Abstract
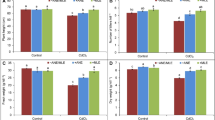
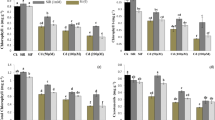
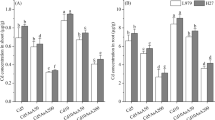
Cadmium (Cd) is one of the dangerous factors that have negative impacts on plants and human health. Recently, many researchers have been looking for biostimulants to use as bioprotectants that can help or ameliorate plants’ tolerance against abiotic stress, including Cd. To test the dangerousness of Cd accumulated in the soil, 200 µM of the latter was applied to sorghum seeds at germination and maturation stages. At the same time, Atriplex halimus water extract (0.1%, 0.25%, 0.5%) was applied to test its efficacy on Cd alleviation in sorghum plants. The obtained results showed that the tested concentrations enhanced the tolerance of sorghum to Cd by enhancing the germination indexes parameters such as germination percentage (GP), seedling vigor index (SVI), and reducing the mean germination time (MGT) of sorghum seeds grown under cadmium stress. On the other hand, the morphological parameters (height and weight) as well as the physiological parameters (chlorophyll and carotenoid) were stimulated in treated maturated sorghum plants under Cd stress. In addition, 0.5% and 0.25% of Atriplex halimus extract (AHE) stimulated the antioxidant enzymes, including superoxide dismutase, catalase, glutathione peroxidase, glutathione-s-transferase, and glutathione reductase. In the same time, an increase in carbon–nitrogen enzymes was recorded in the case of AHE treatment; phosphoenol pyruvate carboxylase, glutamine synthase, glutamate dehydrogenase, and amino acid transferase were all upregulated. These results suggest that using AHE as a biostimulant could be a better strategy to enhance the tolerance of sorghum plants to Cd stress.





Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
The data used during this study is included in the article.
References
Ahmad I, Akhtar MJ, Zahir ZA, Jamil A (2012) Effect of cadmium on seed germination and seedling growth of four wheat (Triticum aestivum L.) cultivars. Pak J Bot 44:1569–1574
Ahmad P, Alyemeni MN, Wijaya L et al (2017) Jasmonic acid alleviates negative impacts of cadmium stress by modifying osmolytes and antioxidants in faba bean (Vicia faba L.). Arch Agron Soil Sci 63:1889–1899. https://doi.org/10.1080/03650340.2017.1313406
Ait Elallem K, Ben Bakrim W, Ennoury A et al (2022) Germination parameters and responses of antioxidant enzymatic activities of two medicinal plants (Peganum harmala L. and Origanum majorana L.) under heavy metal stress. J Soil Sci Plant Nutr. https://doi.org/10.1007/s42729-022-00943-4
Alzahrani Y, Rady MM (2019) Compared to antioxidants and polyamines, the role of maize grain-derived organic biostimulants in improving cadmium tolerance in wheat plants. Ecotoxicol Environ Saf. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ecoenv.2019.109378
An YJ (2004) Soil ecotoxicity assessment using cadmium sensitive plants. Environ Pollut 127:21–26. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0269-7491(03)00263-X
Anjum SA, Tanveer M, Hussain S et al (2015) Cadmium toxicity in Maize (Zea mays L.): consequences on antioxidative systems, reactive oxygen species and cadmium accumulation. Environ Sci Pollut Res 22:17022–17030. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-015-4882-z
Azizi I, Esmaielpour B, Fatemi H (2021) Exogenous nitric oxide on morphological, biochemical and antioxidant enzyme activity on savory (Satureja hortensis L.) plants under cadmium stress. J Saudi Soc Agric Sci 20:417–423. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jssas.2021.05.003
Ben MR, Bouchmaa N, Bouargalne Y et al (2019) Phytochemical characterization, antioxidant and in vitro cytotoxic activity evaluation of Juniperus oxycedrus Subsp Oxycedrus needles and berries. Molecules. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules24030502
Ben Mrid R (2016) Effect of nitrogen source and concentration on growth and activity of nitrogen assimilation enzymes in roots of a Moroccan sorghum ecotype. Plant 4:71. https://doi.org/10.11648/j.plant.20160406.14
Ben Mrid R, El Omari R, Bouargalne Y et al (2017) Activities of carbon and nitrogen metabolism enzymes during germinating sorghum seeds and early seedlings growth. Cereal Res Commun 45:587–597. https://doi.org/10.1556/0806.45.2017.044
Ben Mrid R, Benmrid B, Hafsa J et al (2021) Secondary metabolites as biostimulant and bioprotectant agents: a review. Sci Total Environ. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2021.146204
Ben Mrid R, Bouchmaa N, Ouedrhiri W et al (2022) Synergistic antioxidant effects of natural compounds on H2O2-induced cytotoxicity of human monocytes. Front Pharmacol. https://doi.org/10.3389/fphar.2022.830323
Benhammou N, Bekkara FA, Kadifkova Panovska T (2009) Antioxidant activity of methanolic extracts and some bioactive compounds of Atriplex halimus. C R Chim 12:1259–1266. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.crci.2009.02.004
Bhuyan MHMB, Parvin K, Mohsin SM et al (2020) Modulation of cadmium tolerance in rice: insight into vanillic acid-induced upregulation of antioxidant defense and glyoxalase systems. Plants. https://doi.org/10.3390/plants9020188
Bouargalne Y, Ben MR, El Omari R, Nhiri M (2018) Phosphoenolpyruvate carboxylase during maturation and germination sorghum seeds: enzyme activity and regulation. Russ J Plant Physiol 65:824–832. https://doi.org/10.1134/S1021443718060031
Bouargalne Y, Ben Mrid R, Bouchmaa N et al (2022) Genetic diversity for agromorphological traits, phytochemical profile, and antioxidant activity in Moroccan sorghum ecotypes. Sci Rep. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-022-09810-9
Bouchmaa N, Ben Mrid R, Boukharsa Y et al (2018) Cytotoxicity of new pyridazin-3(2H)-one derivatives orchestrating oxidative stress in human triple-negative breast cancer (MDA-MB-468). Arch Pharm (weinheim). https://doi.org/10.1002/ardp.201800128
Da Rosa Corrêa AX, Rörig LR, Verdinelli MA et al (2006) Cadmium phytotoxicity: quantitative sensitivity relationships between classical endpoints and antioxidative enzyme biomarkers. Sci Total Environ 357:120–127. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2005.05.002
de Morais CL, Pinheiro SS, Martino HSD, Pinheiro-Sant’Ana HM (2017) Sorghum (Sorghum bicolor L.): nutrients, bioactive compounds, and potential impact on human health. Crit Rev Food Sci Nutr 57:372–390. https://doi.org/10.1080/10408398.2014.887057
Doganlar ZBP, Yurekli F (2009) Interactions between cadmium and phytochelatin accumulation in two different sunflower cultivars. Fresenius Environ Bull 18:304–310
El Omari R, Ben Mrid R, Chibi F, Nhiri M (2016) Involvement of phosphoenolpyruvate carboxylase and antioxydants enzymes in nitrogen nutrition tolerance in Sorghum bicolor plants. Russ J Plant Physiol 63:719–726. https://doi.org/10.1134/S102144371606008X
El Rasafi T, Oukarroum A, Haddioui A et al (2022) Cadmium stress in plants: a critical review of the effects, mechanisms, and tolerance strategies. Crit Rev Environ Sci Technol 52:675–726. https://doi.org/10.1080/10643389.2020.1835435
Ennoury A, BenMrid R, Nhhala N et al (2022) River’s Ulva intestinalis extract protects common bean plants (Phaseolus vulgaris L.) against salt stress. S Afr J Bot 150:334–341. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.sajb.2022.07.035
Franclet A, Le Houérou HN (1971) Les Atriplex en Tunisie et en Afrique du Nord. FAO, Rome
Hasanuzzaman M, Nahar K, Anee TI, Fujita M (2017) Glutathione in plants: biosynthesis and physiological role in environmental stress tolerance. Physiol Mol Biol Plants 23:249–268. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12298-017-0422-2
Jung HI, Lee BR, Chae MJ et al (2020) Ascorbate-mediated modulation of cadmium stress responses: reactive oxygen species and redox status in Brassica napus. Front Plant Sci. https://doi.org/10.3389/fpls.2020.586547
Kchikich A, El Omari R, Kabach I et al (2021a) Effect of arbuscular mycorrhizal fungus and the γ-aminobutyric acid treatment in nitrate assimilation under nitrogen deficiency in sorghum plant. Russ J Plant Physiol 68:901–908. https://doi.org/10.1134/S102144372105006X
Kchikich A, Ben MR, Kabach I et al (2021b) Arbuscular mycorrhizal fungi enhance sorghum plant growth under nitrogen-deficient conditions through activation of nitrogen and carbon metabolism enzymes. Int J Agric Biol 26:201–208. https://doi.org/10.17957/IJAB/15.1825
Kubiś J (2008) Exogenous spermidine differentially alters activities of some scavenging system enzymes, H2O2 and superoxide radical levels in water-stressed cucumber leaves. J Plant Physiol 165:397–406. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jplph.2007.02.005
Latique S, Ben MR, Kabach I et al (2021) Foliar application of ulva rigida water extracts improves salinity tolerance in wheat (Triticum durum L.). Agronomy. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy11020265
Li X, Bu N, Li Y et al (2012) Growth, photosynthesis and antioxidant responses of endophyte infected and non-infected rice under lead stress conditions. J Hazard Mater 213–214:55–61. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2012.01.052
Megha T, Mir RA, Jatav KS, Agarwal RM (2020) Supplementation of potassium alleviates water stress induced changes in Sorghum bicolor L. Physiol Plant. https://doi.org/10.1111/ppl.13306
Muratova A, Lyubun Y, German K, Turkovskaya O (2015) Effect of cadmium stress and inoculation with a heavy-metal-resistant bacterium on the growth and enzyme activity of Sorghum bicolor. Environ Sci Pollut Res 22:16098–16109. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-015-4798-7
Naboulsi I, Ben MR, Ennoury A et al (2022a) Crataegus oxyacantha extract as a biostimulant to enhance tolerance to salinity in tomato plants. Plants. https://doi.org/10.3390/plants11101283
Piechalak A, Tomaszewska B, Baralkiewicz D, Malecka A (2002) Accumulation and detoxification of lead ions in legumes. Phytochemistry 60:153–162. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0031-9422(02)00067-5
Rahman SU, Xuebin Q, Riaz L et al (2021) The interactive effect of pH variation and cadmium stress on wheat (Triticum aestivum L.) growth, physiological and biochemical parameters. PLoS ONE. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0253798
Ranal MA, de Santana DG, Ferreira WR, Mendes-Rodrigues C (2009) Calculando medidas de germinação e organizando planilhas eletrônicas. Rev Brasileira Botanica 32:849–855. https://doi.org/10.1590/S0100-84042009000400022
Rayees Ahmad M, Argal S, Ahanger MA, Jatav KS, Agarwal RM (2022) Differential activity of wheat antioxidant defence system and alterations in the accumulation of osmolytes at different developmental stages as influenced by marigold (Tagetes erecta L.) leachates. Front Plant Sci. https://doi.org/10.3389/fpls.2022.1001394
Raziuddin F, Hassan G et al (2011) Effects of cadmium and salinity on growth and photosynthesis parameters of Brassica species. Pak J Bot 43:333–340
Roussi Z, Ben Mrid R, Ennoury A et al (2022a) Insight into Cistus salviifolius extract for potential biostimulant effects in modulating cadmium-induced stress in sorghum plant. Physiol Mol Biol Plants 28:1323–1334. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12298-022-01202-7
Roussi Z, Kchikich A, Nhhala N, Krid A, Ennoury A, Asri SE, Zouaoui Z, Nhiri N, Nhiri M (2022b) Cistus monspeliensis extract as a prospective biostimulant in enhancing tolerance to cadmium in sorghum plant. Biomass Conv Bioref. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13399-022-03542-6
Scott JL, Gabrielides C, Davidson RK et al (2010) Superoxide dismutase downregulation in osteoarthritis progression and end-stage disease. Ann Rheum Dis 69:1502–1510. https://doi.org/10.1136/ard.2009.119966
Sfaxi-Bousbih A, Chaoui A, El Ferjani E (2010) Cadmium impairs mineral and carbohydrate mobilization during the germination of bean seeds. Ecotoxicol Environ Saf 73:1123–1129. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ecoenv.2010.01.005
Shafiei Darabi S, Almodares A, Ebrahimi M (2016) Phytoremediation efficiency of sorghum bicolor (L) Moench in removing cadmium, lead and arsenic. Open J Environ Biol 1:001–006. https://doi.org/10.17352/ojeb.000001
Sharmila P, Kumari PK, Singh K et al (2017) Cadmium toxicity-induced proline accumulation is coupled to iron depletion. Protoplasma 254:763–770. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00709-016-0988-5
Stagos D (2020) Antioxidant activity of polyphenolic plant extracts. Antioxidants. https://doi.org/10.3390/antiox9010019
Tumanyan AF, Seliverstova AP, Zaitseva NA (2020) Effect of heavy metals on ecosystems. Chem Technol Fuels Oils 56:390–394. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10553-020-01149-z
Walker DJ, Lutts S, Sánchez-García M, Correal E (2014) Atriplex halimus L.: its biology and uses. J Arid Environ 100–101:111–121. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jaridenv.2013.09.004
Wang L, Zhou Q, Ding L, Sun Y (2008) Effect of cadmium toxicity on nitrogen metabolism in leaves of Solanum nigrum L. as a newly found cadmium hyperaccumulator. J Hazard Mater 154:818–825. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2007.10.097
Zhou W, Sun QJ, Zhang CF et al (2004) Effect of salt stress on ammonium assimilation enzymes of the roots of rice (Oryza sativa) cultivars differing in salinity resistance. Acta Bot Sin 46:921–927
Funding
The authors did not receive support from any organization for the submitted work.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Conceptualization: AE; Methodology: AE, NN, AK, ZR, SEA, ZZ; Formal analysis and investigation: AE, NN, SEA; Writing—original draft preparation: AE, NN, SEA; Writing—review and editing: AE, MN; Supervision: MN.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors have no competing interests to declare that are relevant to the content of this article.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Ennoury, A., Nhhala, N., Kchikich, A. et al. Saltbuch extract: a bio-solutionfor cadmium stress sorghum plants in germination and maturation. Biometals 36, 997–1012 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10534-023-00499-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10534-023-00499-5