Abstract
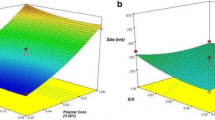
The main objective of this research was to design and optimize novel core–shell-type hybrid nano-sized systems of cucurbitacin B (CuB) based on the design of experiment (DoE) approach. The hybrid formulations consisting of polyethylene glycol (PEG)-conjugated phospholipid, lecithin and poly-lactic-co-glycolic acid (PLGA) were produced by employing self-assembly modified nanoprecipitation technique. A 32 factorial design was utilized to understand the effect of two input factors, namely PEG phospholipid/polymer ratio and total lipids/lecithin ratio, on entrapment efficiency and drug release percentage. The particle size and surface charge analyses, excipient interactions and thermal behavior, particle morphology, presence and thickness of lipid shell, and also storage stability studies were carried out through in vitro characterization. The entrapment efficiency of all nanoparticles of CuB ranged between 49.35 and 80.00%. The prepared lipid–polymer hybrid systems exhibited an average particle size from 94.5 to 127.2 nm with polydispersity in the range from 0.094 to 0.114, which inhibited a narrow size distribution. The nano-sized formulation at the center point of the design was selected as optimum formulation due to its excellent characteristics and the configuration determined using ANOVA and response surface methodology (RSM) approach.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Kaushik U, Aeri V, Mi SR (2015) Cucurbitacins—an insight into medicinal leads from natüre. Pharmacognosy Rev 9(17):12–18
Li Y, Sheng Q, Zhang S, Lu Z, Guo J, Xu H, Deng Y (2010) Feasibility of percutaneous administration of cucurbitain B, an anticancer activity substances isolated from cucurbitaceae plants. Asian J Pharm Sci 5(4):152–160
Bakar F (2016) Cucurbitacin B enhances the anticancer effect of imatinib mesylate through inhibition of MMP-2 expression in MCF-7 and SW480 tumor cell lines. Anti Cancer Agents Med Chem 16(6):747–754
Chan KT, Meng FY, Li Q, Ho CY, Lam TS, To Y, Lee WH, Li M, Chu KH, Toh M (2010) Cucurbitacin B induces apoptosis and S phase cell cycle arrest in BEL-7402 human hepatocellular carcinoma cells and is effective via oral administration. Cancer Lett 294(1):118–124
Haritunians T, Gueller S, Zhang L, Badr R, Yin D, Xing H, Fung MC, Koeffler HP (2008) Cucurbitacin B induces differentiation, cell cycle arrest, and actin cytoskeletal alterations in myeloid leukemia cells. Leuk Res 32(9):1366–1373
Cheng L, Xu P, Shen B, Shen G, Li J, Qju L, Liu C, Yuan H, Han J (2015) Improve bile duct-targeted drug delivery and therapeutic efficacy for cholangiocarcinoma by cucurbitacin B loaded phospholipid complex modified with berberine hydrochloride. Int J Pharm 489:148–157
Jianbo G, Xue L, Hongdan Y, Zhaohui T, Xing T, Chenchen C, Jinghua X, Hui X (2013) The anti-melanoma efficiency of the intratumoral injection of cucurbitacin-loaded sustained-release carriers: a PLGA particle system. J Pharm Sci 102(8):2550–2563
Tang L, Fu L, Zhu Z, Yang Y, Sun B, Sun W, Zhang Z (2018) Modified mixed micelles with collagen peptides enhanced oral absorption of cucurbitacin B: preparation and evaluation. Drug Deliv 25(1):862–871
Ghadi R, Dand N (2017) BCS class IV drugs: highly notorious candidates for formulation development. J Control Release 248:71–95
Hu H, Liu D, Zhao X, Qiao M, Chen D (2013) Preparation, characterization, cellular uptake and evaluation in vivo of solid lipid nanoparticles loaded with cucurbitacin B. Drug Dev Ind Pharm 39:770–779
Wang W, Zhao X, Hu H, Chen D, Gu J, Deng Y, Sun J (2010) Galactosylated solid lipid nanoparticles with cucurbitacin B improves the liver targetability. Drug Deliv 17:114–122
Li Y, Han C, Li J, Quin L, Tang S (2014) Optimization of preparation of nanostructured lipid carriers loaded with cucurbitacin B by central composite design and response surface methodology. Chin J Pharm 45:1042–1045
Shen C, Li R, Shen B, Shen G, Wang L, Zheng J, Li X, Min H, Han J, Yuan H (2015) Influence of drug physicochemical characteristics on in vitro transdermal absorption of hydrophobic drug nanosuspensions. Drug Dev Ind Pharm 41:1997–2005
Lv Q, Li X, Li R, Shen B, Xu H, Shen C, Dai L, Han J, Yuan H (2014) Effective mucoadhesive water-soluble polymers for the solidification transformation of phospholipid-bile salts-mixed micelles. Pharmazie 69:792–798
Lv Q, Li X, Li R, Shen B, Xu H, Shen C, Dai L, Bai J, Yuan H, Han J (2014) Application of spray granulation for conversion of mixed phospholipid-bile salt micelles to dry powder: influence of drug hydrophobicity on nanoparticle reagglomeration. Int J Nanomed 9:505–515
Lv Q, Li X, Shen B, Dai L, Xu H, Shen C, Yuan H, Han J (2014) A solid phospholipid-bile salts-mixed micelles based on the fast dissolving oral films to improve the oral bioavailability of poorly water-soluble drug. J Nanopart Res 16:2455
Lv Q, Shen C, Li X, Shen B, Yu C, Xu P, Xu H, Han J, Yuan H (2015) Mucoadhesive buccal films containing phospholipid-bile salts-mixed micelles as an effective carrier for cucurbitacin B delivery. Drug Deliv 22:351–358
Bai X, Liu S, Yi L (2016) Cucurbitacin B nanometer liposome and preparation thereof. Patent CN 106137966
Zhang J, Chen J, Jiang X, Zhao H, Lei T, Zhang X (2016) A water-in-oil type nanoemulsion for significantly improving insoluble drug bioavailability, and preparation method thereof. Patent CN105977875
Zhang J, Lei T, Zhao H, Jiang X, Chen J, Zhang X (2016) An oil-in-water-type nano-emulsion capable of significantly increasing bioavailability of indissoluvable drugs, and preparation method thereof. Patent CN 10575212
Allen TM, Cullis PR (2013) Liposomal drug delivery systems: from concept to clinical applications. Adv Drug Deliv Rev 65:36–48
Lian T, Ho RJY (2001) Trends and developments in liposome drug delivery systems. J Pharm Sci 90:667–680
Panyam J, Labhasetwar V (2003) Biodegradable nanoparticles for drug and gene delivery to cells and tissue. Adv Drug Deliv Rev 55:329–347
Esim O, Savaser A, Kurbanoglu S, Kose-Ozkan C, Ozkan SA, Ozkan Y (2017) Development of assay for determination of eletriptan hydrobromide in loaded PLGA nanoparticles. J Pharm Biomed Anal 142:74–83
Hascicek C, Sengel-Turk CT, Gumustas M, Ozkan SA, Bakar F, Das-Evcimen N, Savaser A, Ozkan Y (2017) Fulvestrant-loaded polymer-based nanoparticles for local drug delivery: preparation and in vitro characterization. J Drug Deliv Sci Technol 40:73–82
Thanki K, Gangwal RP, Sangamwar AT, Jain S (2013) Oral delivery of anticancer drugs: challenges and opportunities. J Control Release 170:15–40
Sengel-Turk CT, Hascicek C, Bakar F, Simsek E (2017) Comparative evaluation of nimesulide-loaded nanoparticles for anticancer activity against breast cancer cells. AAPS PharmSciTech 18(2):393–403
Pantze SF, Parmentier J, Hofhaus G, Fricker G (2014) Matrix liposomes: a solid liposomal formulation for oral administration. Eur J Lipid Sci Technol 116:1145–1154
Fan Y, Zhang Q (2013) Development of liposomal formulations: from concept to clinical investigations. Asian J Pharm Sci 8:81–87
Mandal B, Bhattacharjee H, Mittal N, Sah H, Balabathula P, Thoma LA, Wood GC (2013) Core–shell-type lipid-polymer hybrid nanoparticles as a drug delivery platform. Nanomed 9:474–491
Sengel-Turk CT, Hascicek C (2017) Design of lipid-polymer hybrid nanoparticles for therapy of BPH: Part I. Formulation optimization using a design of experiment approach. J Drug Deliv Sci Technol 39:16–24
Yalcin TE, Ilbasmis-Tamer S, Takka S (2018) Development and characterization of gemcitabine hydrochloride loaded lipid polymer hybrid nanparticles (LPHNs) using central composite design. Int J Pharm 548:255–262
Mandal B, Mittal NK, Balabathula P, Thoma LA, Wood GC (2016) Development and in vitro evaluation of core-shell type lipid-polymer hybrid nanoparticles for the delivery of erlotinib in non-small cell lung cancer. Eur J Pharm Sci 81:162–171
Tahir N, Madni A, Balasubramanian V, Rehman M, Correia A, Kashif PM, Mäkilä E, Salonen J, Santos HA (2017) Development and optimization of methotrexate-loaded lipid-polymer hybrid nanoparticles for controlled drug delivery applications. Int J Pharm 533:156–168
Khorasani MT, Joorabloo A, Adeli H, Mansoori-Moghadam Z, Moghaddam A (2019) Design and optimization of process parameters of polyvinyl (alcohol)/chitosan/nano zinc oxide hydrogels as wound healing materials. Carbohydr Polym 207:542–554
Partovinia A, Vatankhah E (2019) Experimental investigation into size and sphericity of alginate micro-beads produced by electrospraying technique: operational condition optimization. Carbohydr Polym 209:389–399
Turk CTS, Oz UC, Serim TM, Hascicek C (2014) Formulation and optimization of nonionic surfactants emulsified nimesulide-loaded PLGA-based nanoparticles by design of experiments. AAPS PharmSciTech 15(1):161–176
Sturm S, Stuppner H (2000) Analysis of cucurbitacins in medicinal plants by high-pressure liquid chromatography-mass spectrometry. Phytochem Anal 11(2):121–127
Bajcsik N, Pfab R, Pietsch J (2017) Simultaneous determination of cucurbitacin B, E, I and E-glucoside in plant material and body fluids by HPLC–MS. J Chromatogr B Analyt Technol Biomed Life Sci 1052:128–134
Shoaib M, Bahadur A, Saeed A, Saif ur Rahman M, Naseer MM (2018) Biocompatible, pH-responsive, and biodegradable polyurethanes as smart anti-cancer drug delivery carriers. React Funct Polym 127:153–160
Shoaib M, Saeed A, Saif Ur Rahman M, Naseer MM (2017) Mesoporous nano-bioglass designed for the release of imatinib and in vitro inhibitory effects on cancer cells. Mater Sci Eng C 77:725–730
Shoaib M, Saeed A, Akhtar J, Saif ur Rahman M, Ullahd A, Jurkschat K, Naseer MM (2017) Potassium-doped mesoporous bioactive glass: synthesis, characterization and evaluation of biomedical properties. Mater Sci Eng C 75:836–844
Shoaib M, Bahadur A, Saif ur Rahman M, Iqbal S, Arshad MI, Tahir MA, Mahmood T (2017) Sustained drug delivery of doxorubicin as a function of pH, releasing media, and NCO contents in polyurethane urea elastomers. J Drug Deliv Sci Technol 39:277–282
Shoaib M, Bahadur A, Iqbal S, Saif ur Rahman M, Ahmed S, Shabir G, Javaid MA (2017) Relationship of hard segment concentration in polyurethane-urea elastomers with mechanical, thermal and drug release properties. J Drug Deliv Sci Technol 37:88–96
Leng D, Thanki K, Fattal E, Foged C, Yang M (2018) Engineering of budesonide-loaded lipid-polymer hybrid nanoparticles using a quality-by-design approach. Int J Pharm 548(2):740–746
Aghamohammadi N, Aziz HB, Isa MH, Zinatizadeh AA (2007) Powdered activated carbon augmented activated sludge process for treatment of semi-aerobic landfill leachate using response surface methodology. Bioresour Technol 98(18):3570–3578
Kim CE, Lim SK, Kim JS (2012) In vivo antitumor effect of cromolyn in PEGylated liposomes for pancreatic cancer. J Control Release 157(2):190–195
Zhang L, Chan JM, Gu FX, Rhee JW, Wang AZ, Radovic-Moreno AF, Alexis F, Langer R, Farokhzad OC (2008) Self-assembled lipid-polymer hybrid nanoparticles: a robust drug delivery platform. ACS Nano 2:1696–1702
Pal S, Gauri SK (2018) A desirability functions-based approach for simultaneous optimization of quantitative and ordinal response variables in industrial processes. Int J Engineer Sci Technol 10(1):76–87
Yerlikaya F, Ozgen A, Vural I, Guven O, Karaagaoglu E, Khan MA, Capan Y (2013) Development and evaluation of paclitaxel nanoparticles using a quality-by-design approach. J Pharm Sci 102:3748–3761
Khan BC (2013) Bias in randomised factorial trials. Stat Med 32:4540–4549
Khuroo T, Verma D, Talegaonkar S, Padhi S, Panda AK, Iqbal Z (2014) Topotecan-tamoxifen douple PLGA polymeric nanoparticles: investigation of in vitro, in vivo and cellular uptake potential. Int J Pharm 473:384–394
Bikkad ML, Nathani AH, Mandlik SK, Shrotriya SN, Ranpise NS (2014) Halobetasol propionate-loaded solid lipid nanoparticles (SLN) for skin targeting by topical delivery. J Liposome Res 24:113–123
Shah B, Khunt D, Bhatt H, Misra M, Padh H (2015) Application of quality by design approach for intranasal delivery of rivastigmine loaded solid lipid nanoparticles: effect on formulation and characterization parameters. Eur J Pharm Sci 78:54–66
Chehimi MM, Djouani F, Benzarti K (2011) XPS studies of multiphase phase systems. In: Boudenne A, Ibos L, Candau Y, Thomas S (eds) Handbook of multiphase polymer systems. Wiley, New Delhi, pp 274–277
Acknowledgements
The authors would like to thank The Scientific and Technological Research Council of Turkey (TUBITAK) for their financial support to this research (Grant Number 117S131).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Sengel-Turk, C.T., Ozmen, N. & Bakar-Ates, F. Design, characterization and evaluation of cucurbitacin B-loaded core–shell-type hybrid nano-sized particles using DoE approach. Polym. Bull. 78, 3327–3351 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00289-020-03256-7
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00289-020-03256-7