Abstract
A novel TiO2-supported vanadium-substituted tungstophosphoric acid (PW11V/TiO2) catalyst was designed and applied for selective catalytic reduction of NOx by NH3. Compared with the commercial tungstophosphoric acid (PW12/TiO2), PW11V/TiO2 displayed a nearly 90% activity improvement at 300 °C. In addition, the favorable resistance and stability to SO2 were also obtained over PW11V/TiO2 catalyst. Phase analysis and spectroscopy results indicated the vanadium was successfully incorporated into the molecular structure of PW12, and the Keggin framework still keep stable over the TiO2 support. H2-TPR test proved the incorporation of vanadium promoted the redox ability of PW11V. The present study provides us an effective way to improve the performance of catalytic removal of NOx through tungstophosphoric acid catalyst.
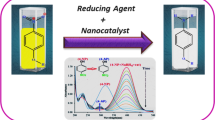
Graphic Abstract

After introduction of V species, the obtained PW11V/TiO2 catalyst show better NH3-SCR performance and N2 selectivity than PW12/TiO2 catalyst.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Chossière GP, Malina R, Ashok A, Dedoussi IC, Eastham SD, Speth RL et al (2017) Public health impacts of excess NOx emissions from volkswagen diesel passenger vehicles in Germany. Environ Res Lett 12(3):034014
Yan L, Wang F, Wang P, Impeng S, Liu X, Han L et al (2020) Unraveling the unexpected offset effects of Cd and SO2 deactivation over CeO2-WO3/TiO2 catalysts for NOx reduction. Environ Sci Technol 54(12):7697–7705
Yan L, Ji Y, Wang P, Feng C, Han L, Li H et al (2020) Alkali and phosphorus resistant zeolite-like catalysts for NOx reduction by NH3. Environ Sci Technol 54(14):9132–9141
Busca G, Lietti L, Ramis G, Berti F (1998) Chemical and mechanistic aspects of the selective catalytic reduction of NOx by ammonia over oxide catalysts : a review. Appl Catal B 18(1–2):1–36
Yan T, Liu Q, Wang S, Xu G, Wu M, Chen J et al (2020) Promoter rather than inhibitor: phosphorus incorporation accelerates the activity of V2O5–WO3/TiO2 catalyst for selective catalytic reduction of NOx by NH3. ACS Catal 10(4):2747–2753
Topsøe N-Y (1994) Mechanism of the selective catalytic reduction of nitric oxide by ammonia elucidated by in situ on-line fourier transform infrared spectroscopy. Science 265(5176):1217
Lietti L, Alemany JL, Forzatti P, Busca G, Ramis G, Giamello E et al (1996) Reactivity of V2O5-WO3/TiO2 catalysts in the selective catalytic reduction of nitric oxide by ammonia. Catal Today 29(1):143–148
Han L, Cai S, Gao M, Hasegawa JY, Wang P, Zhang J et al (2019) Selective catalytic reduction of NOx with NH3 by using novel catalysts: state of the art and future prospects. Chem Rev 119(19):10916–10976
Khan MN, Han L, Wang P, Zhang D (2020) Tailored alkali resistance of DeNOx catalysts by improving redox properties and activating adsorbed reactive species. Iscience 23(6):101173
Timofeeva MN (2003) Acid catalysis by heteropoly acids. Appl Catal A 256(1):19–35
Okuhara T, Mizuno N, Misono M (1996) Catalytic chemistry of heteropoly compounds. In: Eley DD, Haag WO, Gates B (eds) Advances in catalysis, 41st edn. Academic Press, San Siego, pp 113–252
Geng Y, Jin K, Mei J, Su G, Ma L, Yang S (2020) CeO2 grafted with different heteropoly acids for selective catalytic reduction of NOx with NH3. J Hazard Mater 382:121032
Putluru SSR, Jensen AD, Riisager A, Fehrmann R (2011) Heteropoly acid promoted V2O5/TiO2 catalysts for NO abatement with ammonia in alkali containing flue gases. Catal Sci Technol 1(4):631
Putluru SSR, Mossin S, Riisager A, Fehrmann R (2011) Heteropoly acid promoted Cu and Fe catalysts for the selective catalytic reduction of NO with ammonia. Catal Today 176(1):292–297
Zhang Q, Song Z, Ning P, Liu X, Li H, Gu J (2015) Novel promoting effect of acid modification on selective catalytic reduction of NO with ammonia over CeO2 catalyst. Catal Commun 59:170–174
Wu R, Zhang N, Liu X, Li L, Song L, Qiu W et al (2018) The keggin structure: an important factor in governing NH3–SCR activity over the V2O5–MoO3/TiO2 catalyst. Catal Lett 148(4):1228–1235
Ke Y, Huang W, Li S, Liao Y, Li J, Qu Z et al (2019) Surface acidity enhancement of CeO2 catalysts via modification with a heteropoly acid for the selective catalytic reduction of NO with ammonia. Catal Sci Technol 9(20):5774–5785
Mizuno N, Misono M (1997) Heteropolyacid catalysts. Curr Opin Solid State Mater Sci 2(1):84–89
Geng Y, Xiong S, Li B, Liao Y, Xiao X, Yang S (2018) H3PW12O40 grafted on CeO2: a high-performance catalyst for the selective catalytic reduction of NOx with NH3. Ind Eng Chem Res 57(3):856–866
Ren Z, Teng Y, Zhao L, Wang R (2017) Keggin-tungstophosphoric acid decorated Fe2O3 nanoring as a new catalyst for selective catalytic reduction of NOx with ammonia. Catal Today 297:36–45
Putluru SSR, Schill L, Godiksen A, Poreddy R, Mossin S, Jensen AD et al (2016) Promoted V2O5/TiO2 catalysts for selective catalytic reduction of NO with NH3 at low temperatures. Appl Catal B 183:282–290
Tsigdinos GA, Hallada CJ (1968) Molybdovanadophosphoric acids and their salts. I. Investigation of methods of preparation and characterization. Inorg Chem 7(3):437–441
Venkateswara Rao KT, Haribabu B, Sai Prasad PS, Lingaiah N (2013) Vapor-phase selective aerobic oxidation of benzylamine to dibenzylimine over silica-supported vanadium-substituted tungstophosphoric acid catalyst. Green Chem 15(3):837
Tang S, Wu W, Fu Z, Zou S, Liu Y, Zhao H et al (2015) Vanadium-substituted tungstophosphoric acids as efficient catalysts for visible-light-driven oxygenation of cyclohexane by dioxygen. ChemCatChem 7(17):2637–2645
Mioč UB, Dimitrijević RŽ, Davidović M, Nedić ZP, Mitrović MM, Colomban P (1994) Thermally induced phase transformations of 12-tungstophosphoric acid 29-hydrate: synthesis and characterization of PW8O26-type bronzes. J Mater Sci 29(14):3705–3718
Ladera RM, Ojeda M, Fierro JLG, Rojas S (2015) TiO2-supported heteropoly acid catalysts for dehydration of methanol to dimethyl ether: relevance of dispersion and support interaction. Catal Sci Technol 5(1):484–491
Lai J-K, Wachs IE (2018) A perspective on the selective catalytic reduction (SCR) of NO with NH3 by supported V2O5–WO3/TiO2 catalysts. ACS Catal 8(7):6537–6551
Amiridis MD, Wachs IE, Deo G, Jehng JM, Kim DS (1996) Reactivity of V2O5 catalysts for the selective catalytic reduction of NO by NH3: influence of vanadia loading, H2O, and SO2. J Catal 161(1):247–253
Damyanova S, Fierro JLG (1998) Structural features and thermal stability of titania-supported 12-molybdophosphoric heteropoly compounds. Chem Mater 10(3):871–879
Predoeva A, Damyanova S, Gaigneaux EM, Petrov L (2007) The surface and catalytic properties of titania-supported mixed PMoV heteropoly compounds for total oxidation of chlorobenzene. Appl Catal A 319:14–24
Xu Y, Wu X, Lin Q, Hu J, Ran R, Weng D (2019) SO2 promoted V2O5-MoO3/TiO2 catalyst for NH3-SCR of NO at low temperatures. Appl Catal A 570:42–50
Hodnett BK, Moffat JB (1985) Study of heteropoly compounds with the keggin structure by temperature-programmed reduction and H-D exchange. J Catal 91(1):93–103
Parida KM, Mallick S (2009) Phosphotungstic acid promoted zirconia–alumina mixed oxides: a stable and reusable catalysts for epoxidation of trans-stilbene. Catal Commun 11(1):51–57
Acknowledgements
This work was financially supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (21876093, 11675098, 11975147, 12075148), and the National Key Research, Development Program (2017YFC0210700 and 2018YFC0213400) and by Program for Changjiang Scholars. The Innovative Research Team in University No. IRT_17R71 was also acknowledged.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Liu, Q., Wang, S., Xu, G. et al. Vanadium Substitution as an Effective Way to Enhance the Redox Ability of Tungstophosphoric Acid and for Application of NH3-SCR. Catal Lett 151, 2250–2256 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10562-020-03467-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10562-020-03467-7