Abstract
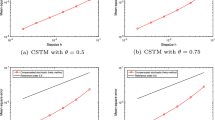
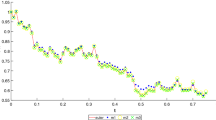
The present article revisits the well-known stochastic theta methods (STMs) for stochastic differential equations (SDEs) with non-globally Lipschitz drift and diffusion coefficients. Under a coupled monotonicity condition in a domain \(D \subset {{\mathbb {R}}}^d, d \in {{\mathbb {N}}}\), we propose a novel approach to achieve upper mean-square error bounds for STMs with the method parameters \(\theta \in [\tfrac{1}{2}, 1]\), which only get involved with the exact solution processes. This enables us to easily recover mean-square convergence rates of the considered schemes, without requiring a priori high-order moment estimates of numerical approximations. As applications of the error bounds, we derive mean-square convergence rates of STMs for SDEs driven by three kinds of noises under further globally polynomial growth condition. In particular, the error bounds are utilized to analyze approximation of SDEs with small noise. It is shown that the stochastic trapezoid formula gives better convergence performance than the other STMs. Furthermore, we apply STMs to the Ait-Sahalia-type interest rate model taking values in the domain \(D = ( 0, \infty )\), and successfully identify a convergence rate of order one-half for STMs with \(\theta \in [\tfrac{1}{2}, 1]\), even in a general critical case. This fills the gap left by Szpruch et al. (BIT Numer Math 51(2):405–425, 2011), where strong convergence of the backward Euler method was proved, without revealing a rate of convergence, for the model in a non-critical case.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ait-Sahalia, Y.: Testing continuous-time models of the spot interest rate. Rev. Financ. Stud. 9(2), 385–426 (1996)
Alfonsi, A.: Strong order one convergence of a drift implicit Euler scheme: application to the cir process. Stat. Probab. Lett. 83(2), 602–607 (2013)
Anderson, D.F., Higham, D.J., Sun, Y.: Multilevel Monte Carlo for stochastic differential equations with small noise. SIAM J. Numer. Anal. 54(2), 505–529 (2016)
Andersson, A., Kruse, R.: Mean-square convergence of the BDF2-Maruyama and backward Euler schemes for SDE satisfying a global monotonicity condition. BIT Numer. Math. 57(1), 21–53 (2017)
Beyn, W.-J., Isaak, E., Kruse, R.: Stochastic C-stability and B-consistency of explicit and implicit Euler-type schemes. J. Sci. Comput. 67(3), 955–987 (2016)
Beyn, W.-J., Kruse, R.: Two-sided error estimates for the stochastic theta method. Discret. Contin. Dyn. Syst. Ser. B 14(2), 389–407 (2010)
Bryden, A., Higham, D.J.: On the boundedness of asymptotic stability regions for the stochastic theta method. BIT Numer. Math. 43(1), 1–6 (2003)
Buckwar, E., Rößler, A., Winkler, R.: Stochastic Runge–Kutta methods for itô SODEs with small noise. SIAM J. Sci. Comput. 32(4), 1789–1808 (2010)
Buckwar, E., Winkler, R.: Multistep methods for SDEs and their application to problems with small noise. SIAM J. Numer. Anal. 44(2), 779–803 (2006)
Chassagneux, J., Jacquier, A., Mihaylov, I.: An explicit Euler scheme with strong rate of convergence for financial SDEs with non-lipschitz coefficients. SIAM J. Financ. Math. 7(1), 993–1021 (2016)
Fang, W., Giles, M.B.: Adaptive Euler-Maruyama method for SDEs with non-globally lipschitz drift: Part i, finite time interval. arXiv preprint arXiv:1609.08101 (2016)
Higham, D.J.: Mean-square and asymptotic stability of the stochastic theta method. SIAM J. Numer. Anal. 38(3), 753–769 (2000)
Higham, D.J., Mao, X., Stuart, A.M.: Strong convergence of Euler-type methods for nonlinear stochastic differential equations. SIAM J. Numer. Anal. 40(3), 1041–1063 (2002)
Higham, D.J., Mao, X., Stuart, A.M.: Exponential mean-square stability of numerical solutions to stochastic differential equations. LMS J. Comput. Math. 6, 297–313 (2003)
Huang, C.: Exponential mean square stability of numerical methods for systems of stochastic differential equations. J. Comput. Appl. Math. 236(16), 4016–4026 (2012)
Hutzenthaler, M., Jentzen, A.: Numerical approximation of stochastic differential equations with non-globally Lipschitz continuous coefficients. Mem. Am. Math. Soc. 236, 1112 (2015)
Hutzenthaler, M., Jentzen, A., Kloeden, P.E.: Strong and weak divergence in finite time of Euler’s method for stochastic differential equations with non-globally Lipschitz continuous coefficients. Proc. R. Soc. Lond. A: Math. Phys. Eng. Sci. 467(2130), 1563–1576 (2011)
Hutzenthaler, M., Jentzen, A., Kloeden, P.E.: Strong convergence of an explicit numerical method for SDEs with nonglobally Lipschitz coefficients. Ann. Appl. Probab. 22(4), 1611–1641 (2012)
Hutzenthaler, M., Jentzen, A., Wang, X.: Exponential integrability properties of numerical approximation processes for nonlinear stochastic differential equations. Math. Comput. 87(311), 1353–1413 (2018)
Kelly, C., Lord, G.J.: Adaptive time-stepping strategies for nonlinear stochastic systems. IMA J. Numer. Anal. 38(3), 1523–1549 (2017)
Kloeden, P.E., Platen, E.: Numerical Solution of Stochastic Differential Equations, vol. 23. Springer, Berlin (1992)
Li, T., Abdulle, A.: Effectiveness of implicit methods for stiff stochastic differential equations. Commun. Comput. Phys. 3, 295–307 (2008)
Li, X., Mao, X., Yin, G.: Explicit numerical approximations for stochastic differential equations in finite and infinite horizons: truncation methods, convergence in pth moment and stability. IMA J. Numer. Anal. 39, 847–892 (2019)
Mao, X.: The truncated Euler-Maruyama method for stochastic differential equations. J. Comput. Appl. Math. 290, 370–384 (2015)
Mao, X.: Convergence rates of the truncated Euler-Maruyama method for stochastic differential equations. J. Comput. Appl. Math. 296, 362–375 (2016)
Mao, X., Szpruch, L.: Strong convergence and stability of implicit numerical methods for stochastic differential equations with non-globally Lipschitz continuous coefficients. J. Comput. Appl. Math. 238, 14–28 (2013)
Mao, X., Szpruch, L.: Strong convergence rates for backward Euler–Maruyama method for non-linear dissipative-type stochastic differential equations with super-linear diffusion coefficients. Stoch. Int. J. Probab. Stoch. Process. 85(1), 144–171 (2013)
Milstein, G., Tretyakov, M.V.: Mean-square numerical methods for stochastic differential equations with small noises. SIAM J. Sci. Comput. 18(4), 1067–1087 (1997)
Milstein, G.N., Tretyakov, M.V.: Stochastic Numerics for Mathematical Physics. Springer, Berlin (2013)
Neuenkirch, A., Szpruch, L.: First order strong approximations of scalar sdes defined in a domain. Numerische Mathematik 128(1), 103–136 (2014)
Römisch, W., Winkler, R.: Stepsize control for mean-square numerical methods for stochastic differential equations with small noise. SIAM J. Sci. Comput. 28(2), 604–625 (2006)
Sabanis, S.: A note on tamed Euler approximations. Electron. Commun. Probab. 18(47), 1–10 (2013)
Sabanis, S.: Euler approximations with varying coefficients: the case of super-linearly growing diffusion coefficients. Ann. Appl. Probab. 26(4), 2083–2105 (2016)
Szpruch, L., Mao, X., Higham, D.J., Pan, J.: Numerical simulation of a strongly nonlinear Ait-Sahalia-type interest rate model. BIT Numer. Math. 51(2), 405–425 (2011)
Szpruch, L., Zhang, X.: V-integrability, asymptotic stability and comparison property of explicit numerical schemes for non-linear SDEs. Math. Comput. 87(310), 755–783 (2018)
Tretyakov, M.V., Zhang, Z.: A fundamental mean-square convergence theorem for SDEs with locally Lipschitz coefficients and its applications. SIAM J. Numer. Anal. 51(6), 3135–3162 (2013)
Wang, X., Gan, S.: The tamed Milstein method for commutative stochastic differential equations with non-globally Lipschitz continuous coefficients. J. Differ. Equ. Appl. 19(3), 466–490 (2013)
Wang, X.: Mean-square convergence rates of implicit Milstein type methods for SDEs with non-Lipschitz coefficients: applications to financial models. Submitted for publication (2020)
Zhang, Z., Ma, H.: Order-preserving strong schemes for SDEs with locally Lipschitz coefficients. Appl. Numer. Math. 112, 1–16 (2017)
Zong, X., Wu, F.: Choice of \(\theta \) and mean-square exponential stability in the stochastic theta method of stochastic differential equations. J. Comput. Appl. Math. 255, 837–847 (2014)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Communicated by David Cohen.
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
This work was supported by NSF of China (11671405, 11971488, 11571373, 91630312, 11561028, 11801238), Innovation Program of Central South University (No. 2017CX017), and Program of Shenghua Yuying at Central South University. We would like to thank the two referees for their helpful comments, which are crucial to the improvements of the work.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Wang, X., Wu, J. & Dong, B. Mean-square convergence rates of stochastic theta methods for SDEs under a coupled monotonicity condition. Bit Numer Math 60, 759–790 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10543-019-00793-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10543-019-00793-0
Keywords
- Stochastic differential equations
- Stochastic theta methods
- Mean-square convergence rates
- Multiplicative noise
- Additive noise
- Small noise
- Ait-Sahalia model