Abstract
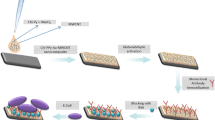
Sensitive and rapid tests of Escherichia coli drug sensitivity is very important for health of human and animals. An E. coli immunosensor was built based on electrochemical detection and immune detection technologies, through pretreating screen-printed electrodes, and analyzing the optimal reaction concentration of antigen antibody binding with the AC impedance method. Based on the detection system combining the immunosensor and electrochemical workstation, tests were carried out to measure the accuracy of E. coli concentration and drug sensitivity, and error of the detection system was calibrated in accordance with data from the electrochemical workstation. E. coli O157:H7 can be detected in the range of 103 cfu/ml ~ 1012 cfu/ml, and the detection error controlled within 5%. Results from the electrochemical workstation and those from the detection device were consistent, and both demonstrated a greater inhibitory effect of antibiotics on E. coli than on Bacillus subtilis. The electrochemical detection system is highly efficient and accurate, and could be widely applied to E. coli drug sensitivity tests in clinical medicine.









Similar content being viewed by others
References
J.Y. Park, K. Park, G. Ok et al., Detection of Escherichia coli O157:H7 Using Automated Immunomagnetic Separation and Enzyme-Based Colorimetric Assay. Sensors 20, 1395 (2020)
Z. Liu, L. Zhao, Q. Zhang et al., Proteomics-Based Mechanistic Investigation of Escherichia coli Inactivation by Pulsed Electric Field. Front. Microbiol. 10, 2644 (2019)
S.M. Saad, J. Abdullah, S.A. Rashid et al., A carbon dots based fluorescence sensing for the determination of Escherichia coli O157:H7. Measurement 107845 (2020)
S.H. Cho, Y.S. Lim, Y.H. Kang, Comparison of Antimicrobial Resistance in Escherichia coli Strains Isolated From Healthy Poultry and Swine Farm Workers Using Antibiotics in Korea. Osong Public Health Res. Perspect. 3, 151–155 (2012)
B. Wu, C. Qi, L. Wang et al., Detection of microbial aerosols in hospital wards and molecular identification and dissemination of drug resistance of Escherichia coli. Environ. Int. 137, 105479 (2020)
R. Maluta, B. Nicholson, C. Logue et al., Complete Genomic Sequence of an Avian Pathogenic Escherichia coli Strain of Serotype O7: HNT. Genome Announc. 4, e01611-15 (2016)
O. Reina, S. Tsutomu, O. Hiroshi et al., Pulmonary tuberculosis misdiagnosed as extensively drug-resistant tuberculosis due to selection of a nontuberculous mycobacterial colony from a preculture dish used for a drug-susceptibility test. Respir. Investig. 58, 216–219 (2020)
M. Mizoguchi, Y. Matsumoto, R. Saito et al., Direct antibiotic susceptibility testing of blood cultures of gram-negative bacilli using the Drug Susceptibility Testing Microfluidic (DSTM) device. J. Infect. Chemother. 26, 554–562 (2020)
A. Ayalew, R. Fikru, A. Dinka et al., Prevalence and antibiotic susceptibility pattern of Escherichia coli O157:H7 isolated from harvested fish at Lake Hayq and Tekeze dam. Northern Ethiopia Heliyon 5, e02996 (2019)
J. Visvalingam, K. Palaniappan, R.A. Holley, In vitro enhancement of antibiotic susceptibility of drug resistant Escherichia coli by cinnamaldehyde. Food Control. 79, 288–291 (2017)
S. Arends, M. Canino, R. Mendes et al., Comparison of minimum inhibitory concentration results for gepotidacin obtained using agar dilution and broth microdilution methods. Diagn. Microbiol. Infect. Dis. 98, 115107 (2020)
G. Igawa, M. Cassey et al., Comparison of agar dilution and broth microdilution methods for Clostridium difficile antimicrobial susceptibility testing. J. Glob. Antimicrob. Resist. 7, 43–45 (2016)
E. Chryssanthou, M. Cuenca-Estrella, Comparison of the Antifungal Susceptibility Testing Subcommittee of the European Committee on Antibiotic Susceptibility Testing Proposed Standard and the E-Test with the NCCLS Broth Microdilution Method for Voriconazole and Caspofungin Susceptibility Testing of Yeast Species. J. Clin. Microbiol. 40, 3841–3844 (2002)
R. Huang, Z. Zhao, X. Ma et al., Targeting of tumor radioiodine therapy by expression of the sodium iodide symporter under control of the survivin promoter. Cancer Gene Ther. 18, 144–152 (2011)
G. Pfyffer, F. Palicova, S. Rusch-Gerdes, Testing of Susceptibility of Mycobacterium tuberculosis to Pyrazinamide with the Nonradiometric BACTEC MGIT 960 System. J. Clin. Microbiol. 40, 1670–1674 (2002)
P. Kohner, R. Patel, J. Uhl et al., Comparison of agar dilution, broth microdilution, E-test, disk diffusion, and automated Vitek methods for testing susceptibilities of Enterococcus spp. to vancomycin. J.Clin. Microbiol. 35, 3258–63 (1997)
P. Ruiz, F. Zerolo, M. Casal, Comparison of Susceptibility Testing of Mycobacterium tuberculosis Using the ESP Culture System II with That Using the BACTEC Method. J. Clin. Microbiol. 38, 4663–4664 (2000)
C. Wenisch, C. Moore, R. Krause et al., Antifungal susceptibility testing of fluconazole by cytometry correlations with clinical outcome. J. Clin. Microbiol. 39, 2458–2462 (2001)
P. Ekong, M. Sanderson, P. Shridhar et al., Bayesian estimation of sensitivity and specificity of culture- and PCR-based methods for the detection of six major non-O157 Escherichia coli serogroups in cattle feces. Prev. Vet. Med. 161, 90–99 (2018)
L. Noll, P. Shridhar, D. Dewsbury et al., A Comparison of Culture- and PCR-Based Methods to Detect Six Major Non-O157 Serogroups of Shiga Toxin-Producing Escherichia coli in Cattle Feces. PLoS One. 10, e0135446 (2015)
Z. Paddock, X. Shi, J. Bai et al., Applicability of a multiplex PCR to detect O26, O45, O103, O111, O121, O145, and O157 serogroups of Escherichia coli in cattle feces. Vet. Microbiol. 156, 381–388 (2012)
S. Sameh, F.I. Sonbol, et al., Molecular characterization of virulence and drug resistance genes-producing Escherichia coli isolated from chicken meat: Metal oxide nanoparticles as novel antibacterial agents. Microb. Pathog. 143, 104164 (2020)
S. Shahbazi, M. Reza et al., Distribution of Extended-Spectrum β-Lactam, Quinolone, and Carbapenem Resistance Genes, and Genetic Diversity among Uropathogenic Escherichia coli isolates in Tehran, Iran. J. Glob. Antimicrob. Resist. 14, 118–125 (2018)
S. Kurbanoglu, C. Erkmen, B. Uslu, Frontiers in electrochemical enzyme based biosensors for food and drug analysis. TrAC Trends Analyt. Chem. 124, 115809 (2020)
C. Yafei, Y. Yajie, W. Yu et al., Development of an Escherichia coli-based electrochemical biosensor for mycotoxin toxicity detection. Bioelectrochemistry 133, 107453 (2020)
Y. Lei, Application of Electrochemical Immuno-sensor Based on Ketamine Hydrochloride for the Detection of Sports Illicit Drugs. J. New Mater. Electrochem. Syst. 19, 139–143 (2016)
K. Theyagarajan, K. Dinakaran, A. Pangajam, Highly sensitive electrochemical detection of E. coli O157:H7 using conductive carbon dot/ZnO nanorod/PANI composite electrode. Sens. Biosensing Res. 29, 100317 (2020)
J. Zhang, J. Wang et al., Rapid detection of Escherichia coli based on 16S rDNA nanogap network electrochemical biosensor. Biosens. Bioelectron. 118, 9–15 (2018)
Funding
The research is supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Grant No. 31772651), Shanxi Foundation for Science and Technology Activities of Returned Students, Central government’s grant to the Shanxi province for local science and technology projects.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
In this article, the author’s contributions are shown below: Methodology, Z.L.; writing—original draft preparation, M.X. and R.Z.; project administration, Z.L.; data curation, Z.Y., H.Z., Y.S., X.S., Y.G., and H.Y. helped to analyze the data. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflicts of interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Xu, M., Liu, Z., Song, Y. et al. Analysis of drug sensitivity of Escherichia Coli O157H7. Biomed Microdevices 23, 29 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10544-021-00565-0
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10544-021-00565-0