Abstract
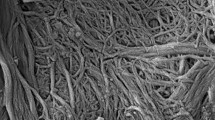
As a biodegradable, inexpensive and universally accessible material, paper is used widely in many applications, including packaging, office supplies and household products. However, the hydrophilic and oleophilic nature of paper often limits its use in applications that involve direct contact with liquids. The main purpose of this study was to create highly amphiphobic paper for products such as low cost medical testing strips, liquid packaging, and breathable and disposable medical apparel. A three-step process was developed to create paper with contact angles greater than 150° for water and motor oil, and greater than 140° for n-hexadecane. First, a commercially available debonding agent was used to manipulate the dimensions of the fiber network through efficient fines removal and modification of inter-fiber hydrogen bonding. Then an oxygen plasma was used to create nano-scale roughness on the micrometer-sized fibers and to remove residual fines that were blocking the inter-fiber pores. Finally, the paper was immersed in a fluorosilane solution to obtain a thin, low surface energy coating. XPS, SEM, mercury porosimetry and profilometry were used to evaluate changes in the fiber network after each step. This study marks the first report that uses debonder agents specifically to modify the anti-wetting properties of paper substrates by controlling the topology of the fiber network. The processes used in this procedure are simple, cost effective and amenable to scale-up.











Similar content being viewed by others
References
Balu B, Breedveld V, Hess DW (2008) Fabrication of “roll-off” and “sticky” superhydrophobic cellulose surfaces via plasma processing. Langmuir 24:4785–4790. doi:10.1021/la703766c
Balu B, Kim JS, Breedveld V, Hess DW (2009) Design of superhydrophobic paper/cellulose surfaces via plasma enhanced etching and deposition. Contact Angle, Wettability Adhes 6:235–249. doi:10.1163/ej.9789004169326.i-400.104
Barshilia HC, Gupta N (2014) Superhydrophobic polytetrafluoroethylene surfaces with leaf-like micro-protrusions through Ar + O-2 plasma etching process. Vacuum 99:42–48. doi:10.1016/j.vacuum.2013.04.020
Choi W, Tuteja A, Chhatre S, Mabry JM, Cohen RE, McKinley GH (2009) Fabrics with tunable oleophobicity. Adv Mater 21:2190. doi:10.1002/adma.200802502
Choi HJ, Shin JH, Choo S, Ryu SW, Kim YD, Lee H (2015) Fabrication of superhydrophobic and oleophobic Al surfaces by chemical etching and surface fluorination. Thin Solid Films 585:76–80. doi:10.1016/j.tsf.2015.03.046
Fatehi P, Outhouse K, Xiao HN (2009) Cationic alkoxylated amine surfactant as a debonding agent for papers made of sulfite-bleached fibers. Ind Eng Chem Res 48:749–754. doi:10.1021/ie800929p
Fatehi P, Outhouse KC, Xiao HN, Ni YH (2010) Debonding performance of various cationic surfactants on networks made of bleached kraft fibers. Ind Eng Chem Res 49:11402–11407. doi:10.1021/ie101442p
Ge DT, Yang LL, Wang CB, Lee E, Zhang YQ, Yang S (2015) A multi-functional oil–water separator from a selectively pre-wetted superamphiphobic paper. Chem Commun 51:6149–6152. doi:10.1039/c4cc09813g
Hao W, Shao ZZ (2014) Superhydrophobic and highly oleophobic nylon surface. Acta Chim Sinica 72:1023–1028. doi:10.6023/a14070510
Hayn RA, Owens JR, Boyer SA, McDonald RS, Lee HJ (2011) Preparation of highly hydrophobic and oleophobic textile surfaces using microwave-promoted silane coupling. J Mater Sci 46:2503–2509. doi:10.1007/s10853-010-5100-5
Im M, Im H, Lee J-H, Yoon J-B, Choi Y-K (2010) A robust superhydrophobic and superoleophobic surface with inverse-trapezoidal microstructures on a large transparent flexible substrate. Soft Matter 6:1401–1404. doi:10.1039/b925970h
Joseleau JP, Chevalier-Billosta V, Ruel K (2012) Interaction between microfibrillar cellulose fines and fibers: influence on pulp qualities and paper sheet properties. Cellulose 19:769–777. doi:10.1007/s10570-012-9693-5
Koubaa A, Koran Z (1995) Measure of the internal bond strength of paper/board. Tappi J 78:103–112
Larsen ST, Andersen NK, Sogaard E, Taboryski R (2014) Structure irregularity impedes drop roll-off at superhydrophobic surfaces. Langmuir 30:5041–5045. doi:10.1021/la5007633
Lee HJ, Willis CR, Stone CA (2011) Modeling and preparation of a super-oleophobic non-woven fabric. J Mater Sci 46:3907–3913. doi:10.1007/s10853-011-5314-1
Li L, Breedveld V, Hess DW (2013) Design and fabrication of superamphiphobic paper surfaces. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces 5:5381–5386. doi:10.1021/am401436m
Li J, Yan L, Ouyang QL, Zha F, Jing ZJ, Li X, Lei ZQ (2014) Facile fabrication of translucent superamphiphobic coating on paper to prevent liquid pollution. Chem Eng J 246:238–243. doi:10.1016/j.cej.2014.02.062
Liu Y, Xiu Y, Hess DW, Wong CP (2010) Silicon surface structure-controlled oleophobicity. Langmuir 26:8908–8913. doi:10.1021/la904686c
Lu TL, Liang GZ, Guo Z (2006) Preparation and characterization of organic–inorganic hybrid composites based on multiepoxy silsesquioxane and cyanate resin. J Appl Polym Sci 101:3652–3658. doi:10.1002/app.22743
Michielsen S, Lee HJ (2007) Design of a superhydrophobic surface using woven structures. Langmuir 23:6004–6010. doi:10.1021/la063157z
Moura MJ, Ferreira PJ, Figueiredo MM (2005) Mercury intrusion porosimetry in pulp and paper technology. Powder Technol 160:61–66. doi:10.1016/j.powtec.2005.08.033
Niskanen K, Sirvio J, Wathen R (2005) Tensile strength of paper revisited. In: Advances in paper science and technology: transactions of the 13th fundamental research symposium, vols 1–3
Rahmawan Y, Moon MW, Kim KS, Lee KR, Suh KY (2010) Wrinkled, dual-scale structures of diamond-like carbon (DLC) for superhydrophobicity. Langmuir 26:484–491. doi:10.1021/la902129k
Seth RS (2003) The measurement and significance of fines—their addition to pulp improves sheet consolidation. Pulp Paper Can 104:41–44
Steele A, Bayer I, Loth E (2009) Inherently superoleophobic nanocomposite coatings by spray atomization. Nano Lett 9:501–505. doi:10.1021/nl8037272
Talaeipoor M, Imani R (2008) Effects of debonding agents and refining on the properties of deinked pulp. Tappi J 7:12–14
Tang Z, Hess DW, Breedveld V (2015) Fabrication of oleophobic paper with tunable hydrophilicity by treatment with non-fluorinated chemicals. J Mater Chem A 3:14651–14660. doi:10.1039/c5ta03520a
Tuteja A et al (2007) Designing superoleophobic surfaces. Science 318:1618–1622. doi:10.1126/science.1148326
Washburn EW (1921) Note on a method of determining the distribution of pore sizes in a porous material. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 7:115–116. doi:10.1073/pnas.7.4.115
Xie L, Tang Z, Jiang L, Breedveld V, Hess DW (2015) Creation of superhydrophobic wood surfaces by plasma etching and thin-film deposition. Surf Coat Technol 281:125–132. doi:10.1016/j.surfcoat.2015.09.052
Yang J, Wu X, Zhang Q, Song H (2014) Fabrication of superamphiphobic-textured surfaces with reversibly switchable wettability. J Adhes Sci Technol 28:1687–1694. doi:10.1080/01694243.2014.913339
Young T (1805) An essay on the cohesion of fluids. Philos Trans R Soc 95:65–87. doi:10.1098/rstl.1805.0005
Zhang G et al (2013) Bi-functional random copolymers for one-pot fabrication of superamphiphobic particulate coatings. J Mater Chem A 1:6226–6237. doi:10.1039/c3ta10722a
Acknowledgments
The authors thank the Georgia Tech Renewable Bioproducts Institute (RBI) for funding support of L. Jiang. The authors also thank Dr. Roman Popil (RBI) for guidance on using the ZD tensile tester and Sonisys 3D ultrasonic test instrument, Georgia Pacific Cellulose for donating pulps, Steve Chaffin (Emerald Performance Materials) for the generous donation of debonder, Dr. Rallming Yang (RBI) for guidance on papermaking and refining techniques, and Dong-Yeun Koh from Dr. Ryan P. Lively’s group (Georgia Tech) for assistance with the mercury porosimetry studies.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Jiang, L., Tang, Z., Clinton, R.M. et al. Fabrication of highly amphiphobic paper using pulp debonder. Cellulose 23, 3885–3899 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10570-016-1048-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10570-016-1048-1