Abstract
Glucose-derived carbon materials were synthesized and used to support Ru–W bimetallic catalysts that provide the one-pot conversion of cellulose to ethylene glycol (EG). The catalysts prepared on the carbonized glucose (after hydrothermal synthesis and carbonization) were the most efficient for the production of EG, with yields around 30% after 5 h. Moreover, the addition of oxygenated groups to the carbon material surface enhanced the yield of EG (48% after 3 h), possibly as a result of the preferential hydrolysis of cellulose to glucose and suppressing of glucose isomerization to fructose. Furthermore, the catalytic system showed excellent stability after repeated uses, at least up to three cycles. As a result, the synthesized catalysts seem to be promising alternatives in order to produce EG directly from cellulose by a more economical (supports derived from biomass), faster (one-pot reaction) and easier (combined catalyst synthesis) process.
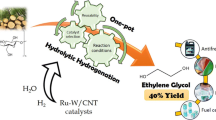
Graphic abstract
Glucose-derived carbon materials were presented as efficient and cheaper alternatives to carbon nanotubes as supports of Ru–W catalysts for the production of EG directly from cellulose.










Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- BET:
-
Brunauer–Emmett–Teller
- CG:
-
Carbonized glucose
- CNT:
-
Carbon nanotubes
- EG:
-
Ethylene glycol
- ERY:
-
Erythritol
- GA:
-
Glycolaldehyde
- GLU:
-
Glucose
- GLY:
-
Glycerol
- HMF:
-
5-Hydroxymethylfurfural
- HPLC:
-
High performance liquid chromatography
- HTC:
-
Hydrothermal carbonization
- PG:
-
Propylene glycol
- RAC:
-
Retro-aldol condensation
- RI:
-
Refractive index
- SOR:
-
Sorbitol
- TG:
-
Thermogravimetry
- TOC:
-
Total organic carbon
References
Alonso DM, Wettstein SG, Dumesic JA (2012) Bimetallic catalysts for upgrading of biomass to fuels and chemicals. Chem Soc Rev 41:7965–8216
Cao Y, Wang J, Kang M, Zhu Y (2014) Efficient synthesis of ethylene glycol from cellulose over Ni–WO3/SBA-15 catalysts. J Mol Catal A: Chem 381:46–53
Cao Y, Wang J, Kang M, Zhu L (2016) Catalytic conversion of glucose and cellobiose into ethylene glycol over various tunsgten-based catalysts. J Fuel Chem Technol 44:845–852
Chai J, Zhu S, Cen Y, Guo J, Wang J, Fan W (2017) Effect of tungsten surface density of WO3–ZrO2 on its catalytic performance in hydrogenolysis of cellulose to ethylene glycol. RSC Adv 7:8567–8574
Dabbawala AA, Mishra DK, Hwang J (2016) Selective hydrogenation of d-glucose using amine functionalized nanoporous polymer supported Ru nanoparticles based catalyst. Catal Today 265:163–173
Deng W, Tan X, Fang W, Zhang Q, Wang Y (2009) Conversion of cellulose into sorbitol over carbon nanotube-supported ruthenium catalyst. Catal Lett 133:167
Deng W, Zhang H, Xue L, Zhang Q, Wang Y (2015) Selective activation of the C–O bonds in lignocellulosic biomass for the efficient production of chemicals. Chin J Catal 36:1440–1460
Falco C, Marco-Lozar JP, Salinas-Torres D, Morallón E, Cazorla-Amorós D, Titirici MM, Lozano-Castelló D (2013) Tailoring the porosity of chemically activated hydrothermal carbons: influence of the precursor and hydrothermal carbonization temperature. Carbon 62:346–355
Guo X, Dong H, Li B, Dong L, Mu X, Chen X (2017) Influence of the functional groups of multiwalled carbon nanotubes on performance of Ru catalysts in sorbitol hydrogenolysis to glycols. J Mol Catal A: Chem 426:79–87
Han JW, Lee H (2012) Direct conversion of cellulose into sorbitol using dual-functionalized catalysts in neutral aqueous solution. Catal Commun 19:115–118
Jain A, Balasubramanian R, Srinivasan MP (2016) Hydrothermal conversion of biomass waste to activated carbon with high porosity: a review. Chem Eng J 283:789–805
Ji N, Zhang T, Zheng M, Wang A, Wang H, Wang X, Chen JG (2008) Direct catalytic conversion of cellulose into ethylene glycol using nickel-promoted tungsten carbide catalysts. Angew Chem Int Ed 47:8510–8513
Ji N, Zhang T, Zheng M, Wang A, Wang H, Wang X, Shu Y, Stottlemyer AL, Chen JG (2009) Catalytic conversion of cellulose into ethylene glycol over supported carbide catalysts. Catal Today 147:77–85
Kambo HS, Dutta A (2015) A comparative review of biochar and hydrochar in terms of production, physico-chemical properties and applications. Renew Sustain Energy Rev 45:359–378
Kobayashi H, Ohta H, Fukuoka A (2012) Conversion of lignocellulose into renewable chemicals by heterogeneous catalysis. Catal Sci Technol 2:869–883
Kruse A, Dahmen N (2018) Hydrothermal biomass conversion: quo vadis? J Supercrit Fluids 134:114
Kumar M, Oyedun AO, Kumar A (2018) A review on the current status of various hydrothermal technologies on biomass feedstock. Renew Sustain Energy Rev 81:1742–1770
Li C, Zheng M, Wang A, Zhang T (2012) One-pot catalytic hydrocracking of raw woody biomass into chemicals over supported carbide catalysts: simultaneous conversion of cellulose, hemicellulose and lignin. Energy Environ Sci 5:6383–6390
Li N, Zheng Y, Wei L, Teng H, Zhou J (2017) Metal nanoparticles supported on WO3 nanosheets for highly selective hydrogenolysis of cellulose to ethylene glycol. Green Chem 19:682–691
Li X, Guo T, Xia Q, Liu X, Wang Y (2018) One-pot catalytic transformation of lignocellulosic biomass into alkylcyclohexanes and polyols. ACS Sustain Chem Eng 6:4390–4399
Liu Y, Luo C, Liu H (2012) Tungsten trioxide promoted selective conversion of cellulose into propylene glycol and ethylene glycol on a ruthenium catalyst. Angew Chem 124:3303–3307
Liu S, Tamura M, Nakagawa Y, Tomishige K (2014) One-pot conversion of cellulose into n-Hexane over the Ir–ReOx/SiO2 catalyst combined with HZSM-5. ACS Sustainable Chem Eng 2:1819–1827
Liu H, Qin L, Wang X, Du C, Sun D, Meng X (2016) Hydrolytic hydro-conversion of cellulose to ethylene glycol over bimetallic CNTs-supported NiWB amorphous alloy catalyst. Catal Commun 77:47–51
Liu Y, Liu Y, Zhang Y (2019) The synergistic effects of Ru and WOx for aqueous-phase hydrogenation of glucose to lower diols. Appl Catal B 242:100–108
Ma J, Shi S, Jia X, Xia F, Ma H, Gao J, Xu J (2019) Advances in catalytic conversion of lignocellulose to chemicals and liquid fuels. J Energy Chem 36:74–86
Manaenkov OV, Mann JJ, Kislitza OV, Losovyj Y, Stein BD, Morgan DG et al (2016) Ru-containing magnetically recoverable catalysts: a sustainable pathway from cellulose to ethylene and propylene glycols. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces 8:21285–21293
Ogo S, Okuno Y, Sekine H, Manabe S, Yabe T, Onda A, Sekine Y (2017) Low-temperature direct catalytic hydrothermal conversion of biomass cellulose to light hydrocarbons over Pt/Zeolite catalysts. ChemistrySelect 2:6201–6205
Rey-Raap N, Ribeiro LS, Órfão JJM, Figueiredo JL, Pereira MFR (2019) Catalytic conversion of cellulose to sorbitol over Ru supported on biomass-derived carbon-based materials. Appl Catal B. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apcatb.2019.117826
Ribeiro LS, Órfão JJM, Pereira MFR (2015) Enhanced direct production of sorbitol by cellulose ball-milling. Green Chem 17:2973–2980
Ribeiro LS, Delgado JJ, De Melo Órfão JJ, Pereira MFR (2017) Direct conversion of cellulose to sorbitol over ruthenium catalysts: influence of the support. Catal Today 279:244–251
Ribeiro LS, Órfão J, Órfão JJM, Pereira MFR (2018a) Hydrolytic hydrogenation of cellulose to ethylene glycol over CNT supported Ru–W bimetallic catalysts. Cellulose 25:2259–2272
Ribeiro LS, Órfão JJM, Pereira MFR (2018b) Insights into the effect of the catalytic functions on selective production of ethylene glycol from lignocellulosic biomass over carbon supported Ru and W catalysts. Bioresour Technol 263:402–409
Ruppert AM, Weinberg K, Palkovits R (2012) Hydrogenolysis goes bio: from carbohydrates and sugar alcohols to platform chemicals. Angew Chem Int Ed 51:2564–2601
Sevilla M, Yu L, Zhao L, Ania CO, Titiricic MM (2014) Surface modification of CNTs with n-doped carbon: an effective way of enhancing their performance in supercapacitors. ACS Sustainable Chem Eng 2:1049–1055
Tai Z, Zhang J, Wang A, Pang J, Zheng M, Zhang T (2013) Catalytic conversion of cellulose to ethylene glycol over a low-cost binary catalyst of raney Ni and Tungstic acid. ChemSusChem 6:652–658
Van De Vyver S, Geboers J, Dusselier M, Schepers H, Vosch T, Zhang L, Van Tendeloo G, Jacobs PA, Sels BF (2010) Selective bifunctional catalytic conversion of cellulose over reshaped ni particles at the tip of carbon nanofibers. ChemSusChem 3:698–701
Van De Vyver S, Geboers J, Jacobs PA, Sels BF (2011) Recent advances in the catalytic conversion of cellulose. ChemCatChem 3:82–94
Wang A, Zhang T (2013) One-pot conversion of cellulose to ethylene glycol with multifunctional tungsten-based catalysts. Acc Chem Res 46:1377–1386
Wang H, Zhu L, Peng S, Peng F, Yu H, Yang J (2012) High efficient conversion of cellulose to polyols with Ru/CNTs as catalyst. Renew Energy 37:192–196
Wataniyakul P, Boonnoun P, Quitain AT, Sasaki M, Kida T, Laosiripojana N, Shotipruk A (2018) Preparation of hydrothermal carbon as catalyst support for conversion of biomass to 5-hydroxymethylfurfural. Catal Commun 104:41–47
Wiesfeld JJ, Peršolja P, Rollier FA, Elemans-Mehring AM, Hensen EJM (2019) Cellulose conversion to ethylene glycol by tungsten oxide-based catalysts. Mol Catal 473:110400
Xi J, Ding D, Shao Y, Liu X, Lu G, Wang Y (2014) Production of ethylene glycol and its monoether derivative from cellulose. ACS Sustain Chem Eng 2:2355–2362
Xiang M, Liu J, Fu W, Tang T, Wu D (2017) Improved activity for cellulose conversion to levulinic acid through hierarchization of ETS-10 zeolite. ACS Sustain Chem Eng 5:5800–5809
Xiao Z, Jin S, Pang M, Liang C (2013) Conversion of highly concentrated cellulose to 1,2-propanediol and ethylene glycol over highly efficient CuCr catalysts. Green Chem 15:891–895
Xiao Z, Fan Y, Cheng Y, Zhang Q, Ge Q, Sha R, Ji J, Mao J (2018a) Metal particles supported on SiO2–OH nanosphere: new insight into interactions with metals for cellulose conversion to ethylene glycol. Fuel 215:406–416
Xiao Z, Zhang Q, Chen T, Wang X, Fan Y, Ge Q et al (2018b) Heterobimetallic catalysis for lignocellulose to ethylene glycol on nickel–tungsten catalysts: influenced by hydroxy groups. Fuel 230:332–343
Xu S, Yan X, Bu Q, Xia H (2017) Catalytic conversion of cellulose into polyols using carbon-nanotube-supported monometallic Pd and bimetallic Pd–Fe catalysts. Cellulose 24:2403–2413
Yabushita M, Kobayashi H, Fukuoka A (2014) Catalytic transformation of cellulose into platform chemicals. Appl Catal B 145:1–9
Yang L, Yan X, Wang Q, Wang Q, Xia H (2015) One-pot catalytic conversion of cellulose into polyols with Pt/CNTs catalysts. Carbohydr Res 404:87–92
Yang Y, Zhang W, Yang F, Brown DE, Ren Y, Lee S, Zeng D, Gao Q, Zhang X (2016) Versatile nickel–tungsten bimetallics/carbon nanofiber catalysts for direct conversion of cellulose to ethylene glycol. Green Chem 18:3949–3955
Zada B, Chen M, Chen C, Yan L, Xu Q, Li W, Guo Q, Fu Y (2017) Recent advances in catalytic production of sugar alcohols and their applications. Sci China Chem 60:853–869
Zhang Y, Wang A, Zhang T (2010) A new 3D mesoporous carbon replicated from commercial silica as a catalyst support for direct conversion of cellulose into ethylene glycol. Chem Commun 46:862–864
Zhang K, Wu S, Yang H, Yin H, Li G (2016) Catalytic conversion of cellulose for efficient ethylene glycol production and insights into the reaction pathways. RSC Adv 6:77499–77506
Zhang B, Hao J, Sha Y, Zhou H, Yang K, Song Y, Ban Y, He R, Liu Q (2018) Utilization of lignite derivatives to construct Zr-based catalysts for the conversion of biomass-derived ethyl levulinate. Fuel 217:122–130
Zhao G, Zheng M, Wang A, Zhang T (2010) Catalytic conversion of cellulose to ethylene glycol over tungsten phosphide catalysts. Chin J Catal 31:928–932
Zhao X, Wang J, Chen C, Huang Y, Wang A, Zhang T (2014) Graphene oxide for cellulose hydrolysis: how it works as a highly active catalyst? Chem Commun 50:3439–3442
Zheng MY, Wang AQ, Ji N, Pang JF, Wang XD, Zhang T (2010) Transition metal-tungsten bimetallic catalysts for the conversion of cellulose into ethylene glycol. ChemSusChem 3:63–66
Zheng M, Pang J, Sun R, Wang A, Zhang T (2017) Selectivity control for cellulose to diols: dancing on eggs. ACS Catalysis 7:1939–1954
Acknowledgments
This work was financially supported by Project “AIProcMat@N2020 - Advanced Industrial Processes and Materials for a Sustainable Northern Region of Portugal 2020”, with the reference NORTE-01-0145-FEDER-000006, supported by Norte Portugal Regional Operational Programme (NORTE 2020), under the Portugal 2020 Partnership Agreement, through the European Regional Development Fund (ERDF); Associate Laboratory LSRE-LCM - UID/EQU/50020/2019 - funded by national funds through FCT/MCTES (PIDDAC); project “UniRCell” with the reference POCI-01-0145-FEDER-016422. The authors are indebted to Dr. Carlos M. Sá (CEMUP) for assistance with the XPS analyses.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Conflicts of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflicts of interest.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ribeiro, L.S., Rey-Raap, N., Figueiredo, J.L. et al. Glucose-based carbon materials as supports for the efficient catalytic transformation of cellulose directly to ethylene glycol. Cellulose 26, 7337–7353 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10570-019-02583-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10570-019-02583-x