Abstract
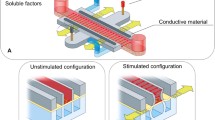
The mechanical and electrical properties of biomaterials are essential in cell function regulation during cell-biomaterial interaction. However, previous studies focused on probing cell regulation mechanisms under one type of stimulus, and a platform that enables the study of electromechanical coupling effects of a biomaterial on cells is still lacking. Here, we present an in-situ electromechanical testing and loading system to image live cells when co-cultured with electroactive biomaterials. The system can provide accurate and repeatable stretch on biomaterials and cells to mimic in vivo tension microenvironment. Besides, the integrated displacement transducer, force sensor, and electrical signal detector enable the real time detection of electromechanical signals on electroactive biomaterials under various stretch loading. Combined with a microscope, live cell imaging can be realized to probe cell behavior. The feasibility of the system is validated by culturing mesenchymal stem cells on piezoelectric nanofiber and conductive hydrogel. Experiment results show the device as a reliable and accurate tool to investigate electromechanical properties of biomaterials and probe essential features of live cells. Our system provides a way to correlate cell behavior with electromechanical cues directly and is useful for exploration of cell function during cell-biomaterial interaction.








Similar content being viewed by others
References
J.C. Anderson, C. Eriksson, Nature 227, 491 (1970)
B.M. Baker, B. Trappmann, W.Y. Wang, M.S. Sakar, I.L. Kim, V.B. Shenoy, J.A. Burdick, C.S. Chen, Nat. Mater. 14, 1262 (2015)
S. Bose, M. Roy, A. Bandyopadhyay, Trends Biotechnol. 30, 546 (2012)
P. Dan, É. Velot, V. Decot, P. Menu, J. Cell Sci. 124, 2415 (2015)
H.M. Estabridis, A. Jana, A. Nain, D.J. Odde, Ann. Biomed. Eng. 46, 392 (2018)
X. Gou, C.H. Ho, S. Hu, A.Y.H. Leung, D. Sun, IEEE Transact. Biomed. Eng. 60, 2308 (2013)
X. Gou, H. Yang, T.M. Fahmy, Y. Wang, D. Sun, Int. J. Robot. Res. 33, 1782 (2014)
C. Halperin, S. Mutchnik, A. Agronin, M. Molotskii, P. Urenski, M. Salai, G. Rosenman, Nano Lett. 4, 1253 (2004)
D.S. Howe, J. Dunning, C. Zorman, S.L. Garverick, K.M. Bogie, Ann. Biomed. Eng. 43, 306 (2015)
J. Huang, X. Hu, L. Lu, Z. Ye, Q. Zhang, Z. Luo, J. Biomed. Mater. Res. A 93, 164 (2010)
J. Imsirovic, T.J. Wellman, J.R. Mondoñedo, E. Bartolák-Suki, B. Suki, PLoS One 10, e0140283 (2015)
J. Jacob, N. More, K. Kalia, G. Kapusetti, Inflamm. Regener. 38, 2 (2018)
J.Y. Lee, C.A. Bashur, A.S. Goldstein, C.E. Schmidt, Biomaterials 30, 4325 (2009)
L. Liu, Z. You, H. Yu, L. Zhou, H. Zhao, X. Yan, D. Li, B. Wang, L. Zhu, Y. Xu, T. Xia, Y. Shi, C. Huang, W. Hou, Y. Du, Nat. Mater. 16, 1252 (2017)
A. Llucià-Valldeperas, B. Sanchez, C. Soler-Botija, C. Gálvez-Montón, C. Prat-Vidal, S. Roura, J. Rosell-Ferrer, R. Bragos, A. Bayes-Genis, J. Tissue Eng. Regen. Med. 9, E76 (2015)
M.R. Love, S. Palee, S.C. Chattipakorn, N. Chattipakorn, J. Cell. Physiol. 233, 1860 (2017)
L. Lu, D. Fan, B.X. Bie, X.X. Ran, M.L. Qi, N. Parab, J.Z. Sun, H.J. Liao, M.C. Hudspeth, B. Claus, K. Fezzaa, T. Sun, W. Chen, X.L. Gong, S.N. Luo, Rev. Sci. Instrum. 85, 076101 (2014)
S. Meng, M. Rouabhia, Z. Zhang, Bioelectromagnetics 34, 189 (2013)
C. Ning, Z. Zhou, G. Tan, Y. Zhu, C. Mao, Prog. Polym. Sci. 81, 144 (2018)
Q. Pang, J.W. Zu, G.M. Siu, R.-K. Li, J. Biomech. Eng. 132, 014503 (2010)
A. Pavesi, G. Adriani, M. Rasponi, I.K. Zervantonakis, G.B. Fiore, R.D. Kamm, Sci. Rep. 5, 11800 (2015)
C. Ribeiro, V. Sencadas, D.M. Correia, S. Lanceros-Méndez, Colloids Surf. B: Biointerfaces 136, 46 (2015)
N.J. Steinmetz, E.A. Aisenbrey, K.K. Westbrook, H.J. Qi, S.J. Bryant, Acta Biomater. 21, 142 (2015)
G. Thrivikraman, S.K. Boda, B. Basu, Biomaterials 150, 60 (2018)
G. Thrivikraman, G. Madras, B. Basu, Biomaterials 35, 6219 (2014)
C.P. Ursekar, S.-K. Teo, H. Hirata, I. Harada, K.-H. Chiam, Y. Sawada, PLoS One 9, e90665 (2014)
N. Wang, J.D. Tytell, D.E. Ingber, Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Bio. 10, 75 (2009)
Y. Wu, L. Wang, B. Guo, P.X. Ma, ACS Nano 11, 5646 (2017)
B. Zhang, H. Li, L. He, Z. Han, T. Zhou, W. Zhi, X. Lu, X. Lu, J. Weng, Mater. Sci. Eng. C 89, 355 (2018)
W. Zhang, P. Feng, J. Chen, Z. Sun, B. Zhao, Prog. Polym. Sci. 88, 220 (2019)
Z. Zhang, Y. Wang, H. Zhang, Z. Tang, W. Liu, Y. Lu, Z. Wang, H. Yang, W. Pang, H. Zhang, D. Zhang, X. Duan, Small 13, 1602962 (2017)
Acknowledgments
The work was supported by Sichuan Science and Technology Program (2019YJ0246) and the Fundamental Research Funds for the Central Universities (2682019CX07).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
All authors contributed to the study conception and design. Material preparation, data collection and analysis were performed by Lingda Meng, Guilan Xue, Qingjie Liu and Tianpeng Xie. The first draft of the manuscript was written by Lingda Meng and Xue Gou. All authors commented on previous versions of the manuscript, and all authors read and approved the final manuscript.
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Meng, L., Xue, G., Liu, Q. et al. In-situ electromechanical testing and loading system for dynamic cell-biomaterial interaction study. Biomed Microdevices 22, 56 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10544-020-00514-3
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10544-020-00514-3