Abstract
Purpose
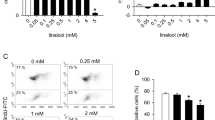
Angiogenesis involves in many pathological processes, including tumor metastasis, diabetic retinopathy, and rheumatoid arthritis. Therefore, identifying therapeutic drugs that target angiogenesis may be a promising strategy for disease treatment. Isoimperatorin is a furanocoumarin with anti-inflammatory and anti-microbial effects. However, the impacts of isoimperatorin on angiogenesis and its underlying mechanisms remain unclear. This study aimed to verify its effects on vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF)-induced endothelial angiogenesis.
Methods
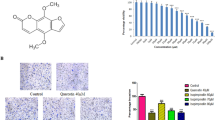
We employed various assays including 5-ethynyl-2′-deoxyuridine incorporation assay, transwell migration assay, wound healing assay, tube formation assay, and Western blot to evaluate the effects of isoimperatorin on angiogenesis in vitro. Additionally, we utilized Western blot and immunofluorescence analysis to examine the activation of vascular endothelial growth factor receptor (VEGFR) 2 and its downstream signaling pathways following isoimperatorin treatment. To further validate the anti-angiogenic effects of isoimperatorin in vivo, we conducted a matrigel plug assay and established an orthotopic tumor model.
Results
We demonstrated that pretreatment with isoimperatorin inhibited VEGF-induced endothelial cell proliferation, migration, and tube formation. Isoimperatorin also suppressed angiogenesis in vivo in a matrigel plug assay and in an orthotopic tumor model. Our results revealed that isoimperatorin exhibited anti-angiogenic effects via inhibiting VEGFR2 and its downstream signaling pathways activation.
Conclusions
Our study showed that isoimperatorin suppressed angiogenesis by targeting the VEGFR2 signaling pathway and could be a potential therapeutic agent for targeting angiogenesis.







Similar content being viewed by others
Data Availability
The data are available from the corresponding author upon reasonable request. The unprocessed Western blot images were in the supplementary data.
References
Liu Y, Ji X, Kang N, Zhou J, Liang X, Li J, et al. Tumor necrosis factor alpha inhibition overcomes immunosuppressive M2b macrophage-induced bevacizumab resistance in triple-negative breast cancer. Cell Death Dis. 2020;11(11):993.
Qin S, Li Q, Gu S, Chen X, Lin L, Wang Z, et al. Apatinib as second-line or later therapy in patients with advanced hepatocellular carcinoma (AHELP): a multicentre, double-blind, randomised, placebo-controlled, phase 3 trial. Lancet Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2021;6(7):559–68.
Peach CJ, Mignone VW, Arruda MA, Alcobia DC, Hill SJ, Kilpatrick LE et al. Molecular pharmacology of VEGF-A isoforms: binding and signalling at VEGFR2. Int J Mol Sci. 2018;19(4).
Simons M, Gordon E, Claesson-Welsh L. Mechanisms and regulation of endothelial VEGF receptor signalling. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. 2016;17(10):611–25.
Cho HD, Lee KW, Won YS, Kim JH, Seo KI. Cultivated orostachys japonicus extract inhibits VEGF-induced angiogenesis via regulation of VEGFR2 signaling pathway in vitro and in vivo. J Ethnopharmacol. 2020;256:112664.
Li J, Peng J, Zhao S, Zhong Y, Wang Y, Hu J, et al. Tussilagone suppresses angiogenesis by inhibiting the VEGFR2 Signaling Pathway. Front Pharmacol. 2019;10:764.
Zhu GS, Tang LY, Lv DL, Jiang M. Total flavones of Abelmoschus manihot exhibits pro-angiogenic activity by activating the VEGF-A/VEGFR2-PI3K/Akt Signaling Axis. Am J Chin Med. 2018;46(3):567–83.
Ouyang J, Jiang H, Fang H, Cui W, Cai D. Isoimperatorin ameliorates osteoarthritis by downregulating the mammalian target of rapamycin C1 signaling pathway. Mol Med Rep. 2017;16(6):9636–44.
Wang J, Zhang Y, Zeng Y, Ge S, Sun X, Jia M, et al. Isoimperatorin reduces the effective dose of dexamethasone in a murine model of asthma by inhibiting mast cell activation. Phytother Res. 2020;34(11):2985–97.
Wijerathne CUB, Seo CS, Song JW, Park HS, Moon OS, Won YS, et al. Isoimperatorin attenuates airway inflammation and mucus hypersecretion in an ovalbumin-induced murine model of asthma. Int Immunopharmacol. 2017;49:67–76.
Lai Y, Han T, Zhan S, Jiang Y, Liu X, Li G. Antiviral activity of Isoimperatorin against Influenza A Virus in vitro and its inhibition of neuraminidase. Front Pharmacol. 2021;12:657826.
Tong K, Xin C, Chen W. Isoimperatorin induces apoptosis of the SGC-7901 human gastric cancer cell line via the mitochondria-mediated pathway. Oncol Lett. 2017;13(1):518–24.
Yang HB, Gao HR, Ren YJ, Fang FX, Tian HT, Gao ZJ, et al. Effects of isoimperatorin on proliferation and apoptosis of human gastric carcinoma cells. Oncol Lett. 2018;15(5):7993–8.
Baudin B, Bruneel A, Bosselut N, Vaubourdolle M. A protocol for isolation and culture of human umbilical vein endothelial cells. Nat Protoc. 2007;2(3):481–5.
Ferrara N. Vascular endothelial growth factor: basic science and clinical progress. Endocr Rev. 2004;25(4):581–611.
Rattner A, Williams J, Nathans J. Roles of HIFs and VEGF in angiogenesis in the retina and brain. J Clin Invest. 2019;129(9):3807–20.
Arnaoutova I, George J, Kleinman HK, Benton G. The endothelial cell tube formation assay on basement membrane turns 20: state of the science and the art. Angiogenesis. 2009;12(3):267–74.
Zhong Y, Yin B, Ye Y, Dekhel O, Xiong X, Jian Z, et al. The bidirectional role of the JAK2/STAT3 signaling pathway and related mechanisms in cerebral ischemia-reperfusion injury. Exp Neurol. 2021;341:113690.
Wang X, Bove AM, Simone G, Ma B. Molecular bases of VEGFR-2-Mediated physiological function and pathological role. Front Cell Dev Biol. 2020;8:599281.
Cheng K, Liu CF, Rao GW. Anti-angiogenic agents: a review on vascular endothelial growth factor Receptor-2 (VEGFR-2) inhibitors. Curr Med Chem. 2021;28(13):2540–64.
Manni S, Kisko K, Schleier T, Missimer J, Ballmer-Hofer K. Functional and structural characterization of the kinase insert and the carboxy terminal domain in VEGF receptor 2 activation. FASEB J. 2014;28(11):4914–23.
Li H, Deng W, Qin Q, Lin Y, Liu T, Mo G, et al. Isoimperatorin attenuates bone loss by inhibiting the binding of RANKL to RANK. Biochem Pharmacol. 2023;211:115502.
Ma T, Liu P, Wei J, Zhao M, Yao X, Luo X, et al. Imperatorin alleviated endometriosis by inhibiting the activation of PI3K/Akt/NF-kappaB pathway in rats. Life Sci. 2021;274:119291.
Chen L, Xu W, Yang Q, Zhang H, Wan L, Xin B, et al. Imperatorin alleviates cancer cachexia and prevents muscle wasting via directly inhibiting STAT3. Pharmacol Res. 2020;158:104871.
Funding
This study was supported by the Natural Science Foundation of Hubei Province (2020CFB429).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
YTX: conducting the experiments, manuscript writing. DX: data analysis. SD: Supervision, study design, manuscript revision. MLL: Supervision, manuscript revision.
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Ethics Approval
Approval for all animal experimental procedures was obtained from the Ethics Committee of Tongji Medical College, Huazhong University of Science and Technology (permit number: [2023] IACUC Number 3393). All animal experimental procedures were conducted in strict adherence to applicable institutional and national regulations and guidelines.
Consent for Publication
Not applicable.
Competing Interests
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Additional information
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Xu, Y., Xia, D., Deng, S. et al. Isoimperatorin Inhibits Angiogenesis by Suppressing VEGFR2 Signaling Pathway. Cardiovasc Drugs Ther (2024). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10557-024-07561-5
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10557-024-07561-5