Abstract
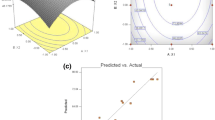
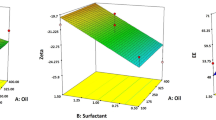
Atorvastatin is a lipid lowering agent with poor oral bioavailability (12%) because of poor solubility and extensive first pass hepatic metabolism. In order to overcome these issues, atorvastatin loaded solid lipid nanoparticles (ATOR-SLNs) were prepared by using glyceryl tripalmitate as lipid carrier, poloxamer 407 as surfactant and soya lecithin as emulsifier. The purpose of this work was to optimize the formulation with the application of response surface methodology to improve the physicochemical properties. The central composite rotatable design consisting of three factored factorial design with three levels was used for the optimization of the formulations. The optimized formulation was composed of drug/lipid ratio of 1:3.64, surfactant concentration of 1.5% with 5 min time for sonication. Fourier transforms infrared (FTIR) spectroscopy and differential scanning calorimetry (DSC) studies confirmed the compatibility of drug and lipid in the formulation. The optimized ATOR- SLNs showed almost spherical shape with a mean particle size of 338.5 nm, zeta potential of -24.7mV, DL of 17.7% and EE of 81.06% respectively. The in vitro drug release study showed a burst release at the initial stage followed by the prolongation of drug release from lipid matrix. Stability study revealed that ATOR-SLNs were more stable at 4±2˚C when compared with storage at 25±2˚C/60±5% RH during the six months storage period. These results indicated that the developed ATOR-SLNs is a promising approach for increment of bioavailability by improving the physicochemical properties.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
J.H. Ahn, Y.P. Kim, Y.M. Lee, E.M. Seo, K.W. Lee, H.S. Kim, Food Chem. 107, 98–105 (2008)
L. Battaglia, M. Trotta, M. Gallarate, M.E. Carlotti, G.P. Zara, A. Bargoni, J. Microencapsul. 7, 660–672 (2007)
M.L. Bondi, R. Di, E.F.C. Gesu, Methods Enzymol. 508, 229–251 (2012)
G.E.P. Box, J.S. Hunter, Ann. Math. Stat. 28, 195–241 (1957)
S. Gande, M. Kopparam, V. Vobalaboina, S. Vemula, AAPS PharmSciTech 8(1), 1–9 (2007)
F.Q. Hu, S.P. Jiang, Y.Z. Du, H. Yuan, Y.Q. Ye, S. Zeng, Colloids Surf. B Biointerfaces 45, 167–173 (2005)
L.J. Jia, D.R. Zhang, Z.Y. Li, F.F. Feng, Y.C. Wang, W.T. Dai, Drug Deliv. 17, 11–18 (2010)
N.K. Kapur, K. Musunuru, Vasc. Health Risk Manag. 4(2), 341–353 (2008)
L.S. Kassama, J. Shi, G.S. Mittal, Sep. Purif. Technol. 60, 278–284 (2008)
Y.C. Kuo, S.J. Cheng, Int. J. Pharm. 499(1–2), 10–19 (2016)
Y.C. Kyo, J.F. Chung, Colloids Surf. B Biointerfaces 83, 299–306 (2011)
M.J. Lawrence, G.D. Rees, Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev. 45(1), 89–121 (2000)
Z. Li, W. Tao, D. Zhang, C. Wu, B. Song, S. Wang, T. Wang, M. Hu, X. Liu, Y. Wang, Y. Sun, J. Sun, Asian J. Pharm. 12, 285–291 (2017)
C. Liu, C. Wu, J. Fang, Drug Dev. Ind. Pharm. 36(7), 751–761 (2010)
W. Mehnert, K. Mader, Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev. 47, 165–196 (2001)
A. Mishra, P.R. Vuddanda, S. Singh, J. Nanotechnol. 2014, 1–12 (2014)
A.K. Mohanty, F. Dilnawaz, C. Mohanty, S.K. Sahoo, Drug Deliv. 17(5), 330–342 (2010)
R.H. Muller, K. Mader, S. Gohla, Eur. J. Pharm. Biopharm. 50, 161–177 (2000)
R.H. Muller, C. Jacob, O. Kayser, Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev. 47, 3–19 (2001)
P. Mura, M.T. Faucci, G.P. Bettinetti, Eur. J. Pharm. Sci. 13(2), 187–194 (2001)
R.H. Myers, D.C. Montgomery, Response Surface Methodology (Wiley, New York, 1995)
R.H. Myers, D.C. Montgomery, Response Surface Methodology: Process and Product Optimization Using Designed Experiments (Wiley, New York, 2002)
A. Parker, P.D. Thompson, Exerc. Sport Sci. Rev. 40(4), 188–194 (2012)
C.W. Pouton, C.J.H. Porter, Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev. 6, 625–637 (2008)
M. Radtke, B.E. Souto, R.H. Muller, Pharm. Technol. Eur. 17(4), 45–50 (2005)
M. Shah, K. Pathak, AAPS PharmSciTech 11, 489–496 (2010)
K.A. Shah, A.A. Date, M.D. Joshi, V.B. Patravale, Int. J. Pharm. 2, 63–171 (2007)
A. Siddiqui, A. Alayoubi, Y. El-Malah, S. Nazzal, Pharm. Dev. Technol., 1–5 (2013)
B. Sjostrom, B. Bergenstahl, B. Kronberg, J. Pharm. Sci. 82, 584–589 (1993)
C. Stancu, A. Sima, J. Cell. Mol. Med. 5, 378–387 (2001)
A.P. Stapleton, G.A. Good Will, E.M. James, W.R. Brock, C.J. Frisbee, J. Inflamm. 7(54), 54 (2010)
V.J. Stella, R.A. Rajewski, Pharm. Res. 14, 556–567 (1997)
N. Tiong, A.A. Elkordy, Eur. J. Pharm. Biopharm. 73(3), 373–384 (2009)
A. Trapani, J. Sitterberg, U. Bakowsky, T. Kissel, Int. J. Pharm. 375, 97–106 (2009)
M. Trotta, F. Debernardi, O. Caputo, Int. J. Pharm. 2, 153–160 (2003)
V. Venkateswarlu, K. Manjunath, J. Control. Release 95(3), 627–638 (2004)
H. Yuan, J. Miao, Y.Z. Du, J. You, F.Q. Hu, S. Zeng, Int. J. Pharm. 348,137–145(2008)
Acknowledgements
Babita Sarangi is thankful to UGC, Government of India, for providing UGC-BSR fellowship. The authors acknowledge M/s Dr. Reddy’s Laboratories Ltd. Hyderabad (India) for providing atorvastatin calcium USP and M/s Sasol (Witten, Germany) for providing glyceryl tripalmitate.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Sarangi, B., Jana, U., Sahoo, J. et al. Systematic approach for the formulation and optimization of atorvastatin loaded solid lipid NANOAPARTICLES using response surface methodology. Biomed Microdevices 20, 53 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10544-018-0285-5
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10544-018-0285-5