Abstract
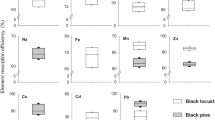
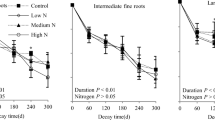
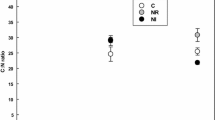
Litter decomposition is a key pathway of metal cycling in terrestrial ecosystems, yet little is known about the dynamics of metals in decomposing roots. A two-year decomposition experiment was conducted to investigate the temporal dynamics of nine metals (Ca, K, Mg, Fe, Al, Mn, Cr, Cu, and Pb) in decomposing roots of three diameter classes (0–2 mm, 2–5 mm, and 5–10 mm) in two subalpine coniferous tree species (Picea asperata and Abies faxoniana) on the eastern Tibetan Plateau of China. Regardless of tree species and root diameters, macro metals (Ca, K, and Mg) and Cu often released over the experimental period and their remaining were 87.7%, 12.5%, 69.4%, and 47.98%, respectively. However, trace metals (Fe, Al, Mn, Cr, and Pb) generally accumulated during the decomposition process and their remaining were 159.6%, 121.5%, 196.4%, 119.6%, and 124.3%, respectively. The concentrations of Ca, K, Mg, Fe, and Al often decreased with increasing root diameters over the experimental period. For Picea asperata, the Ca, K, Fe, and Pb remaining were higher in the 5–10 mm than 0–5 mm roots, but contrasting trends were found for Mg, Mn, Cr, and Cu. For Abies faxoniana, the 5–10 mm roots had lower macronutrients (Ca, K, and Mg) but higher trace metals (Fe, Al, Mn, Cr, Cu, and Pb) remaining compared to 0–5 mm roots. Taken together, root diameter had pronounced influences on metal dynamics, depending on metallic properties, initial root quality, and/or decomposition period. Root initial chemistry (e.g., C, Mn and lignin) were significantly correlated with the metal remaining during the decomposition. Our findings address the importance of root diameter in understanding metal cycling via root decomposition pathways in forest ecosystems.




Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
All data generated during the current study are presented in the manuscript and available from the authors.
References
Akburak S (2020) Variations of element concentrations in roots of different tree species. Cerne 26:118–129
Augusto L, Achat DL, Bakker MR, Bernier F, Bert D, Danjon F, Khlifa R, Meredieu C, Trichet P (2015) Biomass and nutrients in tree root systems-sustainable harvesting of an intensively managed Pinus pinaster (Ait.) planted forest. GCB Bioenergy 7:231–243
Ayres E, Steltzer H, Simmons BL, Simpson RT, Steinweg JM, Wallenstein MD, Mellor N, Parton WJ, Moore JC, Wall DH (2009) Home-field advantage accelerates leaf litter decomposition in forests. Soil Biol Biochem 41:606–610
Berg B (1984) Decomposition of root litter and some factors regulating the process: long-term root litter decomposition in a scots pine forest. Soil Biol Biochem 16:609–617
Berg B, Johansson MB, Liu C, Faituri M, Sanborn P, Vesterdal L, Ni X, Hansen K, Ukonmaanaho L (2017) Calcium in decomposing foliar litter – a synthesis for boreal and temperate coniferous forests. For Ecol Manage 403:137–144
Berg B, McClaugherty C (2014) Plant litter: decomposition, humus formation, carbon sequestration. Springer, Berlin
Bidar G, Garçon G, Pruvot C, Dewaele D, Cazier F, Douay F, Shirali P (2007) Behavior of Trifolium repens and Lolium perenne growing in a heavy metal contaminated field: plant metal concentration and phytotoxicity. Environ Pollut 147:546–553
Brun CB, Peltola P, Åström ME, Johansson M (2010) Spatial distribution of major, trace and ultra trace elements in three Norway spruce (Picea abies) stands in boreal forests, Forsmark, Sweden. Geoderma 159:252–261
Camiré C, Côté B, Brulotte S (1991) Decomposition of roots of black alder and hybrid poplar in short-rotation plantings: Nitrogen and lignin control. Plant Soil 138:123–132
Cao C, Liu SQ, Ma ZB, Lin Y, Su Q, Chen H, Wang JJ (2018) Dynamics of multiple elements in fast decomposing vegetable residues. Sci Total Environ 616–617:614–621
Cervantes C, Campos-García J, Devars S, Gutiérrez-Corona F, Loza-Tavera H, Torres-Guzmán JC, Moreno-Sánchez R (2001) Interactions of chromium with microorganisms and plants. FEMS Microbiol Rev 25:335–347
Chen H, Harmon ME, Sexton J, Fasth B (2002) Fine-root decomposition and N dynamics in coniferous forests of the Pacific Northwest, USA. Can J for Res 32:320–331
Chen W, Koide RT, Adams TS, DeForest JL, Cheng L, Eissenstat DM (2016) Root morphology and mycorrhizal symbioses together shape nutrient foraging strategies of temperate trees. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 113:8741–8746
de Graaff MA, Six J, Jastrow JD, Schadt CW, Wullschleger SD (2013) Variation in root architecture among switchgrass cultivars impacts root decomposition rates. Soil Biol Biochem 58:198–206
Dziadowiec H (1987) The decomposition of plant litter fall in an oak-linden-hornbeam forest and an oak-pine mixed forest of the Białowieża National Park. Acta Soc Bot Pol 56:169–185
Edmonds RL, Tuttle KM (2010) Red alder leaf decomposition and nutrient release in alder and conifer riparian patches in western Washington, USA. For Ecol Manage 259:2375–2381
Fahey TJ, Arthur MA (1994) Studies of root decomposition following harvest of a northern. For Sci 40:618–629
Fahey TJ, Hughes JW, Pu M, Arthur MA (1988) Root decomposition and nutrient flux following whole-tree harvest of northern hardwood forest. For Sci 34:744–768
Freschet GT, Cornwell WK, Wardle DA, Elumeeva TG, Liu W, Jackson BG, Onipchenko VG, Soudzilovskaia NA, Tao J, Cornelissen JH (2013) Linking litter decomposition of above- and below-ground organs to plant-soil feedbacks worldwide. J Ecol 101(943):952
Fujii S, Takeda H (2010) Dominant effects of litter substrate quality on the difference between leaf and root decomposition process above- and belowground. Soil Biol Biochem 42:2224–2230
Guo D, Xia M, Wei X, Chang W, Liu Y, Wang Z (2008) Anatomical traits associated with absorption and mycorrhizal colonization are linked to root branch order in twenty-three Chinese temperate tree species. New Phytol 180:673–683
Guo YY, Wang JJ, Kong DL, Wang W, Guo DL, Wang YB, Xie QL, Liu YS, Zeng H (2013) Fine root branch orders contribute differentially to uptake, allocation, and return of potentially toxic metals. Environ Sci Technol 47:11465–11472
Han SH, Kim S, Chang H, Kim HJ, Khamzina A, Son Y (2019) Soil depth- and root diameter-related variations affect root decomposition in temperate pine and oak forests. J Plant Ecol 12:871–881
He J, Yang W, Xu L, Ni X, Li H, Wu F (2016) Copper and zinc dynamics in foliar litter during decomposition from gap center to closed canopy in an alpine forest. Scand J for Re 31:355–367
Heim A, Brunner I, Frossard E, Luster J (2003) Aluminum effects on Picea abies at low solution concentrations. Soil Sci Soc Am J 67:895–898
Hobbie SE, Oleksyn J, Eissenstat DM, Reich PB (2010) Fine root decomposition rates do not mirror those of leaf litter among temperate tree species. Oecologia 162:505–513
Huttermann A, Arduini DL (2004) Metal pollution and forest decline In heavy metal stress in plants: from biomolecules to ecosystems. Springer-Verlag, Berlin
Islam E, Yang X, Li T, Liu D, Jin X, Meng F (2007) Effect of Pb toxicity on root morphology, physiology and ultrastructure in the two ecotypes of Elsholtzia argyi. J Hazard Mater 147:806–816
IUSS (2007) World reference base for soil resources 2006. First update 2007. World soil resources reports no. 103. FAO, IT EU, Rome
Jani AD, Grossman JM, Smyth TJ, Hu S (2015) Influence of soil inorganic nitrogen and root diameter size on legume cover crop root decomposition and nitrogen release. Plant Soil 393:57–68
Jiang L, Yue K, Yang Y, Wu Q (2016) Leaching and freeze-thaw events contribute to litter decomposition - A review. Sains Malaysiana 45:1041–1047
Jing H, Zhang P, Li J, Yao X, Liu G, Wang G (2019) Effect of nitrogen addition on the decomposition and release of compounds from fine roots with different diameters: the importance of initial substrate chemistry. Plant Soil 438:281–296
Johansson M (2001) Changes in concentrations of Cd, Zn, Mn, Cu and Pb in Spruce (Picea Abies) needle litter during decomposition. Water Air Soil Pollut 132:165–184
John B, Pandey HN, Tripathi RS (2002) Decomposition of fine roots of Pinus kesiya and turnover of organic matter, N and P of coarse and fine pine roots and herbaceous roots and rhizomes in subtropical pine forest stands of different ages. Biol Fertil Soils 35:238–246
Keplin B, Hüttl RF (2001) Decomposition of root litter in Pinus sylvestris L. and Pinus nigra stands on carboniferous substrates in the Lusatian lignite mining district. Ecol Eng 17:285–296
Kou L, Chen W, Zhang X, Gao W, Yang H, Li D, Li S (2015) Differential responses of needle and branch order-based root decay to nitrogen addition: dominant effects of acid-unhydrolyzable residue and microbial enzymes. Plant Soil 394:315–327
Kou L, Chen W, Jiang L, Dai X, Fu X, Wang H, Li S (2018) Simulated nitrogen deposition affects stoichiometry of multiple elements in resource-acquiring plant organs in a seasonally dry subtropical forest. Sci Total Environ 624:611–620
Krantz-Rülcker C, Allard B, Schnürer J (1993) Interactions between a soil fungus, Trichoderma harzianum, and IIb metals-adsorption to mycelium and production of complexing metabolites. Biometals 6:223–230
Laing GD, Van RG, Tack FMG, Verloo MG (2006) Metal accumulation in intertidal litter through decomposing leaf blades, sheaths and stems of Phragmites australis. Chemosphere 63:1815–1823
Lambers H, Raven JA, Shaver GR, Smith SE (2008) Plant nutrient-acquisition strategies change with soil age. Trends Ecol Evol 23:95–103
Laskowski R, Berg B, Johansson MB, McClaugherty C (1995) Release pattern for potassium from decomposing forest needle and leaf litter. Long-term decomposition in a Scots pine forest. IX Can J Bot 73:2019–2027
Li C, Chen P, Kang S, Yan F, Tripathee L, Wu G, Qu B, Sillanpää M, Yang D, Dittmar T, Stubbins A, Raymond PA (2018) Fossil fuel combustion emission from South Asia influences precipitation dissolved organic carbon reaching the remote Tibetan Plateau: isotopic and molecular evidence. J Geophys Res Atmos 123:6248–6258
Liu Q, Yang W, Wu F, Tan B, Zhang L, Xu Z (2019) Variations in root chemistry of three common forest species, southwestern China. J for Res 30:827–834
Luna-Orea P, Wagger MG, Gumpertz ML (1996) Decomposition and nutrient release dynamics of two tropical legume cover crops. Agron J 88:758–764
Makita N, Kawamura A, Osawa A (2015) Size-dependent morphological and chemical property of fine root litter decomposition. Plant Soil 393:283–295
Marañón T, Navarro-Fernández CM, Gil-Martínez M, Domínguez MT, Madejón P, Villar R (2020) Variation in morphological and chemical traits of Mediterranean tree roots: linkage with leaf traits and soil conditions. Plant Soil 449:389–403
Ni X, Yang W, Li H, Xu L, He J, Tan B, Wu F (2014) The responses of early foliar litter humification to reduced snow cover during winter in an alpine forest. Can J Soil Sci 94:453–461
Ni X, Berg B, Yang W, Li H, Liao S, Tan B, Yue K, Xu Z, Zhang L, Wu F (2018) Formation of forest gaps accelerates C, N and P release from foliar litter during 4 years of decomposition in an alpine forest. Biogeochemistry 139:321–335
Nordløkken M, Berg T, Flaten TP, Steinnes E (2015) Essential and non-essential elements in natural vegetation in southern Norway: contribution from different sources. Sci Total Environ 502:391–399
Osono T, Takeda H (2004) Potassium, calcium, and magnesium dynamics during litter decomposition in a cool temperate forest. J for Res 9:23–31
Page V, Weisskopf L, Feller U (2006) Heavy metals in white lupin: uptake, root-to-shoot transfer and redistribution within the plant. New Phytol 171:329–341
Palviainen M, Finér L, Kurka AM, Mannerkoski H, Piirainen S, Starr M (2004) Release of potassium, calcium, iron and aluminium from Norway spruce, Scots pine and silver birch logging residues. Plant Soil 259:123–136
Pang Y, Tian J, Lv X, Wang R, Wang D, Zhang F (2022) Contrasting dynamics and factor controls in leaf compared with different-diameter fine root litter decomposition in secondary forests in the Qinling Mountains after 5 years of whole-tree harvesting. Sci Total Environ 838:156194
Peng Y, Fornara DA, Wu Q, Heděnec P, Yuan J, Yuan C, Yue K, Wu F (2023) Global patterns and driving factors of plant litter iron, manganese, zinc, and copper concentrations. Sci Total Environ 857:159686
Rout GR, Sahoo S (2015) Role of iron in plant growth and metabolism. Rev Agric Sci 3:1–24
See CR, Luke McCormack M, Hobbie SE, Flores-Moreno H, Silver WL, Kennedy PG (2019) Global patterns in fine root decomposition: climate, chemistry, mycorrhizal association and woodiness. Ecol Lett 22:946–953
Shen X, Chen Y, Wang L, Guo L, Zheng H, Zhang J, Xu Z, Tan B, Zhang L, Li H, You C, Liu Y (2020) Mixture of plant functional groups inhibits the release of multiple metallic elements during litter decomposition in alpine timberline ecotone. Sci Total Environ 747:141298
Smith SW, Woodin SJ, Pakeman RJ, Johnson D, van der Wal R (2014) Root traits predict decomposition across a landscape-scale grazing experiment. New Phytol 203:851–862
Sun Z, Mou X, Shuang J (2012) Effects of flooding regimes on the decomposition and nutrient dynamics of Calamagrostis angustifolia litter in the Sanjiang Plain of China. Environ Earth Sci 66:2235–2246
Sun T, Mao Z, Dong L, Hou L, Song Y, Wang X (2013) Further evidence for slow decomposition of very fine roots using two methods: litterbags and intact cores. Plant Soil 366:633–646
Tang SS, Yang WQ, Xiong L, Yin R, Wang HP, Zhang Y, Xu ZF (2015) C, N and P stoichiometric characteristics of different root orders for three dominant tree species in subalpine forests of western Sichuan, China. Chinese J Appl Ecol 26:363–369
Valenzuela-Estrada LR, Vera-Caraballo V, Ruth LE, Eissenstat DM (2008) Root anatomy, morphology, and longevity among root orders in Vaccinium corymbosum (Ericaceae). Am J Bot 95:1506–1514
Valls M, De Lorenzo V (2002) Exploiting the genetic and biochemical capacities of bacteria for the remediation of heavy metal pollution. FEMS Microbiol Rev 26:327–338
Valverde-Barrantes OJ, Smemo KA, Blackwood CB (2015) Fine root morphology is phylogenetically structured, but nitrogen is related to the plant economics spectrum in temperate trees. Funct Ecol 29:796–807
Vanderbilt KL, White CS, Hopkins O, Craig JA (2008) Aboveground decomposition in arid environments: results of a long-term study in central New Mexico. J Arid Environ 72:696–709
Vogt KA, Dahlgren R, Ugolini F, Zabowski D, Moore EE, Zasoski R (1987) Aluminum, Fe, Ca, Mg, K, Mn, Cu, Zn and P in above- and belowground biomass. II. Pools and circulation in a subalpine Abies amabilis stand. Biogeochemistry 4:277–294
Wallace A, Romney EM, Alexander GV, Kinnear J (1977) Phytotoxicity and some interactions of the essential trace metals iron, manganese, molybdenum, zinc, copper, and boron. Commun Soil Sci Plant Anal 8:741–750
Wang JJ, Guo YY, Guo DL, Yin SL, Kong DL, Liu YS, Zeng H (2012) Fine root mercury heterogeneity: metabolism of lower-order roots as an effective route for mercury removal. Environ Sci Technol 46:769–777
Wang W, Zhang X, Tao N, Ao D, Zeng W, Qian Y, Zeng H (2014) Effects of litter types, microsite and root diameters on litter decomposition in Pinus sylvestris plantations of northern China. Plant Soil 374:677–688
Wei T, Dong Z, Kang S, Zong C, Rostami M, Shao Y (2019) Atmospheric deposition and contamination of trace elements in snowpacks of mountain glaciers in the northeastern Tibetan Plateau. Sci Total Environ 689:754–764
Wu F, Yang W, Zhang J, Deng R (2010) Litter decomposition in two subalpine forests during the freeze-thaw season. Acta Oecologica 36:135–140
Xu ZF, Pu XZ, Yin HJ, Zhao CZ, Liu Q, Wu FZ (2012) Warming effects on the early decomposition of three litter types, Eastern Tibetan Plateau, China. Eur J Soil Sci 63:360–367
Xu Z, Zhao C, Yin H, Liu Q (2015) Warming and forest management interactively affect the decomposition of subalpine forests on the eastern Tibetan Plateau: a four-year experiment. Geoderma 239–240:223–228
Xu ZF, Chen L, Tang S, Zhuang L, Yang W, Tu L, Tan B, Zhang L (2016) Sex-specific responses to Pb stress in Populus deltoides: root architecture and Pb translocation. Trees 30:2019–2027
Yue K, Yang W, Peng Y, Zhang C, Huang C, Xu Z, Tan B, Wu F (2016) Dynamics of multiple metallic elements during foliar litter decomposition in an alpine forest river. Ann for Sci 73:547–557
Yue K, Yang W, Tan B, Peng Y, Huang C, Xu Z, Ni X, Yang Y, Zhou W, Zhang L, Wu F (2019) Immobilization of heavy metals during aquatic and terrestrial litter decomposition in an alpine forest. Chemosphere 216:419–427
Yue K, Ni X, Fornara DA, Peng Y, Liao S, Tan S, Wang D, Wu F, Yang Y (2020) Dynamics of calcium, magnesium, and manganese during litter decomposition in alpine forest aquatic and terrestrial ecosystems. Ecosystems 24:516–529
Zhang X, Wang W (2015) The decomposition of fine and coarse roots: their global patterns and controlling factors. Sci Rep 5:1–10
Zhuang L, Tang S, Yang W, Tu L, Yin H, Bo T, Xu Z (2016) Fine root morphology of different branch orders of three dominant subalpine tree species in western Sichuan. Chinese J Appl Environ Biol 22:618–622
Zhuang L, Yang W, Wu F, Tan B, Zhang L, Yang K, He R, Li Z, Xu Z (2018) Diameter-related variations in root decomposition of three common subalpine tree species in southwestern China. Geoderma 311:1–8
Funding
This work was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (32071745, 32001165, 31870602, 31901295, and 31800519), the Program of Sichuan Excellent Youth Sci-Tech Foundation (2020JDJQ0052), the Applied Basic Research Program of Sichuan of China (2021YJ0340).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors have no relevant financial or non-financial interest to disclose.
Additional information
Responsible Editor: Justin B. Richardson
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Ren, Y., Peng, Q., You, C. et al. Diameter-associated dynamics of multiple metallic elements during the root decomposition of two dominant subalpine trees in southwestern China. Biogeochemistry 164, 415–430 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10533-023-01043-w
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10533-023-01043-w