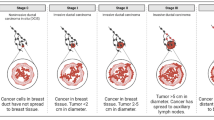
Abstract
Metastasis is a major contributor to treatment failure and death in urological cancers, representing an important biomedical challenge at present. Metastases form as a result of cancer cells leaving the primary site, entering the vasculature and lymphatic vessels, and colonizing clones elsewhere in the body. However, the specific regulatory mechanisms of action underlying the metastatic process of urological cancers remain incompletely elucidated. With the deepening of research, circular RNAs (circRNAs) have been found to not only play a significant role in tumor progression and prognosis but also show aberrant expression in various tumor metastases, consequently impacting tumor metastasis through multiple pathways. Therefore, circRNAs are emerging as potential tumor markers and treatment targets. This review summarizes the research progress on elucidating how circRNAs regulate the urological cancer invasion-metastasis cascade response and related processes, as well as their role in immune microenvironment remodeling and circRNA vaccines. This body of work highlights circRNA regulation as an emerging therapeutic target for urological cancers, which should motivate further specific research in this regard.




Similar content being viewed by others
Data Availability
No datasets were generated or analysed during the current study.
Abbreviations
- CircRNA:
-
Circular RNA
- ccRCC:
-
Clear cell renal cell carcinoma
- RCC:
-
Renal cell carcinoma
- BCa:
-
Bladder cancer
- NcRNA:
-
Non-coding RNA
- LncRNA:
-
Long-stranded non-coding RNA
- EcircRNA:
-
Exon circRNA
- EIcircRNA:
-
Exon-intron circRNA
- CiRNA:
-
Circular intronic RNA
- TricRNA:
-
tRNA intronic circular RNA
- RBP:
-
RNA-binding proteins
- miRNA:
-
microRNA
- AR:
-
Androgen receptor
- U1 snRNPs:
-
U1 small nuclear ribonucleoproteins
- m6A:
-
N6-methyladenosine
- EMT:
-
Epithelial-mesenchymal transition
- CRPC:
-
Castration-resistant prostate cancer
- OS:
-
Overall survival
- MIBC:
-
Muscle-invasive bladder cancer
- DFS:
-
Disease-free survival
- AON:
-
Antisense oligonucleotides
- pre-mRNAs:
-
precursor mRNAs
- CSC:
-
Cancer stem cell
- ACC:
-
Adrenocortical carcinoma
- HPV:
-
Human papillomavirus
- HIF-2:
-
Hypoxia-inducible factor 2
- ceRNA:
-
Competing endogenous RNA
- TFs:
-
Transcription factors
- ADT:
-
Anti-androgen therapy
- CRISPR:
-
Clustered regularly interspaced short palindromic repeat
- EGR1:
-
Early growth response factor 1
- EMT:
-
Epithelial–mesenchymal transition
- FGFR2:
-
Fibroblast growth factor receptor 2
- HNRNPL:
-
Heterogeneous nuclear ribonucleoprotein L
- IGF2BP1:
-
Insulin-like growth factor 2 mRNA-binding protein 1
- MMP:
-
Matrix metalloproteinase
- siRNA:
-
Small interfering RNA
- STAT3:
-
Signal transducer and activator of transcription 3
- TF:
-
Transcription factor
- TIMP-3:
-
Tissue inhibitor of matrix metalloproteinase-3
- UTR:
-
Untranslated region
References
Siegel, R. L., Miller, K. D., Wagle, N. S., & Jemal, A. (2023). Cancer statistics, 2023. CA: a Cancer Journal for Clinicians, 73(1), 17–48.
Amin, M. B., Greene, F. L., Edge, S. B., Compton, C. C., Gershenwald, J. E., Brookland, R. K., et al. (2017). The Eighth Edition AJCC Cancer Staging Manual: Continuing to build a bridge from a population-based to a more “personalized” approach to cancer staging. CA: a Cancer Journal for Clinicians, 67(2), 93–99.
Valastyan, S., & Weinberg, R. A. (2011). Tumor metastasis: molecular insights and evolving paradigms. Cell., 147(2), 275–292.
Kristensen, L. S., Andersen, M. S., Stagsted, L. V. W., Ebbesen, K. K., Hansen, T. B., & Kjems, J. (2019). The biogenesis, biology and characterization of circular RNAs. Nature Reviews Genetics, 20(11), 675–691.
Pisignano, G., Michael, D. C., Visal, T. H., Pirlog, R., Ladomery, M., & Calin, G. A. (2023). Going circular: history, present, and future of circRNAs in cancer. Oncogene, 42.
Sanger, H. L., Klotz, G., Riesner, D., Gross, H. J., & Kleinschmidt, A. K. (1976). Viroids are single-stranded covalently closed circular RNA molecules existing as highly base-paired rod-like structures. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America, 73(11), 3852–3856.
Memczak, S., Jens, M., Elefsinioti, A., Torti, F., Krueger, J., Rybak, A., et al. (2013). Circular RNAs are a large class of animal RNAs with regulatory potency. Nature., 495(7441), 333–338.
Li, X., Ding, J., Wang, X., Cheng, Z., & Zhu, Q. (2020). NUDT21 regulates circRNA cyclization and ceRNA crosstalk in hepatocellular carcinoma. Oncogene., 39(4), 891–904.
Zeng, Z., Xia, L., Fan, S., Zheng, J., Qin, J., Fan, X., et al. (2021). Circular RNA CircMAP3K5 acts as a microRNA-22-3p sponge to promote resolution of intimal hyperplasia Via TET2-mediated smooth muscle cell differentiation. Circulation., 143(4), 354–371.
van Zonneveld, A. J., Kölling, M., Bijkerk, R., & Lorenzen, J. M. (2021). Circular RNAs in kidney disease and cancer. Nature Reviews Nephrology, 17(12), 814–826.
Zhou, Z., Sun, B., Huang, S., & Zhao, L. (2019). Roles of circular RNAs in immune regulation and autoimmune diseases. Cell Death & Disease, 10(7), 503.
Wang, Y., Zhang, Y., Wang, P., Fu, X., & Lin, W. (2020). Circular RNAs in renal cell carcinoma: implications for tumorigenesis, diagnosis, and therapy. Molecular Cancer, 19(1), 149.
Yang, X., Ye, T., Liu, H., Lv, P., Duan, C., Wu, X., et al. (2021). Expression profiles, biological functions and clinical significance of circRNAs in bladder cancer. Molecular Cancer, 20(1), 4.
Hua, J. T., Chen, S., & He, H. H. (2019). Landscape of noncoding RNA in prostate cancer. Trends in Genetics : TIG, 35(11), 840–851.
Goodall, G. J., & Wickramasinghe, V. O. (2021). RNA in cancer. Nature Reviews Cancer, 21(1), 22–36.
Li, X., Yang, L., & Chen, L. L. (2018). The biogenesis, functions, and challenges of circular RNAs. Molecular Cell, 71(3), 428–442.
Zhang, Y., Zhang, X. O., Chen, T., Xiang, J. F., Yin, Q. F., Xing, Y. H., et al. (2013). Circular intronic long noncoding RNAs. Molecular Cell, 51(6), 792–806.
Li, Z., Huang, C., Bao, C., Chen, L., Lin, M., Wang, X., et al. (2017). Corrigendum: Exon-intron circular RNAs regulate transcription in the nucleus. Nature Structural & Molecular Biology, 24(2), 194.
Lu, Z., Filonov, G. S., Noto, J. J., Schmidt, C. A., Hatkevich, T. L., Wen, Y., et al. (2015). Metazoan tRNA introns generate stable circular RNAs in vivo. RNA (New York, NY)., 21(9), 1554–1565.
Hansen, T. B., Jensen, T. I., Clausen, B. H., Bramsen, J. B., Finsen, B., Damgaard, C. K., et al. (2013). Natural RNA circles function as efficient microRNA sponges. Nature, 495(7441), 384–388.
Okholm, T. L. H., Sathe, S., Park, S. S., Kamstrup, A. B., Rasmussen, A. M., Shankar, A., et al. (2020). Transcriptome-wide profiles of circular RNA and RNA-binding protein interactions reveal effects on circular RNA biogenesis and cancer pathway expression. Genome Medicine, 12(1), 112.
Xie, F., Xiao, X., Tao, D., Huang, C., Wang, L., Liu, F., et al. (2020). circNR3C1 suppresses bladder cancer progression through acting as an endogenous blocker of BRD4/C-myc complex. Molecular Therapy--Nucleic Acids, 22, 510–519.
Li, Z., Huang, C., Bao, C., Chen, L., Lin, M., Wang, X., et al. (2015). Exon-intron circular RNAs regulate transcription in the nucleus. Nature Structural & Molecular Biology, 22(3), 256–264.
Chen, C. Y., & Sarnow, P. (1995). Initiation of protein synthesis by the eukaryotic translational apparatus on circular RNAs. Science (New York, N.Y.), 268(5209), 415–417.
Hogg, S. J., Beavis, P. A., Dawson, M. A., & Johnstone, R. W. (2020). Targeting the epigenetic regulation of antitumour immunity. Nature Reviews Drug Discovery, 19(11), 776–800.
Weigel, C., Veldwijk, M. R., Oakes, C. C., Seibold, P., Slynko, A., Liesenfeld, D. B., et al. (2016). Epigenetic regulation of diacylglycerol kinase alpha promotes radiation-induced fibrosis. Nature Communications, 7, 10893.
Pietri, E., Conteduca, V., Andreis, D., Massa, I., Melegari, E., Sarti, S., et al. (2016). Androgen receptor signaling pathways as a target for breast cancer treatment. Endocrine-Related Cancer, 23(10), R485–R498.
Yin, J., Liu, Y. N., Tillman, H., Barrett, B., Hewitt, S., Ylaya, K., et al. (2014). AR-regulated TWEAK-FN14 pathway promotes prostate cancer bone metastasis. Cancer Research, 74(16), 4306–4317.
Yang, L., Huang, W., Bai, X., Wang, H., Wang, X., Xiao, H., et al. (2023). Androgen dihydrotestosterone promotes bladder cancer cell proliferation and invasion via EPPK1-mediated MAPK/JUP signalling. Cell Death & Disease, 14(6), 363.
Deng, G., Wang, R., Sun, Y., Huang, C. P., Yeh, S., You, B., et al. (2021). Targeting androgen receptor (AR) with antiandrogen Enzalutamide increases prostate cancer cell invasion yet decreases bladder cancer cell invasion via differentially altering the AR/circRNA-ARC1/miR-125b-2-3p or miR-4736/PPARγ/MMP-9 signals. Cell Death and Differentiation, 28(7), 2145–2159.
Chen, J., Sun, Y., Ou, Z., Yeh, S., Huang, C. P., You, B., et al. (2020). Androgen receptor-regulated circFNTA activates KRAS signaling to promote bladder cancer invasion. EMBO Reports, 21(4), e48467.
Yang, Z., Qu, C. B., Zhang, Y., Zhang, W. F., Wang, D. D., Gao, C. C., et al. (2019). Dysregulation of p53-RBM25-mediated circAMOTL1L biogenesis contributes to prostate cancer progression through the circAMOTL1L-miR-193a-5p-Pcdha pathway. Oncogene, 38(14), 2516–2532.
Kim, T. K., & Shiekhattar, R. (2015). Architectural and functional commonalities between enhancers and promoters. Cell, 162(5), 948–959.
Chen, W., Cen, S., Zhou, X., Yang, T., Wu, K., Zou, L., et al. (2020). Circular RNA CircNOLC1, upregulated by NF-KappaB, promotes the progression of prostate cancer via miR-647/PAQR4 Axis. Frontiers in Cell and Development Biology, 8, 624764.
Han, Z., Zhang, Y., Sun, Y., Chen, J., Chang, C., Wang, X., et al. (2018). ERβ-mediated alteration of circATP2B1 and miR-204-3p signaling promotes invasion of clear cell renal cell carcinoma. Cancer Research, 78(10), 2550–2563.
Gupta, G. P., & Massagué, J. (2006). Cancer metastasis: building a framework. Cell., 127(4), 679–695.
Vanharanta, S., & Massagué, J. (2013). Origins of metastatic traits. Cancer Cell, 24(4), 410–421.
Bakir, B., Chiarella, A. M., Pitarresi, J. R., & Rustgi, A. K. (2020). EMT, MET, plasticity, and tumor metastasis. Trends in Cell Biology, 30(10), 764–776.
Pastushenko, I., & Blanpain, C. (2019). EMT transition states during tumor progression and metastasis. Trends in Cell Biology, 29(3), 212–226.
Stuelten, C. H., Parent, C. A., & Montell, D. J. (2018). Cell motility in cancer invasion and metastasis: insights from simple model organisms. Nature Reviews Cancer, 18(5), 296–312.
Slattum, G. M., & Rosenblatt, J. (2014). Tumour cell invasion: An emerging role for basal epithelial cell extrusion. Nature Reviews Cancer, 14(7), 495–501.
Li, W., Yang, F. Q., Sun, C. M., Huang, J. H., Zhang, H. M., Li, X., et al. (2020). circPRRC2A promotes angiogenesis and metastasis through epithelial-mesenchymal transition and upregulates TRPM3 in renal cell carcinoma. Theranostics, 10(10), 4395–4409.
Nielsen, J., Kristensen, M. A., Willemoës, M., Nielsen, F. C., & Christiansen, J. (2004). Sequential dimerization of human zipcode-binding protein IMP1 on RNA: A cooperative mechanism providing RNP stability. Nucleic Acids Research, 32(14), 4368–4376.
Xie, F., Huang, C., Liu, F., Zhang, H., Xiao, X., Sun, J., et al. (2021). CircPTPRA blocks the recognition of RNA N(6)-methyladenosine through interacting with IGF2BP1 to suppress bladder cancer progression. Molecular Cancer, 20(1), 68.
Yang, Y., Fan, X., Mao, M., Song, X., Wu, P., Zhang, Y., et al. (2017). Extensive translation of circular RNAs driven by N(6)-methyladenosine. Cell Research, 27(5), 626–641.
Meyer, K. D., Patil, D. P., Zhou, J., Zinoviev, A., Skabkin, M. A., Elemento, O., et al. (2015). 5’ UTR m(6)A promotes Cap-independent translation. Cell, 163(4), 999–1010.
Wang, Y., Liu, J., Ma, J., Sun, T., Zhou, Q., Wang, W., et al. (2019). Exosomal circRNAs: Biogenesis, effect and application in human diseases. Molecular Cancer, 18(1), 116.
Chen, X., Chen, R. X., Wei, W. S., Li, Y. H., Feng, Z. H., Tan, L., et al. (2018). PRMT5 circular RNA promotes metastasis of urothelial carcinoma of the bladder through sponging miR-30c to induce epithelial-mesenchymal transition. Clinical Cancer Research: An Official Journal of the American Association for Cancer Research, 24(24), 6319–6330.
Yang, C., Wu, S., Mou, Z., Zhou, Q., Dai, X., Ou, Y., et al. (2022). Exosome-derived circTRPS1 promotes malignant phenotype and CD8+ T cell exhaustion in bladder cancer microenvironments. Molecular Therapy : The Journal of the American Society of Gene Therapy, 30(3), 1054–1070.
Tang, Y., Liu, J., Li, X., & Wang, W. (2021). Exosomal circRNA HIPK3 knockdown inhibited cell proliferation and metastasis in prostate cancer by regulating miR-212/BMI-1 pathway. Journal of Biosciences, 46.
Ding, L., Zheng, Q., Lin, Y., Wang, R., Wang, H., Luo, W., et al. (2023). Exosome-derived circTFDP2 promotes prostate cancer progression by preventing PARP1 from caspase-3-dependent cleavage. Clinical and Translational Medicine, 13(1), e1156.
Cen, J., Liang, Y., Huang, Y., Pan, Y., Shu, G., Zheng, Z., et al. (2021). Circular RNA circSDHC serves as a sponge for miR-127-3p to promote the proliferation and metastasis of renal cell carcinoma via the CDKN3/E2F1 axis. Molecular Cancer, 20(1), 19.
Lu, Q., Liu, T., Feng, H., Yang, R., Zhao, X., Chen, W., et al. (2019). Circular RNA circSLC8A1 acts as a sponge of miR-130b/miR-494 in suppressing bladder cancer progression via regulating PTEN. Molecular Cancer, 18(1), 111.
Chao, F., Song, Z., Wang, S., Ma, Z., Zhuo, Z., Meng, T., et al. (2021). Novel circular RNA circSOBP governs amoeboid migration through the regulation of the miR-141-3p/MYPT1/p-MLC2 axis in prostate cancer. Clinical and Translational Medicine, 11(3), e360.
Shen, Z., Zhou, L., Zhang, C., & Xu, J. (2020). Reduction of circular RNA Foxo3 promotes prostate cancer progression and chemoresistance to docetaxel. Cancer Letters, 468, 88–101.
Yang, C., Yuan, W., Yang, X., Li, P., Wang, J., Han, J., et al. (2018). Circular RNA circ-ITCH inhibits bladder cancer progression by sponging miR-17/miR-224 and regulating p21, PTEN expression. Molecular Cancer, 17(1), 19.
Dong, W., Bi, J., Liu, H., Yan, D., He, Q., Zhou, Q., et al. (2019). Circular RNA ACVR2A suppresses bladder cancer cells proliferation and metastasis through miR-626/EYA4 axis. Molecular Cancer, 18(1), 95.
Zhang, X., Liu, X., Jing, Z., Bi, J., Li, Z., Liu, X., et al. (2020). The circINTS4/miR-146b/CARMA3 axis promotes tumorigenesis in bladder cancer. Cancer Gene Therapy, 27(3–4), 189–202.
Else, T., Kim, A. C., Sabolch, A., Raymond, V. M., Kandathil, A., Caoili, E. M., et al. (2014). Adrenocortical carcinoma. Endocrine Reviews, 35(2), 282–326.
Li, W., Liu, R., Wei, D., Zhang, W., Zhang, H., Huang, W., et al. (2020). Circular RNA circ-CCAC1 facilitates adrenocortical carcinoma cell proliferation, migration, and invasion through regulating the miR-514a-5p/C22orf46 axis. BioMed Research International, 2020, 3501451.
Hakenberg, O. W., Dräger, D. L., Erbersdobler, A., Naumann, C. M., Jünemann, K. P., & Protzel, C. (2018). The diagnosis and treatment of penile cancer. Deutsches Ärzteblatt International, 115(39), 646–652.
Heideman, D. A., Waterboer, T., Pawlita, M., Delis-van Diemen, P., Nindl, I., Leijte, J. A., et al. (2007). Human papillomavirus-16 is the predominant type etiologically involved in penile squamous cell carcinoma. Journal of Clinical Oncology: Official Journal of the American Society of Clinical Oncology, 25(29), 4550–4556.
Bonelli, P., Borrelli, A., Tuccillo, F. M., Buonaguro, F. M., & Tornesello, M. L. (2021). The Role of circRNAs in Human Papillomavirus (HPV)-Associated Cancers. Cancers, 13(5).
Bockhorn, M., Jain, R. K., & Munn, L. L. (2007). Active versus passive mechanisms in metastasis: Do cancer cells crawl into vessels, or are they pushed? The Lancet Oncology, 8(5), 444–448.
Lin, Y., Xu, J., & Lan, H. (2019). Tumor-associated macrophages in tumor metastasis: Biological roles and clinical therapeutic applications. Journal of Hematology & Oncology, 12(1), 76.
Dua, R. S., Gui, G. P., & Isacke, C. M. (2005). Endothelial adhesion molecules in breast cancer invasion into the vascular and lymphatic systems. European Journal of Surgical Oncology : The Journal of the European Society of Surgical Oncology and the British Association of Surgical Oncology, 31(8), 824–832.
Follain, G., Herrmann, D., Harlepp, S., Hyenne, V., Osmani, N., Warren, S. C., et al. (2020). Fluids and their mechanics in tumour transit: shaping metastasis. Nature Reviews Cancer, 20(2), 107–124.
Cheng, X., & Cheng, K. (2021). Visualizing cancer extravasation: from mechanistic studies to drug development. Cancer Metastasis Reviews, 40(1), 71–88.
Weis, S., Cui, J., Barnes, L., & Cheresh, D. (2004). Endothelial barrier disruption by VEGF-mediated Src activity potentiates tumor cell extravasation and metastasis. The Journal of Cell Biology, 167(2), 223–229.
Dufies, M., Giuliano, S., Ambrosetti, D., Claren, A., Ndiaye, P. D., Mastri, M., et al. (2017). Sunitinib stimulates expression of VEGFC by tumor cells and promotes lymphangiogenesis in clear cell renal cell carcinomas. Cancer Research, 77(5), 1212–1226.
Ndiaye, P. D., Dufies, M., Giuliano, S., Douguet, L., Grépin, R., Durivault, J., et al. (2019). VEGFC acts as a double-edged sword in renal cell carcinoma aggressiveness. Theranostics, 9(3), 661–675.
Nisato, R. E., Tille, J. C., & Pepper, M. S. (2003). Lymphangiogenesis and tumor metastasis. Thrombosis and Haemostasis, 90(4), 591–597.
Zhong, Z., Huang, M., Lv, M., He, Y., Duan, C., Zhang, L., et al. (2017). Circular RNA MYLK as a competing endogenous RNA promotes bladder cancer progression through modulating VEGFA/VEGFR2 signaling pathway. Cancer Letters, 403, 305–317.
Dai, Y., Li, D., Chen, X., Tan, X., Gu, J., Chen, M., et al. (2018). Circular RNA myosin light chain kinase (MYLK) promotes prostate cancer progression through modulating Mir-29a expression. Medical Science Monitor : International Medical Journal of Experimental and Clinical Research, 24, 3462–3471.
Li, J., Huang, C., Zou, Y., Yu, J., & Gui, Y. (2020). Circular RNA MYLK promotes tumour growth and metastasis via modulating miR-513a-5p/VEGFC signalling in renal cell carcinoma. Journal of Cellular and Molecular Medicine, 24(12), 6609–6621.
Miles, F. L., Pruitt, F. L., van Golen, K. L., & Cooper, C. R. (2008). Stepping out of the flow: capillary extravasation in cancer metastasis. Clinical & Experimental Metastasis, 25(4), 305–324.
Sadik, C. D., Kim, N. D., & Luster, A. D. (2011). Neutrophils cascading their way to inflammation. Trends in Immunology, 32(10), 452–460.
García-Román, J., & Zentella-Dehesa, A. (2013). Vascular permeability changes involved in tumor metastasis. Cancer Letters, 335(2), 259–269.
Sawant Dessai, A., Dominguez, M. P., Chen, U. I., Hasper, J., Prechtl, C., Yu, C., et al. (2021). Transcriptional repression of SIRT3 potentiates mitochondrial aconitase activation to drive aggressive prostate cancer to the bone. Cancer Research, 81(1), 50–63.
Gilardi, M., Bersini, S., Valtorta, S., Proietto, M., Crippa, M., Boussommier-Calleja, A., et al. (2021). The driving role of the Cdk5/Tln1/FAK(S732) axis in cancer cell extravasation dissected by human vascularized microfluidic models. Biomaterials, 276, 120975.
Liu, H., Bi, J., Dong, W., Yang, M., Shi, J., Jiang, N., et al. (2018). Invasion-related circular RNA circFNDC3B inhibits bladder cancer progression through the miR-1178-3p/G3BP2/SRC/FAK axis. Molecular Cancer, 17(1), 161.
Cruz-Munoz, W., Sanchez, O. H., Di Grappa, M., English, J. L., Hill, R. P., & Khokha, R. (2006). Enhanced metastatic dissemination to multiple organs by melanoma and lymphoma cells in timp-3-/- mice. Oncogene, 25(49), 6489–6496.
Xie, X., Sun, F. K., Huang, X., Wang, C. H., Dai, J., Zhao, J. P., et al. (2021). A circular RNA, circSMARCA5, inhibits prostate cancer proliferative, migrative, and invasive capabilities via the miR-181b-5p/miR-17-3p-TIMP3 axis. Aging, 13(15), 19908–19919.
Chambers, A. F., Groom, A. C., & MacDonald, I. C. (2002). Dissemination and growth of cancer cells in metastatic sites. Nature Reviews Cancer, 2(8), 563–572.
Hart, I. R., & Fidler, I. J. (1980). Role of organ selectivity in the determination of metastatic patterns of B16 melanoma. Cancer Research, 40(7), 2281–2287.
Turajlic, S., & Swanton, C. (2016). Metastasis as an evolutionary process. Science (New York, N.Y.), 352(6282), 169–175.
Ntziachristos, P., Lim, J. S., Sage, J., & Aifantis, I. (2014). From fly wings to targeted cancer therapies: a centennial for notch signaling. Cancer Cell, 25(3), 318–334.
Wieland, E., Rodriguez-Vita, J., Liebler, S. S., Mogler, C., Moll, I., Herberich, S. E., et al. (2017). Endothelial Notch1 Activity Facilitates Metastasis. Cancer Cell, 31(3), 355–367.
Huang, Z., Ding, Y., Zhang, L., He, S., Jia, Z., Gu, C., et al. (2020). Upregulated circPDK1 promotes RCC cell migration and invasion by regulating the miR-377-3P-NOTCH1 axis in renal cell carcinoma. OncoTargets and Therapy, 13, 11237–11252.
Chaffer, C. L., Brennan, J. P., Slavin, J. L., Blick, T., Thompson, E. W., & Williams, E. D. (2006). Mesenchymal-to-epithelial transition facilitates bladder cancer metastasis: Role of fibroblast growth factor receptor-2. Cancer Research, 66(23), 11271–11278.
Yang, C., Wu, S., Wu, X., Zhou, X., Jin, S., & Jiang, H. (2019). Silencing circular RNA UVRAG inhibits bladder cancer growth and metastasis by targeting the microRNA-223/fibroblast growth factor receptor 2 axis. Cancer Science, 110(1), 99–106.
Li, L., Ameri, A. H., Wang, S., Jansson, K. H., Casey, O. M., Yang, Q., et al. (2019). EGR1 regulates angiogenic and osteoclastogenic factors in prostate cancer and promotes metastasis. Oncogene, 38(35), 6241–6255.
Lu, J., Zhong, C., Luo, J., Shu, F., Lv, D., Liu, Z., et al. (2021). HnRNP-L-regulated circCSPP1/miR-520h/EGR1 axis modulates autophagy and promotes progression in prostate cancer. Molecular Therapy--Nucleic Acids, 26, 927–944.
Xiao, Y., & Yu, D. (2021). Tumor microenvironment as a therapeutic target in cancer. Pharmacology & Therapeutics, 221, 107753.
Hinshaw, D. C., & Shevde, L. A. (2019). The tumor microenvironment innately modulates cancer progression. Cancer Research, 79(18), 4557–4566.
Xiang, X., Wang, J., Lu, D., & Xu, X. (2021). Targeting tumor-associated macrophages to synergize tumor immunotherapy. Signal Transduction and Targeted Therapy, 6(1), 75.
Huang, X., Wang, J., Guan, J., Zheng, Z., Hao, J., Sheng, Z., et al. (2022). Exosomal Circsafb2 reshaping tumor environment to promote renal cell carcinoma progression by mediating M2 macrophage polarization. Frontiers in Oncology, 12, 808888.
Du, C., Yan, Q., Wang, Y., Ren, L., Lu, H., Han, M., et al. (2023). Circular RNA AGAP1 stimulates immune escape and distant metastasis in renal cell carcinoma. Molecular Biotechnology, 66.
Lv, J., Li, K., Yu, H., Han, J., Zhuang, J., Yu, R., et al. (2023). HNRNPL induced circFAM13B increased bladder cancer immunotherapy sensitivity via inhibiting glycolysis through IGF2BP1/PKM2 pathway. Journal of experimental & clinical cancer research : CR, 42(1), 41.
Sun, J., Zhang, H., Wei, W., Xiao, X., Huang, C., Wang, L., et al. (2023). Regulation of CD8(+) T cells infiltration and immunotherapy by circMGA/HNRNPL complex in bladder cancer. Oncogene, 42(15), 1247–1262.
Liu, Q., You, B., Meng, J., Huang, C. P., Dong, G., Wang, R., et al. (2022). Targeting the androgen receptor to enhance NK cell killing efficacy in bladder cancer by modulating ADAR2/circ_0001005/PD-L1 signaling. Cancer Gene Therapy, 29(12), 1988–2000.
Meng, M., & Wu, Y. C. (2022). LMX1B activated circular RNA GFRA1 modulates the tumorigenic properties and immune escape of prostate cancer. Journal of Immunology Research, 2022, 7375879.
Fidler, I. J. (2003). The pathogenesis of cancer metastasis: the ‘seed and soil’ hypothesis revisited. Nature Reviews Cancer, 3(6), 453–458.
Liu, Q., Zhang, H., Jiang, X., Qian, C., Liu, Z., & Luo, D. (2017). Factors involved in cancer metastasis: a better understanding to “seed and soil” hypothesis. Molecular Cancer, 16(1), 176.
Brodt, P. (2016). Role of the microenvironment in liver metastasis: from pre- to prometastatic niches. Clinical Cancer Research : an Official Journal of the American Association for Cancer Research, 22(24), 5971–5982.
Adekoya, T. O., & Richardson, R. M. (2020). Cytokines and chemokines as mediators of prostate cancer metastasis. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 21(12).
Coussens, L. M., & Werb, Z. (2002). Inflammation and cancer. Nature, 420(6917), 860–867.
Bianchi, M., Sun, M., Jeldres, C., Shariat, S. F., Trinh, Q. D., Briganti, A., et al. (2012). Distribution of metastatic sites in renal cell carcinoma: a population-based analysis. Annals of Oncology : Official Journal of the European Society for Medical Oncology, 23(4), 973–980.
Grünwald, V., Eberhardt, B., Bex, A., Flörcken, A., Gauler, T., Derlin, T., et al. (2018). An interdisciplinary consensus on the management of bone metastases from renal cell carcinoma. Nature Reviews Urology, 15(8), 511–521.
Chow, W. H., Dong, L. M., & Devesa, S. S. (2010). Epidemiology and risk factors for kidney cancer. Nature Reviews Urology, 7(5), 245–257.
Gong, D., Sun, Y., Guo, C., Sheu, T. J., Zhai, W., Zheng, J., et al. (2021). Androgen receptor decreases renal cell carcinoma bone metastases via suppressing the osteolytic formation through altering a novel circEXOC7 regulatory axis. Clinical and Translational Medicine, 11(3), e353.
Altorki, N. K., Markowitz, G. J., Gao, D., Port, J. L., Saxena, A., Stiles, B., et al. (2019). The lung microenvironment: an important regulator of tumour growth and metastasis. Nature Reviews Cancer, 19(1), 9–31.
Erler, J. T., Bennewith, K. L., Cox, T. R., Lang, G., Bird, D., Koong, A., et al. (2009). Hypoxia-induced lysyl oxidase is a critical mediator of bone marrow cell recruitment to form the premetastatic niche. Cancer Cell, 15(1), 35–44.
Liu, Y., Gu, Y., Han, Y., Zhang, Q., Jiang, Z., Zhang, X., et al. (2016). Tumor exosomal rnas promote lung pre-metastatic niche formation by activating alveolar epithelial TLR3 to recruit neutrophils. Cancer Cell, 30(2), 243–256.
Li, W., Song, Y. Y., Rao, T., Yu, W. M., Ruan, Y., Ning, J. Z., et al. (2022). CircCSNK1G3 up-regulates miR-181b to promote growth and metastasis via TIMP3-mediated epithelial to mesenchymal transitions in renal cell carcinoma. Journal of Cellular and Molecular Medicine, 26(6), 1729–1741.
Liu, H., Hu, G., Wang, Z., Liu, Q., Zhang, J., Chen, Y., et al. (2020). circPTCH1 promotes invasion and metastasis in renal cell carcinoma via regulating miR-485-5p/MMP14 axis. Theranostics, 10(23), 10791–10807.
Lv, Q., Wang, G., Zhang, Y., Shen, A., Tang, J., Sun, Y., et al. (2021). CircAGAP1 promotes tumor progression by sponging miR-15-5p in clear cell renal cell carcinoma. Journal of Experimental & Clinical Cancer Research : CR, 40(1), 76.
Liang, Y., Cen, J., Huang, Y., Fang, Y., Wang, Y., Shu, G., et al. (2022). CircNTNG1 inhibits renal cell carcinoma progression via HOXA5-mediated epigenetic silencing of Slug. Molecular Cancer, 21(1), 224.
Zhao, B., Huang, C., Pan, J., Hu, H., Liu, X., Zhang, K., et al. (2022). circPLIN2 promotes clear cell renal cell carcinoma progression by binding IGF2BP proteins and miR-199a-3p. Cell Death & Disease, 13(12), 1030.
Xie, F., Li, Y., Wang, M., Huang, C., Tao, D., Zheng, F., et al. (2018). Circular RNA BCRC-3 suppresses bladder cancer proliferation through miR-182-5p/p27 axis. Molecular Cancer, 17(1), 144.
Bi, J., Liu, H., Dong, W., Xie, W., He, Q., Cai, Z., et al. (2019). Circular RNA circ-ZKSCAN1 inhibits bladder cancer progression through miR-1178-3p/p21 axis and acts as a prognostic factor of recurrence. Molecular Cancer, 18(1), 133.
Zhu, J., Luo, Y., Zhao, Y., Kong, Y., Zheng, H., Li, Y., et al. (2021). circEHBP1 promotes lymphangiogenesis and lymphatic metastasis of bladder cancer via miR-130a-3p/TGFβR1/VEGF-D signaling. Molecular Therapy : The Journal of the American Society of Gene Therapy, 29(5), 1838–1852.
Su, H., Tao, T., Yang, Z., Kang, X., Zhang, X., Kang, D., et al. (2019). Circular RNA cTFRC acts as the sponge of MicroRNA-107 to promote bladder carcinoma progression. Molecular Cancer, 18(1), 27.
Gu, C., Zhou, N., Wang, Z., Li, G., Kou, Y., Yu, S., et al. (2018). circGprc5a promoted bladder oncogenesis and metastasis through Gprc5a-targeting peptide. Molecular Therapy--Nucleic Acids, 13, 633–641.
Li, Y., Kong, Y., An, M., Luo, Y., Zheng, H., Lin, Y., et al. (2023). ZEB1-mediated biogenesis of circNIPBL sustains the metastasis of bladder cancer via Wnt/β-catenin pathway. Journal of Experimental & Clinical Cancer Research : CR, 42(1), 191.
Kong, Z., Wan, X., Lu, Y., Zhang, Y., Huang, Y., Xu, Y., et al. (2020). Circular RNA circFOXO3 promotes prostate cancer progression through sponging miR-29a-3p. Journal of Cellular and Molecular Medicine, 24(1), 799–813.
Lilja, H., Ulmert, D., & Vickers, A. J. (2008). Prostate-specific antigen and prostate cancer: Prediction, detection and monitoring. Nature Reviews Cancer, 8(4), 268–278.
Unger, F. T., Witte, I., & David, K. A. (2015). Prediction of individual response to anticancer therapy: historical and future perspectives. Cellular and Molecular Life Sciences: CMLS, 72(4), 729–757.
Ragnarsson, O. (2020). Cushing’s syndrome - Disease monitoring: Recurrence, surveillance with biomarkers or imaging studies. Best Practice & Research. Clinical Endocrinology & Metabolism, 34(2), 101382.
Jeck, W. R., Sorrentino, J. A., Wang, K., Slevin, M. K., Burd, C. E., Liu, J., et al. (2013). Circular RNAs are abundant, conserved, and associated with ALU repeats. RNA (New York, NY), 19(2), 141–157.
Schwanhäusser, B., Busse, D., Li, N., Dittmar, G., Schuchhardt, J., Wolf, J., et al. (2011). Global quantification of mammalian gene expression control. Nature, 473(7347), 337–342.
Rybak-Wolf, A., Stottmeister, C., Glažar, P., Jens, M., Pino, N., Giusti, S., et al. (2015). Circular RNAs in the mammalian brain are highly abundant, conserved, and dynamically expressed. Molecular Cell, 58(5), 870–885.
Shen, T., Han, M., Wei, G., & Ni, T. (2015). An intriguing RNA species--Perspectives of circularized RNA. Protein & Cell, 6(12), 871–880.
Wang, P. L., Bao, Y., Yee, M. C., Barrett, S. P., Hogan, G. J., Olsen, M. N., et al. (2014). Circular RNA is expressed across the eukaryotic tree of life. PLoS One, 9(6), e90859.
Danan, M., Schwartz, S., Edelheit, S., & Sorek, R. (2012). Transcriptome-wide discovery of circular RNAs in Archaea. Nucleic Acids Research, 40(7), 3131–3142.
Li, Y., Zheng, Q., Bao, C., Li, S., Guo, W., Zhao, J., et al. (2015). Circular RNA is enriched and stable in exosomes: A promising biomarker for cancer diagnosis. Cell Research, 25(8), 981–984.
Luo, J., Li, Y., Zheng, W., Xie, N., Shi, Y., Long, Z., et al. (2019). Characterization of a Prostate- and Prostate Cancer-Specific Circular RNA Encoded by the Androgen Receptor Gene. Molecular Therapy--Nucleic Acids, 18, 916–926.
Dahl, M., Husby, S., Eskelund, C. W., Besenbacher, S., Fjelstrup, S., Côme, C., et al. (2022). Expression patterns and prognostic potential of circular RNAs in mantle cell lymphoma: A study of younger patients from the MCL2 and MCL3 clinical trials. Leukemia, 36(1), 177–188.
Zuo, L., Zhang, L., Zu, J., Wang, Z., Han, B., Chen, B., et al. (2020). Circulating circular RNAs as biomarkers for the diagnosis and prediction of outcomes in acute ischemic stroke. Stroke, 51(1), 319–323.
Wang, Y., Zhang, S., Li, F., Zhou, Y., Zhang, Y., Wang, Z., et al. (2020). Therapeutic target database 2020: enriched resource for facilitating research and early development of targeted therapeutics. Nucleic Acids Research, 48(D1), D1031-D1d41.
Williford, J. M., Wu, J., Ren, Y., Archang, M. M., Leong, K. W., & Mao, H. Q. (2014). Recent advances in nanoparticle-mediated siRNA delivery. Annual Review of Biomedical Engineering, 16, 347–370.
Yu, C., Zhang, Y., Wang, N., Wei, W., Cao, K., Zhang, Q., et al. (2022). Treatment of bladder cancer by geoinspired synthetic chrysotile nanocarrier-delivered circPRMT5 siRNA. Biomaterials Research, 26(1), 6.
Mao, W., Wang, K., Xu, B., Zhang, H., Sun, S., Hu, Q., et al. (2021). ciRS-7 is a prognostic biomarker and potential gene therapy target for renal cell carcinoma. Molecular Cancer, 20(1), 142.
Ran, F. A., Hsu, P. D., Wright, J., Agarwala, V., Scott, D. A., & Zhang, F. (2013). Genome engineering using the CRISPR-Cas9 system. Nature Protocols, 8(11), 2281–2308.
Zheng, Q., Bao, C., Guo, W., Li, S., Chen, J., Chen, B., et al. (2016). Circular RNA profiling reveals an abundant circHIPK3 that regulates cell growth by sponging multiple miRNAs. Nature Communications, 7, 11215.
Piwecka, M., Glažar, P., Hernandez-Miranda, L. R., Memczak, S., Wolf, S. A., Rybak-Wolf, A., et al. (2017). Loss of a mammalian circular RNA locus causes miRNA deregulation and affects brain function. Science (New York, NY), 357(6357).
Huang, S., Li, X., Zheng, H., Si, X., Li, B., Wei, G., et al. (2019). Loss of super-enhancer-regulated circRNA Nfix induces cardiac regeneration after myocardial infarction in adult mice. Circulation, 139(25), 2857–2876.
Li, S., Li, X., Xue, W., Zhang, L., Yang, L. Z., Cao, S. M., et al. (2021). Screening for functional circular RNAs using the CRISPR-Cas13 system. Nature Methods, 18(1), 51–59.
Bennett, C. F., & Swayze, E. E. (2010). RNA targeting therapeutics: Molecular mechanisms of antisense oligonucleotides as a therapeutic platform. Annual Review of Pharmacology and Toxicology, 50, 259–293.
Wesselhoeft, R. A., Kowalski, P. S., & Anderson, D. G. (2018). Engineering circular RNA for potent and stable translation in eukaryotic cells. Nature Communications, 9(1), 2629.
Verduci, L., Strano, S., Yarden, Y., & Blandino, G. (2019). The circRNA-microRNA code: Emerging implications for cancer diagnosis and treatment. Molecular Oncology, 13(4), 669–680.
Holdt, L. M., Kohlmaier, A., & Teupser, D. (2018). Circular RNAs as Therapeutic Agents and Targets. Frontiers in Physiology, 9, 1262.
Wurster, S. E., & Maher, L. J., 3rd. (2008). Selection and characterization of anti-NF-kappaB p65 RNA aptamers. RNA (New York, NY), 14(6), 1037–1047.
Filonov, G. S., Moon, J. D., Svensen, N., & Jaffrey, S. R. (2014). Broccoli: Rapid selection of an RNA mimic of green fluorescent protein by fluorescence-based selection and directed evolution. Journal of the American Chemical Society, 136(46), 16299–16308.
Pfafenrot, C., Schneider, T., Müller, C., Hung, L. H., Schreiner, S., Ziebuhr, J., et al. (2021). Inhibition of SARS-CoV-2 coronavirus proliferation by designer antisense-circRNAs. Nucleic Acids Research, 49(21), 12502–12516.
Qu, L., Yi, Z., Shen, Y., Lin, L., Chen, F., Xu, Y., et al. (2022). Circular RNA vaccines against SARS-CoV-2 and emerging variants. Cell, 185(10), 1728–44.e16.
Greene, J., Baird, A. M., Brady, L., Lim, M., Gray, S. G., McDermott, R., et al. (2017). Circular RNAs: Biogenesis, function and role in human diseases. Frontiers in Molecular Biosciences, 4, 38.
Shim, M. S., & Kwon, Y. J. (2010). Efficient and targeted delivery of siRNA in vivo. The FEBS Journal, 277(23), 4814–4827.
Huang, L., & Liu, Y. (2011). In vivo delivery of RNAi with lipid-based nanoparticles. Annual Review of Biomedical Engineering, 13, 507–530.
Fan, Q., Yang, L., Zhang, X., Peng, X., Wei, S., Su, D., et al. (2018). The emerging role of exosome-derived non-coding RNAs in cancer biology. Cancer Letters, 414, 107–115.
Wang, A. Z., Langer, R., & Farokhzad, O. C. (2012). Nanoparticle delivery of cancer drugs. Annual Review of Medicine, 63, 185–198.
Du, W. W., Fang, L., Yang, W., Wu, N., Awan, F. M., Yang, Z., et al. (2017). Induction of tumor apoptosis through a circular RNA enhancing Foxo3 activity. Cell Death and Differentiation, 24(2), 357–370.
Liu, X., Zhang, Y., Zhou, S., Dain, L., Mei, L., & Zhu, G. (2022). Circular RNA: An emerging frontier in RNA therapeutic targets, RNA therapeutics, and mRNA vaccines. Journal of Controlled Release: Official Journal of the Controlled Release Society, 348, 84–94.
Li, H., Peng, K., Yang, K., Ma, W., Qi, S., Yu, X., et al. (2022). Circular RNA cancer vaccines drive immunity in hard-to-treat malignancies. Theranostics, 12(14), 6422–6436.
Acknowledgements
This work was supported in part by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (grants 81672523), Xisike-Pilot Cancer Research Foundation (grants 20201030), and Applied Basic Research Program of Liaoning Province in 2023 (grants 2023010409133159830).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
The work presented here was carried out in collaboration with all authors. YYZ identified the topic of the review and directed the completion of the article. YX, JL, and MY conceived the structure of the article; YX, ZPG, XYS, and DS drafted the original draft; YX, TO, and YYZ revised the article. All of the authors had participated in the preparation of this article.
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Xu, Y., Gao, Z., Sun, X. et al. The role of circular RNA during the urological cancer metastasis: exploring regulatory mechanisms and potential therapeutic targets. Cancer Metastasis Rev (2024). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10555-024-10182-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10555-024-10182-x