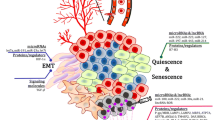
Abstract
Exosomes comprise a subtype of extracellular vesicles involved in cell-to-cell communication, specifically by transporting biological molecules, such as proteins and nucleic acids, to either local or more distant recipient cells, thus triggering distinct biological behaviors. Included in the exosome cargo is frequently a wide range of proteolytic enzymes, such as the matrix metalloproteinases (MMPs), the disintegrin and metalloproteinases (ADAMs), and the ADAM with thrombospondin-like motifs (ADAMTSs), whose functions contribute to the development and progression of cancer. In recent years, extensive research on the potential use of exosomes in diagnostic and therapeutic applications for personalized medicine has emerged, but the targeting of the proteolytic cargo of exosomes has not been fully exploited in this direction. In this review, we aim to explore both the mechanistic and the translational importance of proteolytic enzymes carried by the tumor cell–derived exosomes, as well as their role in the acquisition and support of certain hallmarks of cancer.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Mathieu, M., Martin-Jaular, L., Lavieu, G., & Thery, C. (2019). Specificities of secretion and uptake of exosomes and other extracellular vesicles for cell-to-cell communication. Nature Cell Biology, 21(1), 9–17. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41556-018-0250-9
Bebelman, M. P., Janssen, E., Pegtel, D. M., & Crudden, C. (2021). The forces driving cancer extracellular vesicle secretion. Neoplasia (New York, N. Y.), 23(1), 149–157. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neo.2020.11.011
Zhang, H. G., & Grizzle, W. E. (2011). Exosomes and cancer: A newly described pathway of immune suppression. Clinical Cancer Research, 17(5), 959–964. https://doi.org/10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-10-1489
Zhang, C., Ji, Q., Yang, Y., Li, Q., & Wang, Z. (2018). Exosome: Function and role in cancer metastasis and drug resistance. Technology in Cancer Research & Treatment, 17, 1533033818763450. https://doi.org/10.1177/1533033818763450
Zhang, X., Yuan, X., Shi, H., Wu, L., Qian, H., & Xu, W. (2015). Exosomes in cancer: Small particle, big player. Journal of Hematology & Oncology, 8, 83. https://doi.org/10.1186/s13045-015-0181-x
Couto, N., Caja, S., Maia, J., Strano Moraes, M. C., & Costa-Silva, B. (2018). Exosomes as emerging players in cancer biology. Biochimie, 155, 2–10. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biochi.2018.03.006
McAndrews, K. M., & Kalluri, R. (2019). Mechanisms associated with biogenesis of exosomes in cancer. Molecular Cancer, 18(1), 52. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12943-019-0963-9
Trams, E. G., Lauter, C. J., Salem, N., Jr., & Heine, U. (1981). Exfoliation of membrane ecto-enzymes in the form of micro-vesicles. Biochimica et Biophysica Acta, 645(1), 63–70. https://doi.org/10.1016/0005-2736(81)90512-5
Sancho-Albero, M., Navascues, N., Mendoza, G., Sebastian, V., Arruebo, M., Martin-Duque, P., et al. (2019). Exosome origin determines cell targeting and the transfer of therapeutic nanoparticles towards target cells. J Nanobiotechnology, 17(1), 16. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12951-018-0437-z
Ferguson, S. W., & Nguyen, J. (2016). Exosomes as therapeutics: The implications of molecular composition and exosomal heterogeneity. Journal of Controlled Release, 228, 179–190. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jconrel.2016.02.037
Sanderson, R. D., Bandari, S. K., & Vlodavsky, I. (2019). Proteases and glycosidases on the surface of exosomes: Newly discovered mechanisms for extracellular remodeling. Matrix Biology, 75–76, 160–169. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.matbio.2017.10.007
Zhang, L., & Yu, D. (2019). Exosomes in cancer development, metastasis, and immunity. Biochimica et Biophysica Acta - Reviews on Cancer, 1871(2), 455–468. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bbcan.2019.04.004
Schubert, A., & Boutros, M. (2021). Extracellular vesicles and oncogenic signaling. Molecular Oncology, 15(1), 3–26. https://doi.org/10.1002/1878-0261.12855
Wortzel, I., Dror, S., Kenific, C. M., & Lyden, D. (2019). Exosome-mediated metastasis: Communication from a distance. Developmental Cell, 49(3), 347–360. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.devcel.2019.04.011
Hoshino, A., Costa-Silva, B., Shen, T. L., Rodrigues, G., Hashimoto, A., Tesic Mark, M., et al. (2015). Tumour exosome integrins determine organotropic metastasis. Nature, 527(7578), 329–335. https://doi.org/10.1038/nature15756
García-Silva, S., Benito-Martín, A., Nogués, L., Hernández-Barranco, A., Mazariegos, M. S., Santos, V., et al. (2021). Melanoma-derived small extracellular vesicles induce lymphangiogenesis and metastasis through an NGFR-dependent mechanism. Nature Cancer, 2(12), 1387–1405. https://doi.org/10.1038/s43018-021-00272-y
Quesnel, A., Karagiannis, G. S., & Filippou, P. S. (2020). Extracellular proteolysis in glioblastoma progression and therapeutics. Biochimica et Biophysica Acta - Reviews on Cancer, 1874(2), 188428. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bbcan.2020.188428
Yekula, A., Yekula, A., Muralidharan, K., Kang, K., Carter, B. S., & Balaj, L. (2019). Extracellular vesicles in glioblastoma tumor microenvironment. Frontiers in Immunology, 10, 3137. https://doi.org/10.3389/fimmu.2019.03137
Tamkovich, S. N., Yunusova, N. V., Tugutova, E., Somov, A. K., Proskura, K. V., Kolomiets, L. A., et al. (2019). Protease cargo in circulating exosomes of breast cancer and ovarian cancer patients. Asian Pac J Cancer Prev, 20(1), 255–262. https://doi.org/10.31557/APJCP.2019.20.1.255
Nawaz, M., Shah, N., Zanetti, B. R., Maugeri, M., Silvestre, R. N., Fatima, F., et al. (2018). Extracellular vesicles and matrix remodeling enzymes: The emerging roles in extracellular matrix remodeling, progression of diseases and tissue repair. Cells, 7(10), https://doi.org/10.3390/cells7100167.
Shimoda, M., & Khokha, R. (2013). Proteolytic factors in exosomes. PROTEOMICS, 13(10–11), 1624–1636. https://doi.org/10.1002/pmic.201200458
Shimoda, M., & Khokha, R. (2017). Metalloproteinases in extracellular vesicles. Biochimica et Biophysica Acta (BBA) - Molecular Cell Research, 1864(11, Part A), 1989–2000. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bbamcr.2017.05.027
Inamdar, S., Nitiyanandan, R., & Rege, K. (2017). Emerging applications of exosomes in cancer therapeutics and diagnostics. Bioengineering & Translational Medicine, 2(1), 70–80. https://doi.org/10.1002/btm2.10059
Karagiannis, G. S., Pavlou, M. P., & Diamandis, E. P. (2010). Cancer secretomics reveal pathophysiological pathways in cancer molecular oncology. Molecular Oncology, 4(6), 496–510. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.molonc.2010.09.001
Bunggulawa, E. J., Wang, W., Yin, T., Wang, N., Durkan, C., Wang, Y., et al. (2018). Recent advancements in the use of exosomes as drug delivery systems. J Nanobiotechnology, 16(1), 81. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12951-018-0403-9
Arrighetti, N., Corbo, C., Evangelopoulos, M., Pasto, A., Zuco, V., & Tasciotti, E. (2019). Exosome-like nanovectors for drug delivery in cancer. Current Medicinal Chemistry, 26(33), 6132–6148. https://doi.org/10.2174/0929867325666180831150259
Doyle, L. M., & Wang, M. Z. (2019). Overview of extracellular vesicles, their origin, composition, purpose, and methods for exosome isolation and analysis. Cells, 8(7), https://doi.org/10.3390/cells8070727.
Javeed, N., & Mukhopadhyay, D. (2017). Exosomes and their role in the micro-/macro-environment: A comprehensive review. Journal of Biomedical Research, 31(5), 386–394. https://doi.org/10.7555/JBR.30.20150162
Qin, W., Tsukasaki, Y., Dasgupta, S., Mukhopadhyay, N., Ikebe, M., & Sauter, E. R. (2016). Exosomes in human breast milk promote EMT. Clinical Cancer Research, 22(17), 4517–4524. https://doi.org/10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-16-0135
Kalluri, R. (2016). The biology and function of exosomes in cancer. The Journal of Clinical Investigation, 126(4), 1208–1215. https://doi.org/10.1172/JCI81135
Ghaemmaghami, A. B., Mahjoubin-Tehran, M., Movahedpour, A., Morshedi, K., Sheida, A., Taghavi, S. P., et al. (2020). Role of exosomes in malignant glioma: MicroRNAs and proteins in pathogenesis and diagnosis. Cell Communication and Signaling: CCS, 18(1), 120. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12964-020-00623-9
Ruivo, C. F., Adem, B., Silva, M., & Melo, S. A. (2017). The biology of cancer exosomes: Insights and new perspectives. Cancer Research, 77(23), 6480–6488. https://doi.org/10.1158/0008-5472.can-17-0994
Taraboletti, G., D’Ascenzo, S., Giusti, I., Marchetti, D., Borsotti, P., Millimaggi, D., et al. (2006). Bioavailability of VEGF in tumor-shed vesicles depends on vesicle burst induced by acidic pH. Neoplasia, 8(2), 96–103. https://doi.org/10.1593/neo.05583
Baghban, R., Roshangar, L., Jahanban-Esfahlan, R., Seidi, K., Ebrahimi-Kalan, A., Jaymand, M., et al. (2020). Tumor microenvironment complexity and therapeutic implications at a glance. Cell Communication and Signaling, 18(1), 59. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12964-020-0530-4
Han, L., Lam, E. W. F., & Sun, Y. (2019). Extracellular vesicles in the tumor microenvironment: Old stories, but new tales. Molecular Cancer, 18(1), 59. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12943-019-0980-8
Stoeck, A., Keller, S., Riedle, S., Sanderson, M. P., Runz, S., Le Naour, F., et al. (2006). A role for exosomes in the constitutive and stimulus-induced ectodomain cleavage of L1 and CD44. The Biochemical journal, 393(Pt 3), 609–618. https://doi.org/10.1042/BJ20051013
Gutwein, P., Stoeck, A., Riedle, S., Gast, D., Runz, S., Condon, T. P., et al. (2005). Cleavage of L1 in exosomes and apoptotic membrane vesicles released from ovarian carcinoma cells. Clinical Cancer Research, 11(7), 2492–2501. https://doi.org/10.1158/1078-0432.ccr-04-1688
Shimoda, M. (2019). Extracellular vesicle-associated MMPs: A modulator of the tissue microenvironment. Advances in Clinical Chemistry, 88, 35–66. https://doi.org/10.1016/bs.acc.2018.10.006
Morad, G., & Moses, M. A. (2019). Brainwashed by extracellular vesicles: The role of extracellular vesicles in primary and metastatic brain tumour microenvironment. Journal of extracellular vesicles, 8(1), 1627164–1627164. https://doi.org/10.1080/20013078.2019.1627164
Mu, W., Rana, S., & Zöller, M. (2013). Host matrix modulation by tumor exosomes promotes motility and invasiveness. Neoplasia (New York, N.Y.), 15(8), 875–887. https://doi.org/10.1593/neo.13786
Walker, C., Mojares, E., & Del Rio Hernandez, A. (2018). Role of extracellular matrix in development and cancer progression. Int J Mol Sci, 19(10), https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms19103028.
Leeman, M. F., Curran, S., & Murray, G. I. (2003). New insights into the roles of matrix metalloproteinases in colorectal cancer development and progression. The Journal of Pathology, 201(4), 528–534. https://doi.org/10.1002/path.1466
Hakulinen, J., Sankkila, L., Sugiyama, N., Lehti, K., & Keski-Oja, J. (2008). Secretion of active membrane type 1 matrix metalloproteinase (MMP-14) into extracellular space in microvesicular exosomes. Journal of Cellular Biochemistry, 105(5), 1211–1218. https://doi.org/10.1002/jcb.21923
Muralidharan-Chari, V., Clancy, J., Plou, C., Romao, M., Chavrier, P., Raposo, G., et al. (2009). ARF6-regulated shedding of tumor cell-derived plasma membrane microvesicles. Current Biology, 19(22), 1875–1885. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cub.2009.09.059
Castro-Castro, A., Marchesin, V., Monteiro, P., Lodillinsky, C., Rossé, C., & Chavrier, P. (2016). Cellular and molecular mechanisms of MT1-MMP-dependent cancer cell invasion. Annual Review of Cell and Developmental Biology, 32, 555–576. https://doi.org/10.1146/annurev-cellbio-111315-125227
Ginestra, A., Monea, S., Seghezzi, G., Dolo, V., Nagase, H., Mignatti, P., et al. (1997). Urokinase plasminogen activator and gelatinases are associated with membrane vesicles shed by human HT1080 fibrosarcoma cells. Journal of Biological Chemistry, 272(27), 17216–17222. https://doi.org/10.1074/jbc.272.27.17216
Zhao, Y., Lyons, C. E., Jr., Xiao, A., Templeton, D. J., Sang, Q. A., Brew, K., et al. (2008). Urokinase directly activates matrix metalloproteinases-9: A potential role in glioblastoma invasion. Biochemical and biophysical research communications, 369(4), 1215–1220. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bbrc.2008.03.038
Schnaeker, E. M., Ossig, R., Ludwig, T., Dreier, R., Oberleithner, H., Wilhelmi, M., et al. (2004). Microtubule-dependent matrix metalloproteinase-2/matrix metalloproteinase-9 exocytosis: Prerequisite in human melanoma cell invasion. Cancer Research, 64(24), 8924–8931. https://doi.org/10.1158/0008-5472.can-04-0324
Jacob, A., Linklater, E., Bayless, B. A., Lyons, T., & Prekeris, R. (2016). The role and regulation of Rab40b-Tks5 complex during invadopodia formation and cancer cell invasion. Journal of cell science, 129(23), 4341–4353. https://doi.org/10.1242/jcs.193904
McCready, J., Sims, J. D., Chan, D., & Jay, D. G. (2010). Secretion of extracellular hsp90α via exosomes increases cancer cell motility: A role for plasminogen activation. BMC Cancer, 10(1), 294. https://doi.org/10.1186/1471-2407-10-294
Lo Cicero, A., Majkowska, I., Nagase, H., Di Liegro, I., & Troeberg, L. (2012). Microvesicles shed by oligodendroglioma cells and rheumatoid synovial fibroblasts contain aggrecanase activity. Matrix Biology, 31(4), 229–233. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.matbio.2012.02.005
You, Y., Shan, Y., Chen, J., Yue, H., You, B., Shi, S., et al. (2015). Matrix metalloproteinase 13-containing exosomes promote nasopharyngeal carcinoma metastasis. Cancer science, 106(12), 1669–1677. https://doi.org/10.1111/cas.12818
Saber, S. H., Ali, H. E. A., Gaballa, R., Gaballah, M., Ali, H. I., Zerfaoui, M., et al. (2020). Exosomes are the driving force in preparing the soil for the metastatic seeds: Lessons from the prostate cancer. Cells, 9(3), 564. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells9030564
Melo, S. A., Sugimoto, H., O’Connell, J. T., Kato, N., Villanueva, A., Vidal, A., et al. (2014). Cancer exosomes perform cell-independent microRNA biogenesis and promote tumorigenesis. Cancer Cell, 26(5), 707–721. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ccell.2014.09.005
Skog, J., Würdinger, T., van Rijn, S., Meijer, D. H., Gainche, L., Sena-Esteves, M., et al. (2008). Glioblastoma microvesicles transport RNA and proteins that promote tumour growth and provide diagnostic biomarkers. Nature cell biology, 10(12), 1470–1476. https://doi.org/10.1038/ncb1800
Raimondi, L., De Luca, A., Amodio, N., Manno, M., Raccosta, S., Taverna, S., et al. (2015). Involvement of multiple myeloma cell-derived exosomes in osteoclast differentiation. Oncotarget, 6(15), 13772–13789. https://doi.org/10.18632/oncotarget.3830
Sánchez, C. A., Andahur, E. I., Valenzuela, R., Castellón, E. A., Fullá, J. A., Ramos, C. G., et al. (2016). Exosomes from bulk and stem cells from human prostate cancer have a differential microRNA content that contributes cooperatively over local and pre-metastatic niche. Oncotarget, 7(4), 3993–4008. https://doi.org/10.18632/oncotarget.6540
Wang, J., Zhang, Q., Wang, D., Yang, S., Zhou, S., Xu, H., et al. (2020). Microenvironment-induced TIMP2 loss by cancer-secreted exosomal miR-4443 promotes liver metastasis of breast cancer. 235(7–8), 5722–5735, https://doi.org/10.1002/jcp.29507.
Hatanaka, M., Higashi, Y., Fukushige, T., Baba, N., Kawai, K., Hashiguchi, T., et al. (2014). Cleaved CD147 shed from the surface of malignant melanoma cells activates MMP2 produced by fibroblasts. Anticancer Research, 34(12), 7091–7096.
Aoki, M., Koga, K., Hamasaki, M., Egawa, N., & Nabeshima, K. (2017). Emmprin, released as a microvesicle in epithelioid sarcoma, interacts with fibroblasts. International Journal of Oncology, 50(6), 2229–2235. https://doi.org/10.3892/ijo.2017.3986
Zhang, W., Zhao, P., Xu, X. L., Cai, L., Song, Z. S., Cao, D. Y., et al. (2013). Annexin A2 promotes the migration and invasion of human hepatocellular carcinoma cells in vitro by regulating the shedding of CD147-harboring microvesicles from tumor cells. PLoS ONE, 8(8), e67268. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0067268
Yokoi, A., Yoshioka, Y., Yamamoto, Y., Ishikawa, M., Ikeda, S. I., Kato, T., et al. (2017). Malignant extracellular vesicles carrying MMP1 mRNA facilitate peritoneal dissemination in ovarian cancer. Nature Communications, 8, 14470. https://doi.org/10.1038/ncomms14470
Dos Anjos Pultz, B., Andrés Cordero da Luz, F., Socorro Faria, S., Peixoto Ferreira de Souza, L., Cristina Brígido Tavares, P., Alonso Goulart, V., et al. (2017). The multifaceted role of extracellular vesicles in metastasis: Priming the soil for seeding. 140(11), 2397–2407, https://doi.org/10.1002/ijc.30595.
Maji, S., Chaudhary, P., Akopova, I., Nguyen, P. M., Hare, R. J., Gryczynski, I., et al. (2017). Exosomal annexin II promotes angiogenesis and breast cancer metastasis. Molecular Cancer Research, 15(1), 93–105. https://doi.org/10.1158/1541-7786.Mcr-16-0163
Stephens, D. C., Osunsanmi, N., Sochacki, K. A., Powell, T. W., & Taraska, J. W. (2019). Spatiotemporal organization and protein dynamics involved in regulated exocytosis of MMP-9 in breast cancer cells. 151(12), 1386–1403, https://doi.org/10.1085/jgp.201812299.
Becker, A., Thakur, B. K., Weiss, J. M., Kim, H. S., Peinado, H., & Lyden, D. (2016). Extracellular vesicles in cancer: Cell-to-cell mediators of metastasis. Cancer Cell, 30(6), 836–848. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ccell.2016.10.009
Peinado, H., Lavotshkin, S., & Lyden, D. (2011). The secreted factors responsible for pre-metastatic niche formation: Old sayings and new thoughts. Seminars in Cancer Biology, 21(2), 139–146. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.semcancer.2011.01.002
Clancy, J. W., Sedgwick, A., Rosse, C., Muralidharan-Chari, V., Raposo, G., Method, M., et al. (2015). Regulated delivery of molecular cargo to invasive tumour-derived microvesicles. Nature Communications, 6, 6919. https://doi.org/10.1038/ncomms7919
Hoshino, D., Kirkbride, K. C., Costello, K., Clark, E. S., Sinha, S., Grega-Larson, N., et al. (2013). Exosome secretion is enhanced by invadopodia and drives invasive behavior. Cell Reports, 5(5), 1159–1168. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.celrep.2013.10.050
Kajita, M., Itoh, Y., Chiba, T., Mori, H., Okada, A., Kinoh, H., et al. (2001). Membrane-type 1 matrix metalloproteinase cleaves CD44 and promotes cell migration. Journal of Cell Biology, 153(5), 893–904. https://doi.org/10.1083/jcb.153.5.893
Colangelo, N. W., & Azzam, E. I. (2020). Extracellular vesicles originating from glioblastoma cells increase metalloproteinase release by astrocytes: The role of CD147 (EMMPRIN) and ionizing radiation. Cell Communication and Signaling, 18(1), 21. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12964-019-0494-4
Shoucair, I., Weber Mello, F., Jabalee, J., Maleki, S., & Garnis, C. (2020). The role of cancer-associated fibroblasts and extracellular vesicles in tumorigenesis. Int J Mol Sci, 21(18), https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms21186837.
Xu, G., Zhang, B., Ye, J., Cao, S., Shi, J., Zhao, Y., et al. (2019). Exosomal miRNA-139 in cancer-associated fibroblasts inhibits gastric cancer progression by repressing MMP11 expression. International Journal of Biological Sciences, 15(11), 2320–2329. https://doi.org/10.7150/ijbs.33750
Li, Y. Y., Tao, Y. W., Gao, S., Li, P., Zheng, J. M., Zhang, S. E., et al. (2018). Cancer-associated fibroblasts contribute to oral cancer cells proliferation and metastasis via exosome-mediated paracrine miR-34a-5p. eBioMedicine, 36, 209–220. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ebiom.2018.09.006
Miyoshi, A., Kitajima, Y., Kido, S., Shimonishi, T., Matsuyama, S., Kitahara, K., et al. (2005). Snail accelerates cancer invasion by upregulating MMP expression and is associated with poor prognosis of hepatocellular carcinoma. British Journal of Cancer, 92(2), 252–258. https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.bjc.6602266
Tauro, B. J., Mathias, R. A., Greening, D. W., Gopal, S. K., Ji, H., Kapp, E. A., et al. (2013). Oncogenic H-ras reprograms Madin-Darby canine kidney (MDCK) cell-derived exosomal proteins following epithelial-mesenchymal transition. Molecular and Cellular Proteomics, 12(8), 2148–2159. https://doi.org/10.1074/mcp.M112.027086
Janowska-Wieczorek, A., Wysoczynski, M., Kijowski, J., Marquez-Curtis, L., Machalinski, B., Ratajczak, J., et al. (2005). Microvesicles derived from activated platelets induce metastasis and angiogenesis in lung cancer. International Journal of Cancer, 113(5), 752–760. https://doi.org/10.1002/ijc.20657
Ramteke, A., Ting, H., Agarwal, C., Mateen, S., Somasagara, R., Hussain, A., et al. (2015). Exosomes secreted under hypoxia enhance invasiveness and stemness of prostate cancer cells by targeting adherens junction molecules. Molecular Carcinogenesis, 54(7), 554–565. https://doi.org/10.1002/mc.22124
Deep, G., Jain, A., Kumar, A., Agarwal, C., Kim, S., Leevy, W. M., et al. (2020). Exosomes secreted by prostate cancer cells under hypoxia promote matrix metalloproteinases activity at pre-metastatic niches. Molecular Carcinogenesis, 59(3), 323–332. https://doi.org/10.1002/mc.23157
Hanahan, D. (2022). Hallmarks of cancer: New dimensions. Cancer Discovery, 12(1), 31–46. https://doi.org/10.1158/2159-8290.Cd-21-1059
Jakhar, R., & Crasta, K. (2019). Exosomes as emerging pro-tumorigenic mediators of the senescence-associated secretory phenotype. International journal of molecular sciences, 20(10), 2547. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms20102547
Wallis, R., Mizen, H., & Bishop, C. L. (2020). The bright and dark side of extracellular vesicles in the senescence-associated secretory phenotype. Mechanisms of Ageing and Development, 189, 111263. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.mad.2020.111263
Cavallo, F., De Giovanni, C., Nanni, P., Forni, G., & Lollini, P.-L. (2011). 2011: The immune hallmarks of cancer. Cancer immunology, immunotherapy : CII, 60(3), 319–326. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00262-010-0968-0
Edsparr, K., Basse, P. H., Goldfarb, R. H., & Albertsson, P. (2011). Matrix metalloproteinases in cytotoxic lymphocytes impact on tumour infiltration and immunomodulation. Cancer microenvironment : Official journal of the International Cancer Microenvironment Society, 4(3), 351–360. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12307-010-0057-0
Deryugina, E. I., Zajac, E., Juncker-Jensen, A., Kupriyanova, T. A., Welter, L., & Quigley, J. P. (2014). Tissue-infiltrating neutrophils constitute the major in vivo source of angiogenesis-inducing MMP-9 in the tumor microenvironment. Neoplasia, 16(10), 771–788. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neo.2014.08.013
Young, D., Das, N., Anowai, A., & Dufour, A. (2019). Matrix metalloproteases as influencers of the cells’ social media. Int J Mol Sci, 20(16), https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms20163847.
Condeelis, J., & Pollard, J. W. (2006). Macrophages: Obligate partners for tumor cell migration, invasion, and metastasis. Cell, 124(2), 263–266. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cell.2006.01.007
Sanchez, L. R., Borriello, L., Entenberg, D., Condeelis, J. S., Oktay, M. H., & Karagiannis, G. S. (2019). The emerging roles of macrophages in cancer metastasis and response to chemotherapy. Journal of Leukocyte Biology, 106(2), 259–274. https://doi.org/10.1002/jlb.mr0218-056rr
Asiry, S., Kim, G., Filippou, P. S., Sanchez, L. R., Entenberg, D., Marks, D. K., et al. (2021). The cancer cell dissemination machinery as an immunosuppressive niche: A new obstacle towards the era of cancer immunotherapy. [Review]. Frontiers in Immunology, 12, https://doi.org/10.3389/fimmu.2021.654877.
Chanmee, T., Ontong, P., Konno, K., & Itano, N. (2014). Tumor-associated macrophages as major players in the tumor microenvironment. Cancers, 6(3), 1670–1690. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers6031670
Wu, Q., Wu, X., Ying, X., Zhu, Q., Wang, X., Jiang, L., et al. (2017). Suppression of endothelial cell migration by tumor associated macrophage-derived exosomes is reversed by epithelial ovarian cancer exosomal lncRNA. Cancer Cell International, 17, 62. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12935-017-0430-x
Linton, S. S., Abraham, T., Liao, J., Clawson, G. A., Butler, P. J., Fox, T., et al. (2018). Tumor-promoting effects of pancreatic cancer cell exosomes on THP-1-derived macrophages. 13(11), e0206759, https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0206759.
Baig, M. S., Roy, A., Rajpoot, S., Liu, D., Savai, R., Banerjee, S., et al. (2020). Tumor-derived exosomes in the regulation of macrophage polarization. Inflammation Research, 69(5), 435–451. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00011-020-01318-0
de Vrij, J., Maas, S. L., Kwappenberg, K. M., Schnoor, R., Kleijn, A., Dekker, L., et al. (2015). Glioblastoma-derived extracellular vesicles modify the phenotype of monocytic cells. International Journal of Cancer, 137(7), 1630–1642. https://doi.org/10.1002/ijc.29521
Wu, J., Gao, W., Tang, Q., Yu, Y., You, W., Wu, Z., et al. (2021). M2 macrophage-derived exosomes facilitate HCC metastasis by transferring α(M) β(2) integrin to tumor cells. Hepatology, 73(4), 1365–1380. https://doi.org/10.1002/hep.31432
Hon, K. W., Abu, N., Ab Mutalib, N.-S., & Jamal, R. (2017). Exosomes as potential biomarkers and targeted therapy in colorectal cancer: A mini-review. [Mini Review]. Frontiers in Pharmacology, 8(583), https://doi.org/10.3389/fphar.2017.00583.
Nilsson, J., Skog, J., Nordstrand, A., Baranov, V., Mincheva-Nilsson, L., Breakefield, X. O., et al. (2009). Prostate cancer-derived urine exosomes: A novel approach to biomarkers for prostate cancer. British Journal of Cancer, 100(10), 1603–1607. https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.bjc.6605058
Sharma, R., Huang, X., Brekken, R. A., & Schroit, A. J. (2017). Detection of phosphatidylserine-positive exosomes for the diagnosis of early-stage malignancies. British Journal of Cancer, 117(4), 545–552. https://doi.org/10.1038/bjc.2017.183
Zhou, B., Xu, K., Zheng, X., Chen, T., Wang, J., Song, Y., et al. (2020). Application of exosomes as liquid biopsy in clinical diagnosis. Signal Transduction and Targeted Therapy, 5(1), 144. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41392-020-00258-9
Shay, G., Lynch, C. C., & Fingleton, B. (2015). Moving targets: Emerging roles for MMPs in cancer progression and metastasis. Matrix Biology, 44–46, 200–206. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.matbio.2015.01.019
Monea, S., Lehti, K., Keski-Oja, J., & Mignatti, P. (2002). Plasmin activates pro-matrix metalloproteinase-2 with a membrane-type 1 matrix metalloproteinase-dependent mechanism. Journal of Cellular Physiology, 192(2), 160–170. https://doi.org/10.1002/jcp.10126
Garimella, R., Washington, L., Isaacson, J., Vallejo, J., Spence, M., Tawfik, O., et al. (2014). Extracellular membrane vesicles derived from 143B osteosarcoma cells contain pro-osteoclastogenic cargo: A novel communication mechanism in osteosarcoma bone microenvironment. Translational Oncology, 7(3), 331–340. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tranon.2014.04.011
Reiner, A. T., Tan, S., Agreiter, C., Auer, K., Bachmayr-Heyda, A., Aust, S., et al. (2017). EV-associated MMP9 in high-grade serous ovarian cancer is preferentially localized to annexin V-binding EVs. Disease Markers, 2017, 9653194. https://doi.org/10.1155/2017/9653194
Kucharzewska, P., Christianson, H. C., Welch, J. E., Svensson, K. J., Fredlund, E., Ringnér, M., et al. (2013). Exosomes reflect the hypoxic status of glioma cells and mediate hypoxia-dependent activation of vascular cells during tumor development. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A, 110(18), 7312–7317. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.1220998110
Zheng, J., Hernandez, J. M., Doussot, A., Bojmar, L., Zambirinis, C. P., Costa-Silva, B., et al. (2018). Extracellular matrix proteins and carcinoembryonic antigen-related cell adhesion molecules characterize pancreatic duct fluid exosomes in patients with pancreatic cancer. HPB: The Official Journal of the International Hepato Pancreato Biliary Association, 20(7), 597–604. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.hpb.2017.12.010
Keller, S., König, A. K., Marmé, F., Runz, S., Wolterink, S., Koensgen, D., et al. (2009). Systemic presence and tumor-growth promoting effect of ovarian carcinoma released exosomes. Cancer Letters, 278(1), 73–81. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.canlet.2008.12.028
Yoneyama, T., Gorry, M., Sobo-Vujanovic, A., Lin, Y., Vujanovic, L., Gaither-Davis, A., et al. (2018). ADAM10 sheddase activity is a potential lung-cancer biomarker. Journal of Cancer, 9(14), 2559–2570. https://doi.org/10.7150/jca.24601
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher's note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Agathe Quesnel and Amy Broughton are co-first authors.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Quesnel, A., Broughton, A., Karagiannis, G.S. et al. Message in the bottle: regulation of the tumor microenvironment via exosome-driven proteolysis. Cancer Metastasis Rev 41, 789–801 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10555-022-10030-w
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10555-022-10030-w