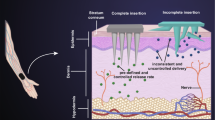
Abstract
The main issue of transdermal drug delivery is that macromolecular drugs cannot diffuse through the stratum corneum of skin. Many studies have pursued micro-sized needles encapsulated with drugs to overcome this problem, as these needles can pierce the stratum corneum and allow drugs to enter the circulatory system of the human body. However, most microneedle fabrication processes are time-consuming and require expensive equipment. In this study, we demonstrate a rapid method for fabricating a microneedle mold using drawing lithography and a UV-cured resin. The mold was filled with a water-soluble material, polyvinylpyrrolidone (PVP), which was then demolded to produce a water-soluble microneedle array. The results of an in vitro skin insertion test using PVP microneedles and pig ear skin demonstrated the feasibility of the microneedle mold. In addition, by controlling the viscosity of the UV-cured resin through various heat treatments, microneedles with different heights and aspect ratios were produced. Compared with other methods, this technology significantly simplifies and accelerates the mold fabrication process. In addition, the required equipment is relatively simple and inexpensive. Through this technology, we can rapidly fabricate microneedle molds with controllable dimensions for various applications.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
B. P. Chaudhri, F. Ceyssens, P. De Moor, C. Van Hoof, R. Puers, A high aspect ratio SU-8 fabrication technique for hollow microneedles for transdermal drug delivery and blood extraction. J. Micromech. Microeng. 20, 064006 (2010)
C. K. Choi, K. J. Lee, Y. N. Youn, E. H. Jang, W. Kim, B. K. Min, W. Ryu, Spatially discrete thermal drawing of biodegradable microneedles for vascular drug delivery. Eur. J. Pharm. Biopharm. 83, 224–233 (2013)
Y. K. Demir, Z. Akan, O. Kerimoglu, Characterization of polymeric microneedle arrays for transdermal drug delivery. Plos One 8, e77289 (2013)
R. F. Donnelly, M. J. Garland, D. I. Morrow, K. Migalska, T. R. Singh, R. Majithiya, A. D. Woolfson, Optical coherence tomography is a valuable tool in the study of the effects of microneedle geometry on skin penetration characteristics and in-skin dissolution. J. Control. Release 147, 333–341 (2010)
F. Duboeuf, A. Basarab, H. Liebgott, E. Brusseau, P. Delachartre, D. Vray, Investigation of PVA cryogel Young’s modulus stability with time, controlled by a simple reliable technique. Med. Phys. 36, 656–661 (2009)
L. J. Fernández, A. Altuna, M. Tijero, G. Gabriel, R. Villa, M. J. Rodríguez, M. Batlle, R. Vilares, J. Berganzo, F. J. Blanco, Study of functional viability of SU-8-based microneedles for neural applications. J. Micromech. Microeng. 19, 025007 (2009)
C. Fu, H. Huang, Different methods for the fabrication of UV-LIGA molds using SU-8 with tapered de-molding angles. Microsyst. Technol. 13, 293–298 (2006)
E. L. Giudice, J. D. Campbell, Needle-free vaccine delivery. Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev. 58, 68–89 (2006)
H. Huang, C. Fu, Different fabrication methods of out-of-plane polymer hollow needle arrays and their variations. J. Micromech. Microeng. 17, 393–402 (2007)
H. Huang, W. Yang, T. Wang, T. Chuang, C. Fu, 3D high aspect ratio micro structures fabricated by one step UV lithography. J. Micromech. Microeng. 17, 291–296 (2007)
J. Ji, F. E. H. Tay, J. Miao, Microfabricated hollow microneedle array using ICP etcher. J. Phys. Conf. Ser. 34, 1132–1136 (2006)
e.-S. Khafagy, M. Morishita, Y. Onuki, K. Takayama, Current challenges in non-invasive insulin delivery systems: a comparative review. Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev. 59, 1521–1546 (2007)
E. Larrañeta, J. Moore, E. M. Vicente-Perez, P. Gonzalez-Vazquez, R. Lutton, A. D. Woolfson, R. F. Donnelly, A proposed model membrane and test method for microneedle insertion studies. Int. J. Pharm. 472, 65–73 (2014)
K. Lee, H. Jung, Drawing lithography for microneedles: a review of fundamentals and biomedical applications. Biomaterials 33, 7309–7326 (2012)
K. Lee, H. C. Lee, D. Lee, H. Jung, Drawing lithography: three-dimensional fabrication of an ultrahigh-aspect-ratio microneedle. Adv. Mater. 22, 483–486 (2010)
K. Lee, C. Y. Lee, H. Jung, Dissolving microneedles for transdermal drug administration prepared by stepwise controlled drawing of maltose. Biomaterials 32, 3134–3140 (2011)
I. C. Lee, J. He, M. Tsai, K. Lin, Fabrication of a novel partially dissolving polymer microneedle patch for transdermal drug delivery. J. Mater. Chem. B 3, 276–285 (2015)
C. G. Li, C. Y. Lee, K. Lee, H. Jung, An optimized hollow microneedle for minimally invasive blood extraction. Biomed. Microdevices 15, 17–25 (2013)
M. H. Ling, M. C. Chen, Dissolving polymer microneedle patches for rapid and efficient transdermal delivery of insulin to diabetic rats. Acta Biomater. 9, 8952–8961 (2013)
D. V. McAllister, P. M. Wang, S. P. Davis, J.-H. Park, P. J. Canatella, M. G. Allen, M. R. Prausnitz, Microfabricated needles for transdermal delivery of macromolecules and nanoparticles: fabrication methods and transport studies. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U. S. A. 100, 13755–13760 (2003)
Y. Nir, A. Paz, E. Sabo, I. Potasman, Fear of injections in young adults: prevalence and associations. Am.J.Trop. Med. Hyg. 68, 341–344 (2003)
J. J. Norman, J. M. Arya, M. A. McClain, P. M. Frew, M. I. Meltzer, M. R. Prausnitz, Microneedle patches: usability and acceptability for self-vaccination against influenza. Vaccine 32, 1856–1862 (2014)
S. M. Pond, T. N. Tozer, First-pass elimination. Basic concepts and clinical consequences. Clin. Pharmacokinet. 9, 1–25 (1984)
M. R. Prausnitz, R. Langer, Transdermal drug delivery. Nat. Biotechnol. 26, 1261–1268 (2008)
M. R. Prausnitz, S. Mitragotri, R. Langer, Current status and future potential of transdermal drug delivery. Nat. Rev. Drug Discov. 3, 115–124 (2004)
S. P. Sullivan, D. G. Koutsonanos, M. Del Pilar Martin, J. W. Lee, V. Zarnitsyn, S. O. Choi, N. Murthy, R. W. Compans, I. Skountzou, M. R. Prausnitz, Dissolving polymer microneedle patches for influenza vaccination. Nat. Med. 16, 915–920 (2010)
J. C. Trim, T. S. J. Elliott, A review of sharps injuries and preventative strategies. J. Hosp. Infect. 53, 237–242 (2003)
K. Tsioris, W. K. Raja, E. M. Pritchard, B. Panilaitis, D. L. Kaplan, F. G. Omenetto, Fabrication of silk microneedles for controlled-release drug delivery. Adv. Funct. Mater. 22, 330–335 (2012)
G. Valdés-Ramírez, J. R. Windmiller, J. C. Claussen, A. G. Martinez, F. Kuralay, M. Zhou, N. Zhou, R. Polsky, P. R. Miller, R. Narayan, J. Wang, Multiplexed and switchable release of distinct fluids from microneedle platforms via conducting polymer nanoactuators for potential drug delivery. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 161, 1018–1024 (2012)
N. Wilke, A. Morrissey, Silicon microneedle formation using modified mask designs based on convex corner undercut. J. Micromech. Microeng. 17, 238–244 (2007)
Z. Xiang, H. Wang, A. Pant, G. Pastorin, C. Lee, Development of vertical SU-8 microtubes integrated with dissolvable tips for transdermal drug delivery. Biomicrofluidics 7, 26502 (2013)
Z. Xiang, H. Wang, S. K. Murugappan, S. Yen, G. Pastorin, C. Lee, Dense vertical SU-8 microneedles drawn from a heated mold with precisely controlled volume. J. Micromech. Microeng. 25, 025013 (2015)
Acknowledgments
The authors would like to thank the Ministry of Science and Technology of Taiwan and Chang Gung Memorial Hospital for their funding support (No. MOST 103-2221-E-182-016-MY2, CMRPD3E0381, BMRPC01).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Yen-Heng Lin and I.-Chi Lee contributed equally to this work.
Electronic supplementary material
ESM 1
(WMV 8335 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Lin, YH., Lee, IC., Hsu, WC. et al. Rapid fabrication method of a microneedle mold with controllable needle height and width. Biomed Microdevices 18, 85 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10544-016-0113-8
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10544-016-0113-8