Abstract
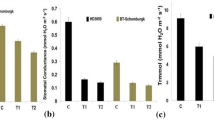
Exposure to low temperatures is one of the most important factors that generate abiotic stress in plants, and the rapid accumulation of soluble sugars belongs to significant metabolic responses to cold stress. The accumulation of soluble sugars may be at least partially triggered by an increased rate of starch degradation. The analysis of transcript profiles and starch degrading enzyme activities in leaves of two potato cultivars was performed during a 12-h exposure to 2 °C. An induction of β-amylase expression and activity as well as an accumulation of reducing sugars were observed in cv. Desiree. No accumulation of reducing sugars and no significant changes in the β-amylase activity were initially observed in cv. Russet Burbank. Surprisingly, an increased α-amylase activity was observed in the last hours of the experiment, which was accompanied by an increased amount of reducing sugars. The results indicate that the leaves of Desiree and Russet Burbank potatoes growing under cold stress may degrade starch via different pathways.
Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- DPE1:
-
disproportionating enzyme 1
- DPE2:
-
disproportionating enzyme 2
- G1P:
-
glucose 1-phosphate
- LDA:
-
limit dextrinase
- SGH:
-
soluble heteroglycan
- SPS:
-
sucrose-6-phosphate synthase
References
Albrecht, T., Koch, A., Lode, A., Greve, B., Schneider-Mergener, J., Steup, M.: Plastidic (Pho1-type) phosphorylase isoforms in potato (Solanum tuberosum L.) plants: expression analysis and immunochemical characterization. — Planta 213: 602–613, 2001.
Asatsuma, S., Sawada, C., Itoh, K., Okito, M., Kitajima, A., Mitsui T.: Involvement of α-amylase I-1 in starch degradation in rice chloroplasts. — Plant Cell Physiol. 46: 858–869, 2005.
Bradford, M.M.: A rapid and sensitive method for the quantification of microgram quantities of protein utilizing the principle of protein-dye binding. — Anal Biochem 72: 248–254, 1976.
Critchley, J.H., Zeeman, S.C., Takaha, T., Smith, A.M., Smith, S.M. A critical role for disproportionating enzyme in starch breakdown is revealed by a knock-out mutant in Arabidopsis. — Plant J. 26: 89–100, 2001.
Doehlert, D.C., Duke, S.H.: Specific determination of α-amylase activity in crude plant extracts containing β-amylase. — Plant Physiol. 71: 229–234, 1983.
Espinoza, C., Degenkolbe, T., Caldana, C., Zuther, E., Leisse, A., Willmitzer, L., Hincha, D.K., Hannah, M.A.: Interaction with diurnal and circadian regulation results in dynamic metabolic and transcriptional changes during cold acclimation in Arabidopsis. — PLoS ONE 5: e14101, 2010.
Fettke, J., Chia, T., Eckermann, N., Smith, A.M., Steup, M.: A transglucosidase necessary for starch degradation and maltose metabolism in leaves at night acts on cytosolic heteroglycans (SHG). — Plant J. 46: 668–684, 2006.
Fettke, J., Eckermann, N., Tiessen, A., Geigenberger, P., Steup, M.: Identification, subcellular localization and biochemical characterization of water-soluble heteroglycans (SHG) in leaves of Arabidopsis thaliana L.: distinct SHG reside in the cytosol and in the apoplast. — Plant J. 43: 568–585, 2005.
Grabowska, A., Kwinta, J., Bielawski, W.: Glutamine synthetase and glutamate dehydrogenase in triticale seeds: molecular cloning and genes expression. — Acta Physiol Plant. 34: 2393–2406, 2012.
Hejazi, M., Fettke, J., Haebel, S., Edner, C., Paris, O., Frohberg, C., Steup, M., Ritte, G.: Glucan, water dikinase phosphorylates crystalline maltodextrins and thereby initiates solubilization. — Plant J. 55: 323–34, 2008.
Illeperuma, C., Schlimme, D., Solomos, T.: Changes in sugars and activities of sucrose phosphate synthase, sucrose synthase, and invertase during potato tuber (Russet Burbank) reconditioning at 10 °C in air and 253 kPa oxygen after storage for 28 days at 1 °C. — J. amer. Soc. hort. Sci. 123: 311–316, 1998.
Jain, M.: Emerging role of metabolic pathways in abiotic stress tolerance. — J. Plant Biochem. Physiol. 1: 108, 2013.
Kaminski, K.P., Petersen, A.H., Sønderkær, M., Pedersen, L.H., Pedersen, H., Feder, C., Nielsen, K.L.: Transcriptome analysis suggests that starch synthesis may proceed via multiple metabolic routes in high yielding potato cultivars. — PLoS ONE 7: e51248, 2012.
Kaplan, F., Guy, C.: β-amylase induction and the protective role of maltose during temperature shock. — Plant Physiol. 135: 1674–1684, 2004.
Kaplan, F., Kopka, J., Sung, D.Y., Zhao, W., Popp, M., Porat, R., Guy, C.L.: Transcript and metabolite profiling during cold acclimation of Arabidopsis reveals an intricate relationship of cold-regulated gene expression with modifications in metabolite content. — Plant J. 50: 967–981, 2007.
Kosová, K., Vítámvás, P., Prášil, I.T.: The role of dehydrins in plant response to cold. — Biol. Plant. 51: 601–617, 2007.
Krasensky, J., Jonak, C.: Drought, salt, and temperature stressinduced metabolic rearrangements and regulatory networks. — J. exp. Bot. 63: 1593–1608, 2012.
Kumar, D., Singh, B.P., Kumar, P.: An overview of the factors affecting sugar content of potatoes. — Ann. appl. Biol. 145: 247–256, 2004.
Lee, J.H., Yu, D.J., Kim, S.J., Choi, D., Lee, H.J.: Intraspecies differences in cold hardiness, carbohydrate content and β- amylase gene expression of Vaccinium corymbosum during cold acclimation and deacclimation. — Tree Physiol. 32: 1533–1540, 2012.
Lindsay, H.: A colorimetric estimation of reducing sugars in potatoes with 3,5-dinitrosalicylic acid. — Potato Res. 16: 176–179, 1973.
Lu, Y., Steichen, J.M., Yao, J., Sharkey, T.D.: The role of cytosolic alpha-glucan phosphorylase in maltose metabolism and the comparison of amylomaltase in Arabidopsis and Escherichia coli. — Plant Physiol. 142: 878–889, 2006.
Lütken, H., Lloyd, J.R., Glaring, M.A., Baunsgaard, L., Laursen, K.H., Haldrup, A., Kossmann, J., Blennow, A.: Repression of both isoforms of disproportionating enzyme leads to higher malto-oligosaccharide content and reduced growth in potato. — Planta 232: 1127–1139, 2010.
Orzechowski, S.: Starch metabolism in leaves. Acta biochim. polon. 55: 435–445, 2008.
Orzechowski, S., Grabowska, A., Sitnicka, D., Simińska, J., Feluś, M., Dudkiewicz, M., Fudali, S., Sobczak, M.: Analysis of the expression, subcellular and tissue localisation of phosphoglucan, water dikinase (PWD/GWD3) in Solanum tuberosum L.: a bioinformatics approach for the comparative analysis of two α-glucan, water dikinases (GWDs) from Solanum tuberosum L. — Acta Physiol Plant. 35: 483–500, 2013.
Patrick, J.W., Botha, F.C., Birch, R.G.: Metabolic engineering of sugars and simple sugar derivatives in plants. — Plant Biotechnol. J. 11: 142–156, 2013.
Ruelland, E., Vaultier, M.N., Zachowski, A., Hurry, V.: Cold signalling and cold acclimation in plant. — Adv. bot. Res. 49: 35–150, 2009.
Saropulos, A.S., Drennan, D.S.H.: Ultrastructural alterations in mesophyll and bundle sheath chloroplasts of two maize cultivars in response to chilling at high irradiance. — Biol. Plant. 51: 690–698, 2007.
Seung, D., Thalmann, M., Sparla, F., Hachem, M.A., Lee, S.K., Bourguet, E.I., Svensson, B., Zeeman, S.C., Santelia, D.: The Arabidopsis AtAMY3 is a unique redox-regulated chloroplastic α-amylase. — J. biol. Chem. 288: 33620–33633, 2013.
Smith, A.M., Zeeman, S.C., Smith, S.M.: Starch degradation. — Annu. Rev. Plant. Biol. 56:73–98, 2005.
Smith, S.M., Fulton, D.C., Chia, T., Thorneycroft, D., Chapple, A., Dunstan, H., Hylton, C., Zeeman, S.C., Smith, A.M.: Diurnal changes in the transcriptome encoding enzymes of starch metabolism provide evidence for both transcriptional and posttranscriptional regulation of starch metabolism in Arabidopsis leaves. — Plant. Physiol. 136: 2687–2699, 2004.
Stanley, D., Farnden, K.J.F., MacRae, E.A.: Plant α-amylases: functions and roles in carbohydrate metabolism. — Biológia 16: 65–71, 2005.
Stanley, D., Fitzgerald, A.M., Farnden, K.J.F. and McRae, E.A.: Characterization of putative amylases from apple (Malus domestica) and Arabidopsis thaliana. — Biológia 57: 137–148, 2002.
Stark, J.C., Novy, R.G., Love, S.L., Whitworth, J.L., Corsini, D.L., Pavek, J.J., Mosley, A.R., Pavek, M.J., Knowles, N.R., Thornton, R.E., James, S.R., Hane, D.C., Olsen, N., Vales, M.I. and Brown, C.R.: Blazer Russet: an early to mid-season potato cultivar with high U.S. no. 1 yields and good processing and culinary qualities. — Amer. J. Potato Res. 84: 467–477, 2007.
Steichen, J.M., Petty, R.V., Sharkey, D. Domain characterrization of a 4-α-glucanotransferase essential for maltose metabolism in photosynthetic leaves. — J. biol. Chem. 283: 20797–20804, 2008.
Steup, M., Latzko, E.: Intracellular localization of phosphorylases in spinach and pea leaves. — Planta 145: 69–75, 1979.
Viksø-Nielsen, A,. Christensen, T.M.I.E., Bojko, M., Marcussen, J.: Purification and characterization of β- amylase from leaves of potato (Solanum tuberosum). — Physiol. Plant. 99: 190–196, 1997.
Wang, D.H., Li, X.X., Su, Z.K., Ren, H.X. The role of salicylic acid in response of two rice cultivars to chilling stress. — Biol. Plant. 53: 545–552, 2009.
Weise, S.E., Schrader, S.M., Kleinbeck, K.R., Sharkey, T.D.: Carbon balance and circadian regulation of hydrolytic and phosphorolytic breakdown of transitory starch. — Plant. Physiol. 141: 879–886, 2006.
Wessa, P.: Free Statistics Software, Office for Research Development and Education, version 1.1.23-r7, URL http://www.wessa.net/, 2014.
Yu, T.S., Zeeman, S.C., Thorneycroft, D., Fulton, D.C., Dunstan, H., Lue, W.L., Hegemann, B., Tung, S.Y., Umemoto, T., Chapple, A., Tsai, D.L., Wang, S.M., Smith, A.M., Chen, J., Smith, S.M.I.: Alpha-amylase is not required for breakdown of transitory starch in Arabidopsis leaves. — J. biol. Chem. 280: 9773–9779, 2005.
Yuanyuan, M., Yali, Z., Jiang, L., Hongbo, S.: Roles of plant soluble sugars and their responses to plant cold stress. — Afr. J. Biotechnol. 8: 2004–2010, 2009.
Zeeman, S.C., Northrop, F., Smith, A.M., Rees, T.: A starch- accumulating mutant of Arabidopsis thaliana deficient in a chloroplastic starch hydrolyzing enzyme. — Plant J. 15: 357–365, 1998a.
Zeeman, S.C., Umemoto, T., Lue, W.L., Au-Yeung, P., Martin, C., Smith, A.M., Chen, J.: A mutant of Arabidopsis lacking a chloroplastic isoamylase accumulates both starch and phytoglycogen. — Plant Cell 10: 1699–1711, 1998b.
Zhou, D., Solomos, T.: Effect of hypoxia on sugar accumulation, respiration, activities of amylase and starch phosphorylase, and induction of alternative oxidase and acid invertase during storage of potato tubers (Solanum tuberosum cv. Russet Burbank) at 1 °C. — Physiol. Plant. 104: 255–265, 1998.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Sitnicka, D., Orzechowski, S. Cold-induced starch degradation in potato leaves — intercultivar differences in the gene expression and activity of key enzymes. Biol Plant 58, 659–666 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10535-014-0453-2
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10535-014-0453-2