by cationizing for enriched coating of negatively charged graphene oxide. Carbohyd Polym 130:299–306. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.carbpol.2015.05.010
Seddon H, Hall M, Horrocks AR (1996) The flame retardancy of lyocell fibres. Polym Degrad Stab 54:401–402. https://doi.org/10.1016/s0141-3910(96)00070-5
Shateri-Khalilabad M, Yazdanshenas ME (2013) Preparation of superhydrophobic electroconductive graphene-coated cotton cellulose. Cellulose 20:963–972. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10570-013-9873-y
Wan CY, Liu MS, Tian PX, Zhang GX, Zhang FX (2019) Renewable vitamin B5 reactive N-P flame retardant endows cotton with excellent fire resistance and durability. Cellulose 27:1745–1761. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10570-019-02886-z
Wang LH, Ren YL, Wang XL, Zhao JY, Zhang Y, Zeng Q, Gu YT (2016) Fire retardant viscose fiber fabric produced by graft polymerization of phosphorus and nitrogen-containing monomer. Cellulose 23:2689–2700. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10570-016-0970-6
Wang DF, Zhong L, Zhang C, Li SN, Tian PX, Zhang FG, Zhang GX (2018) Eco-friendly synthesis of a highly efficient phosphorus flame retardant based on xylitol and application on cotton fabric. Cellulose 26:2123–2138. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10570-018-2193-5
Xie KL, Gao AQ, Zhang YS (2013) Flame retardant finishing of cotton fabric based on synergistic compounds containing boron and nitrogen. Carbohyd Polym 98:706–710. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.carbpol.2013.06.014
Yan JC, Sun R, Shen LH, Bai HC, Jiang SX, Xiao Y, Song T (2020) Hydrogen-rich syngas production with tar elimination via biomass chemical looping gasification (BCLG) using BaFe2O4/Al2O3 as oxygen carrier. Chem Eng J 387:124107. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cej.2020.124107
Yoshioka-Tarver M, Condon BD, Santiago Cintrón M, Chang S, Easson MW, Fortier CA, Madison CA, Bland JM, Nguyen TMD (2012) Enhanced flame retardant property of fiber reactive halogen-free organophosphonate. Ind Eng Chem Res 51:11031–11037. https://doi.org/10.1021/ie300964g
Zeng FX, Qin ZY, Li T, Chen YY, Yang LF (2020) Boosting phosphorus–nitrogen–silicon synergism through introducing graphene nanobrick wall structure for fabricating multifunctional cotton fabric by spray assisted layer-by-layer assembly. Cellulose 27:6691–6705. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10570-020-03235-1
Zhang JJ, Ji Q, Shen XH, Xia YZ, Tan LW, Kong QS (2011) Pyrolysis products and thermal degradation mechanism of intrinsically flame-retardant calcium alginate fibre. Polym Degrad Stab 96:936–942. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.polymdegradstab.2011.01.029
Zhang JJ, Ji Q, Shen XH, Xia YZ, Tan LW, Kong QS (2012) Effects of divalent metal ions on the flame retardancy and pyrolysis products of alginate fibres. Polym Degrad Stab 97:1034–1040. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.polymdegradstab.2012.03.004
Zhang Y, Ren YL, Liu XH, Huo TG, Qin YW (2018) Preparation of durable flame retardant PAN fabrics based on amidoximation and phosphorylation. Appl Surf Sci 428:395–403. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apsusc.2017.09.155
Zhao P, Han XL, Wang WJ, Zhao MF, Zhang FS (2020) Exfoliation inhibition on aluminum alloy 7075 by water-soluble phthalocyanine derivates in 1 mol/L HCl. J Adhes Sci Technol 34:1331–1347. https://doi.org/10.1080/01694243.2019.1707562
Zhou KQ, Gui Z, Hu Y (2016) Synthesis and characterization of Cu-MoS2 hybrids and their influence on the thermal behavior of polyvinyl chloride composites. RSC Adv 6:88707–88712. https://doi.org/10.1039/c6ra17558a
Zhou QQ, Chen JY, Zhou TC, Shao JZ (2020) In situ polymerization of polyaniline on cotton fabrics with phytic acid as a novel efficient dopant for flame retardancy and conductivity switching. New J Chem 44:3504–3513. https://doi.org/10.1039/c9nj05689k
Acknowledgements
The authors are very grateful for the financial supports of the National Natural Science Foundation of China (No. 51573134) and the National Key Research and Development Program of China (2017YFB0309000).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
XG and YW contributed equally to this work. XG conceived the idea and designed the experiments. YW contributed to the material fabrication. YW conducted the thermal properties measurement and analyzed the corresponding results. XG was responsible for the SEM images, the combustion testing, FT–IR measurements. XG and YW contributed to the microscale combustion calorimetry and the corresponding analysis. YLR and XHL co-wrote and revised the manuscript. All authors commented on the final manuscript.
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no known competing financial interests or personal relationships that could have appeared to influence the work reported in this paper. All the authors listed have approved the manuscript enclosed.
Ethical approval
All authors state that they adhere to the Ethical Responsibilities of Authors. In addition, the work is compliance with ethical standards.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Guo, X., Wang, Y., Ren, Y. et al. Fabrication of flame retardant lyocell fibers based on carboxymethylation and aluminum ion chelation. Cellulose 28, 6679–6698 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10570-021-03931-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10570-021-03931-6