Abstract
Objectives
LncRNAs (long noncoding RNAs) have been reported to critically regulate colorectal cancer (CRC). We prospectively investigated effects and mechanisms of lncRNA LINC00858 on regulation of CRC progression.
Methods
Expression of LINC00858 and its target were analyzed by quantitative real-time polymerase chain reaction and in situ hybridization. MTT and bromodeoxyuridine/5-bromo-2′-deoxyuridine (BrdU) staining to assess cell proliferation ability. Flow cytometry, wound healing, and transwell assays were conducted to evaluate cell apoptosis, migration, and invasion, respectively. Interaction between LINC00858 and its target was confirmed by luciferase activity assay and RNA immunoprecipitation. Subcutaneous xenotransplanted tumor model was established and employed to detect tumorigenic functions of LINC00858, and further evaluated by qRT-PCR, western blot, immunohistochemistry, and hematoxylin and eosin staining.
Results
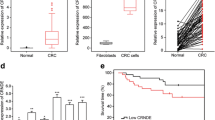
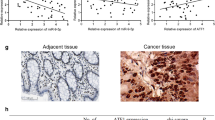
With a predicted poor prognosis, LINC00858 was upregulated in CRC patients. LINC00858 knockdown suppressed cell proliferation, invasion, and migration abilities, meanwhile induced cell apoptosis. Moreover, LINC00858 could target and inhibit the miR-4766-5p expression, thus promoting CRC progression. miR-4766-5p further suppressed serine/threonine kinase PAK2. Interestingly, interference of LINC00858 suppressed tumorigenic ability of CRC in vivo by downregulating PAK2.
Conclusions
LINC00858 promoted CRC progression by sponging miR-4766 to upregulate PAK2, shedding lights on LINC00858 as a potential therapeutic target candidate in CRC treatment from bench to clinic.








Similar content being viewed by others
References
Araujo RF Jr, Lira GA, Vilaca JA, Guedes HG, Leitao MC, Lucena HF, et al. Prognostic and diagnostic implications of MMP-2, MMP-9, and VEGF-alpha expressions in colorectal cancer. Pathol Res Pract. 2015;211(1):71–7. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.prp.2014.09.007.
Buhrmann C, Yazdi M, Popper B, Kunnumakkara AB, Aggarwal BB, Shakibaei M. Induction of the epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition of human colorectal cancer by human TNF-beta (lymphotoxin) and its reversal by resveratrol. Nutrients. 2019;11(3). https://doi.org/10.3390/nu11030704.
Carter JH, Douglass LE, Deddens JA, Colligan BM, Bhatt TR, Pemberton JO, et al. Pak-1 expression increases with progression of colorectal carcinomas to metastasis. Clin Cancer Res. 2004;10(10):3448–56. https://doi.org/10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-03-0210.
Chapuis PH, Dent OF, Newland RC, Bokey EL, Pheils MT. An evaluation of the American Joint Committee (pTNM) staging method for cancer of the colon and rectum. Dis Colon Rectum. 1986;29(1):6–10.
Chen DL, Lu YX, Zhang JX, Wei XL, Wang F, Zeng ZL, et al. Long non-coding RNA UICLM promotes colorectal cancer liver metastasis by acting as a ceRNA for microRNA-215 to regulate ZEB2 expression. Theranostics. 2017;7(19):4836–49. https://doi.org/10.7150/thno.20942.
Consortium EP, Birney E, Stamatoyannopoulos JA, Dutta A, Guigo R, Gingeras TR, et al. Identification and analysis of functional elements in 1% of the human genome by the ENCODE pilot project. Nature. 2007;447(7146):799–816. https://doi.org/10.1038/nature05874.
Damodharan U, Ganesan R, Radhakrishnan UC. Expression of MMP2 and MMP9 (gelatinases A and B) in human colon cancer cells. Appl Biochem Biotechnol. 2011;165(5–6):1245–52. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12010-011-9342-8.
Diaz-Moralli S, Tarrado-Castellarnau M, Miranda A, Cascante M. Targeting cell cycle regulation in cancer therapy. Pharmacol Ther. 2013;138(2):255–71. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.pharmthera.2013.01.011.
Ebert MS, Sharp PA. Emerging roles for natural microRNA sponges. Curr Biol. 2010;20(19):R858–61. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cub.2010.08.052.
Fatica A, Bozzoni I. Long non-coding RNAs: new players in cell differentiation and development. Nat Rev Genet. 2014;15(1):7–21. https://doi.org/10.1038/nrg3606.
Fender AW, Nutter JM, Fitzgerald TL, Bertrand FE, Sigounas G. Notch-1 promotes stemness and epithelial to mesenchymal transition in colorectal cancer. J Cell Biochem. 2015;116(11):2517–27. https://doi.org/10.1002/jcb.25196.
Geisler S, Coller J. RNA in unexpected places: long non-coding RNA functions in diverse cellular contexts. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. 2013;14(11):699–712. https://doi.org/10.1038/nrm3679.
Gu Z, Hou Z, Zheng L, Wang X, Wu L, Zhang C. Long noncoding RNA LINC00858 promotes osteosarcoma through regulating miR-139-CDK14 axis. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2018;503(2):1134–40. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bbrc.2018.06.131.
Han X, Wang L, Ning Y, Li S, Wang Z. Long non-coding RNA AFAP1-AS1 facilitates tumor growth and promotes metastasis in colorectal cancer. Biol Res. 2016;49(1):36. https://doi.org/10.1186/s40659-016-0094-3.
Han F, Wang C, Wang Y, Zhang L. Long noncoding RNA ATB promotes osteosarcoma cell proliferation, migration and invasion by suppressing miR-200s. Am J Cancer Res. 2017;7(4):770–83.
Hashim D, Boffetta P, La Vecchia C, Rota M, Bertuccio P, Malvezzi M, et al. The global decrease in cancer mortality: trends and disparities. Ann Oncol. 2016;27(5):926–33. https://doi.org/10.1093/annonc/mdw027.
Khodapasand E, Jafarzadeh N, Farrokhi F, Kamalidehghan B, Houshmand M. Is Bax/Bcl-2 ratio considered as a prognostic marker with age and tumor location in colorectal cancer? Iran Biomed J. 2015;19(2):69–75.
Kornienko AE, Guenzl PM, Barlow DP, Pauler FM. Gene regulation by the act of long non-coding RNA transcription. BMC Biol. 2013;11:59. https://doi.org/10.1186/1741-7007-11-59.
Lee JJ, Chu E. The adjuvant treatment of stage III colon cancer: might less be more? Oncology. 2018;32(9):437–42 44.
Li X, Hu F, Wang Y, Yao X, Zhang Z, Wang F, et al. CpG island methylator phenotype and prognosis of colorectal cancer in Northeast China. Biomed Res Int. 2014;2014:236361. https://doi.org/10.1155/2014/236361.
Liang Y, Song X, Li Y, Sang Y, Zhang N, Zhang H, et al. A novel long non-coding RNA-PRLB acts as a tumor promoter through regulating miR-4766-5p/SIRT1 axis in breast cancer. Cell Death Dis. 2018;9(5):563. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41419-018-0582-1.
Lv C, Wang H, Tong Y, Yin H, Wang D, Yan Z, et al. The function of BTG3 in colorectal cancer cells and its possible signaling pathway. J Cancer Res Clin Oncol. 2018;144(2):295–308. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00432-017-2561-9.
Noble P, Vyas M, Al-Attar A, Durrant S, Scholefield J, Durrant L. High levels of cleaved caspase-3 in colorectal tumour stroma predict good survival. Br J Cancer. 2013;108(10):2097–105. https://doi.org/10.1038/bjc.2013.166.
Pasz-Walczak G, Kordek R, Faflik M. P21 (WAF1) expression in colorectal cancer: correlation with P53 and cyclin D1 expression, clinicopathological parameters and prognosis. Pathol Res Pract. 2001;197(10):683–9. https://doi.org/10.1078/0344-0338-00146.
Pino MS, Kikuchi H, Zeng M, Herraiz MT, Sperduti I, Berger D, et al. Epithelial to mesenchymal transition is impaired in colon cancer cells with microsatellite instability. Gastroenterology. 2010;138(4):1406–17. https://doi.org/10.1053/j.gastro.2009.12.010.
Qiu JJ, Yan JBJTB. Long non-coding RNA LINC01296 is a potential prognostic biomarker in patients with colorectal cancer. 2015;36(9):7175–83.
Senapedis W, Crochiere M, Baloglu E, Landesman Y. Therapeutic potential of targeting PAK signaling. Anti Cancer Agents Med Chem. 2016;16(1):75–88.
Sha Q-K, Chen L, Xi J-Z, Song H. Long non-coding RNA LINC00858 promotes cells proliferation, migration and invasion by acting as a ceRNA of miR-22-3p in colorectal cancer. Artif Cells Nanomed Biotechnol. 2019;47(1):1057–66. https://doi.org/10.1080/21691401.2018.1544143.
Shi XN, Li H, Yao H, Liu X, Li L, Leung KS, et al. Adapalene inhibits the activity of cyclin-dependent kinase 2 in colorectal carcinoma. Mol Med Rep. 2015;12(5):6501–8. https://doi.org/10.3892/mmr.2015.4310.
Smolle M, Uranitsch S, Gerger A, Pichler M, Haybaeck J. Current status of long non-coding RNAs in human cancer with specific focus on colorectal cancer. Int J Mol Sci. 2014;15(8):13993–4013. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms150813993.
Wilusz JE, Sunwoo H, Spector DL. Long noncoding RNAs: functional surprises from the RNA world. Genes Dev. 2009;23(13):1494–504. https://doi.org/10.1101/gad.1800909.
Yamada A, Yu P, Lin W, Okugawa Y, Boland CR, Goel A. A RNA-sequencing approach for the identification of novel long non-coding RNA biomarkers in colorectal cancer. Sci Rep. 2018;8(1):575. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-017-18407-6.
Yang Y, Junjie P, Sanjun C, Ma Y. Long non-coding RNAs in colorectal cancer: progression and future directions. J Cancer. 2017;8(16):3212–25. https://doi.org/10.7150/jca.19794.
Ye DZ, Field J. PAK signaling in cancer. Cell Logist. 2012;2(2):105–16. https://doi.org/10.4161/cl.21882.
Yu J, Han Z, Sun Z, Wang Y, Zheng M, Song C. LncRNA SLCO4A1-AS1 facilitates growth and metastasis of colorectal cancer through beta-catenin-dependent Wnt pathway. J Exp Clin Cancer Res. 2018;37(1):222. https://doi.org/10.1186/s13046-018-0896-y.
Zhu H, Yu J, Zhu H, Guo Y, Feng S. Identification of key lncRNAs in colorectal cancer progression based on associated protein-protein interaction analysis. World J Surg Oncol. 2017a;15(1):153. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12957-017-1211-7.
Zhu SP, Wang JY, Wang XG, Zhao JP. Long intergenic non-protein coding RNA 00858 functions as a competing endogenous RNA for miR-422a to facilitate the cell growth in non-small cell lung cancer. Aging. 2017b;9(2):475–86. https://doi.org/10.18632/aging.101171.
Funding
This work was supported by Special Project of Academic New Seedling Cultivation and Innovation Exploration of Guizhou Medical University (Grant No. [2018]5779-30), Science and Technology Fund Project of Guizhou Health and Family Planning Commission (Grant No. gzwjkj-2018-1-035), Science and Technology Fund Project of Guizhou Health and Family Planning Commission (Grant No. gzwjkj-2018-1-075), State science and technology plan project of Qiandongnan Prefecture in 2019(145) and State science and technology plan project of Qiandongnan Prefecture in 2019(146).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Wei Zhan and Xin Liao and Rui Li conceived and designed the experiments, Tian Tian analyzed and interpreted the results of the experiments, Cheng Zhongsheng and LiangheLi and Lei Yu performed the experiments.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Ethics approval and consent to participate
The present study was approved by the Ethics Committee on Drug Clinical Trials in Affiliated Hospital of Guizhou Medical University (Approval No. 2018-123-01). Written informed consent was obtained from each of the participants. All methods were performed in accordance with the relevant guidelines and regulations as per the instructions of the Ethical Research Board.
Additional information
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zhan, W., Liao, X., Chen, Z. et al. LINC00858 promotes colorectal cancer by sponging miR-4766-5p to regulate PAK2. Cell Biol Toxicol 36, 333–347 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10565-019-09506-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10565-019-09506-3