Abstract
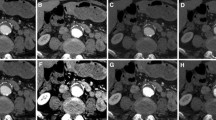
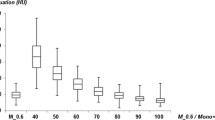
To compare quantitative image quality in dual-energy CT angiography (DE-CTA) studies of the aorta using different virtual monoenergetic imaging (MEI) and advanced image-based virtual monoenergetic (MEI+) settings at varying kiloelectron volt (keV) levels. Fifty consecutive patients with clinically-indicated CT of the whole aorta to evaluate suspected aortic disease underwent DE-CTA on a third-generation dual-source CT scanner. Quantitative image quality indices were assessed. Contrast material, saline flush and flow rate were kept equal for optimum comparability. DE-CTA MEI and MEI+ series ranging from 40 to 100 keV (10-keV intervals) were reconstructed. Signal intensity, noise, signal-to-noise ratio and contrast-to-noise ratio (CNR) of multiple aortic segments were evaluated. Comparisons between the different MEI and MEI+ datasets were performed. Three-hundred aortic segments total were evaluated. In the MEI+ series the 40, 50 and 100 keV MEI+ showed superior noise and CNR levels (+84, +58, +103 % on average; all p < 0.05) compared to MEI. However, signal intensity between MEI+ and MEI at nearly all aortic segments showed no significant difference (p > 0.1). MEI+ shows lower image noise compared to MEI, resulting in superior quantitative image quality, in particular at low keV levels (40 or 50 keV).




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Carrascosa P, Capunay C, Rodriguez-Granillo GA, Deviggiano A, Vallejos J, Leipsic JA (2014) Substantial iodine volume load reduction in CT angiography with dual-energy imaging: insights from a pilot randomized study. Int J Cardiovasc Imaging 30(8):1613–1620. doi:10.1007/s10554-014-0501-1
He J, Wang Q, Ma X, Sun Z (2014) Dual-energy CT angiography of abdomen with routine concentration contrast agent in comparison with conventional single-energy CT with high concentration contrast agent. Eur J Radiol. doi:10.1016/j.ejrad.2014.11.025
Purysko AS, Primak AN, Baker ME, Obuchowski NA, Remer EM, John B, Herts BR (2014) Comparison of radiation dose and image quality from single-energy and dual-energy CT examinations in the same patients screened for hepatocellular carcinoma. Clin Radiol 69(12):e538–e544. doi:10.1016/j.crad.2014.08.021
Sommer WH, Johnson TR, Becker CR, Arnoldi E, Kramer H, Reiser MF, Nikolaou K (2009) The value of dual-energy bone removal in maximum intensity projections of lower extremity computed tomography angiography. Invest Radiol 44(5):285–292. doi:10.1097/RLI.0b013e31819b70ba
Park JH, Choi SI, Chun EJ (2012) Multidetector CT evaluation of various aortic diseases: diagnostic tips, pitfalls, and remedies for imaging artifacts. Int J Cardiovasc Imaging 28(Suppl 1):45–60. doi:10.1007/s10554-012-0071-z
Yu L, Leng S, McCollough CH (2012) Dual-energy CT-based monochromatic imaging. Am J Roentgenol 199(5 Suppl):S9–S15. doi:10.2214/AJR.12.9121
Apfaltrer P, Sudarski S, Schneider D, Nance JW Jr, Haubenreisser H, Fink C, Schoenberg SO, Henzler T (2014) Value of monoenergetic low-kV dual energy CT datasets for improved image quality of CT pulmonary angiography. Eur J Radiol 83(2):322–328. doi:10.1016/j.ejrad.2013.11.005
Marin D, Boll DT, Mileto A, Nelson RC (2014) State of the art: dual-energy CT of the abdomen. Radiology 271(2):327–342. doi:10.1148/radiol.14131480
Sudarski S, Apfaltrer P, Nance JW Jr, Schneider D, Meyer M, Schoenberg SO, Fink C, Henzler T (2013) Optimization of keV-settings in abdominal and lower extremity dual-source dual-energy CT angiography determined with virtual monoenergetic imaging. Eur J Radiol 82(10):e574–e581. doi:10.1016/j.ejrad.2013.04.040
Grant KL, Flohr TG, Krauss B, Sedlmair M, Thomas C, Schmidt B (2014) Assessment of an advanced image-based technique to calculate virtual monoenergetic computed tomographic images from a dual-energy examination to improve contrast-to-noise ratio in examinations using iodinated contrast media. Invest Radiol 49(9):586–592. doi:10.1097/RLI.0000000000000060
Albrecht MH, Scholtz JE, Kraft J, Bauer RW, Kaup M, Dewes P, Bucher AM, Burck I, Wagenblast J, Lehnert T, Kerl JM, Vogl TJ, Wichmann JL (2015) Assessment of an advanced monoenergetic reconstruction technique in dual-energy computed tomography of head and neck cancer. Eur Radiol. doi:10.1007/s00330-015-3627-1
Bongers MN, Schabel C, Krauss B, Tsiflikas I, Ketelsen D, Mangold S, Claussen CD, Nikolaou K, Thomas C (2015) Noise-optimized virtual monoenergetic images and iodine maps for the detection of venous thrombosis in second-generation dual-energy CT (DECT): an ex vivo phantom study. Eur Radiol 25(6):1655–1664. doi:10.1007/s00330-014-3544-8
Schabel C, Bongers M, Sedlmair M, Korn A, Grosse U, Mangold S, Claussen CD, Thomas C (2014) Assessment of the hepatic veins in poor contrast conditions using dual energy CT: evaluation of a novel monoenergetic extrapolation software algorithm. RoFo: Fortschritte auf dem Gebiete der Rontgenstrahlen und der Nuklearmedizin 186(6):591–597. doi:10.1055/s-0034-1366423
Delesalle MA, Pontana F, Duhamel A, Faivre JB, Flohr T, Tacelli N, Remy J, Remy-Jardin M (2013) Spectral optimization of chest CT angiography with reduced iodine load: experience in 80 patients evaluated with dual-source, dual-energy CT. Radiology 267(1):256–266. doi:10.1148/radiol.12120195
Sudarski S, Apfaltrer P, Nance JW Jr, Schneider D, Meyer M, Schoenberg SO, Fink C, Henzler T (2013) Optimization of keV-settings in abdominal and lower extremity dual-source dual-energy CT angiography determined with virtual monoenergetic imaging. Eur J Radiol 82(10):e574–e581. doi:10.1016/j.ejrad.2013.04.040
Ippolito D, Talei Franzesi C, Fior D, Bonaffini PA, Minutolo O, Sironi S (2015) Low kV settings CT angiography (CTA) with low dose contrast medium volume protocol in the assessment of thoracic and abdominal aorta disease: a feasibility study. Br J Radiol 88(1049):20140140. doi:10.1259/bjr.20140140
Komatsu S, Kamata T, Imai A, Ohara T, Takewa M, Ohe R, Miyaji K, Yoshida J, Kodama K (2013) Coronary computed tomography angiography using ultra-low-dose contrast media: radiation dose and image quality. Int J Cardiovasc Imaging 29(6):1335–1340. doi:10.1007/s10554-013-0201-2
Siegel MJ, Schmidt B, Bradley D, Suess C, Hildebolt C (2004) Radiation dose and image quality in pediatric CT: effect of technical factors and phantom size and shape. Radiology 233(2):515–522. doi:10.1148/radiol.2332032107
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Beeres, M., Trommer, J., Frellesen, C. et al. Evaluation of different keV-settings in dual-energy CT angiography of the aorta using advanced image-based virtual monoenergetic imaging. Int J Cardiovasc Imaging 32, 137–144 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10554-015-0728-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10554-015-0728-5