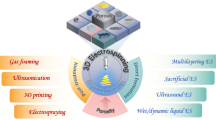
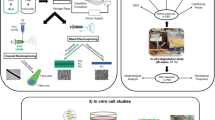
Abstract
Purpose
Bone tissue engineering aims to create a three-dimensional, matured, angiogenic scaffold with a suitable thickness that resembles a natural bone matrix. On the other hand, electrospun fibers, which researchers have considered due to their good biomimetic properties, are considered 2D structures. Due to the highly interwoven network and small pore size, achieving the desired thickness for bone lesions has always been challenging. In bone tissue engineering, bioreactors are crucial for achieving initial tissue maturity and introducing certain signals as flow parameters for differentiation.
Methods
In the present study, Human bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells (hBMSCs) and human umbilical vein endothelial cells (HUVECs) were co-cultured in a perfusion bioreactor on treated (improved pore size by gelatin sacrification and subsequent ultrasonication) 5-layer polycaprolactone-nano hydroxyapatite-nano zinc oxide (T-PHZ) scaffolds to investigate osteogenesis and angiogenesis simultaneously. The flow parameters and stresses on the cells were studied using two patterns of parallel and vertical scaffolds relative to the flow of the culture medium. In dynamic vertical flow (DVF), the culture medium flows perpendicular to the scaffolds, and in dynamic parallel flow (DPF), the culture medium flows parallel to the scaffolds. In all evaluations, static samples (S) served as the control group.
Results
Live/dead, and MTT assays demonstrated the biocompatibility of the 5-layer scaffolds and the suitability of the bioreactor's functional conditions. ALP activity, EDAX analysis, and calcium content measurements exhibited greater osteogenesis for T-PHZ scaffolds in DVF conditions. Calcium content increased by a factor of 2.2, 1.8, and 1.6 during days 7 to 14 of culture under DVF, DPF and S conditions, respectively. After 21 days of co-culturing, an immunohistochemistry (IHC) test was performed to investigate angiogenesis and osteogenesis. Five antibodies were investigated in DVF, CD31, VEGFA, and VEGFR2 for angiogenesis, osteocalcin, and RUNX2 for osteogenesis. Compressive stress applied in DVF mode has increased osteogenic activity compared to DPF.
Conclusion
The results indicated the development of ideal systems for osteogenesis and angiogenesis on the treated multilayer electrospun scaffolds in the perfusion bioreactor.
Graphical abstract















Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abhinand CS, Raju R, Soumya SJ, Arya PS, Sudhakaran PR (2016) VEGF-A/VEGFR2 signaling network in endothelial cells relevant to angiogenesis. J Cell Commun Signal 10(4):347–354. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12079-016-0352-8
Ameer JM, Pr AK, Kasoju N (2019) Strategies to tune electrospun scaffold porosity for effective cell response in tissue engineering. J Funct Biomater 10(3):30. https://doi.org/10.3390/jfb10030030
Ashinsky BG, Gullbrand SE, Bonnevie ED, Wang C, Kim DH, Han L, Mauck RL, Smith HE (2020) Sacrificial fibers improve matrix distribution and micromechanical properties in a tissue-engineered intervertebral disc. Acta Biomater 111:232–241. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.actbio.2020.05.019
Baker BM, Gee AO, Metter RB, Nathan AS, Marklein RA, Burdick JA, Mauck RL (2008) The potential to improve cell infiltration in composite fiber-aligned electrospun scaffolds by the selective removal of sacrificial fibers. Biomaterials 29(15):2348–2358. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biomaterials.2008.01.032
Bancroft GN, Sikavitsas VI, Van Den Dolder J, Sheffield TL, Ambrose CG, Jansen JA, Mikos AG (2002) Fluid flow increases mineralized matrix deposition in 3D perfusion culture of marrow stromal osteoblasts in a dose-dependent manner. Proc Natl Acad Sci 99(20):12600–12605. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.202296599
Battafarano G, Rossi M, De Martino V, Marampon F, Borro L, Secinaro A, Del Fattore A (2021) Strategies for bone regeneration: from graft to tissue engineering. Int J Mol Sci 22(3):1128. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms22031128
Bhaskar B, Owen R, Bahmaee H, Rao PS, Reilly GC (2018) Design and assessment of a dynamic perfusion bioreactor for large bone tissue engineering scaffolds. Appl Biochem Biotechnol 185(2):555–563. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12010-017-2671-5
Chen Z, Zhang Z, Ma X, Duan Z, Hui J, Zhu C, Zhang D, Fan D, Shang L, Chen F (2019) Newly designed human-like collagen to maximize sensitive release of BMP-2 for remarkable repairing of bone defects. Biomolecules 9(9):450. https://doi.org/10.3390/biom9090450
Chen S, John JV, McCarthy A, Xie J (2020) New forms of electrospun nanofiber materials for biomedical applications. J Mater Chem B 8(17):3733–3746
Chen J, Li X, Liu Q, Wu Y, Shu L, He Z, Ye C, Ma M (2021) Fabrication of multilayered electrospun poly (lactic-co-glycolic acid)/polyvinyl pyrrolidone+ poly (ethylene oxide) scaffolds and biocompatibility evaluation. J Biomed Mater Res A 109(8):1468–1478. https://doi.org/10.1002/jbm.a.37137
Gambari L, Amore E, Raggio R, Bonani W, Barone M, Lisignoli G, Grigolo B, Motta A, Grassi F (2019) Hydrogen sulfide-releasing silk fibroin scaffold for bone tissue engineering. Mater Sci Eng C 102:471–482. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.msec.2019.04.039
Gautam S, Sharma C, Purohit SD, Singh H, Dinda AK, Potdar PD, Chou C-F, Mishra NC (2021) Gelatin-polycaprolactone-nanohydroxyapatite electrospun nanocomposite scaffold for bone tissue engineering. Mater Sci Eng C 119:111588. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.msec.2020.111588
Harvestine J, Gonzalez-Fernandez T, Sebastian A, Hum N, Genetos D, Loots G, Leach J (2020) Osteogenic preconditioning in perfusion bioreactors improves vascularization and bone formation by human bone marrow aspirates. Sci Adv 6(7):eaay2387. https://doi.org/10.1126/sciadv.aay2387
He Y, Lin S, Ao Q, He X (2020) The co-culture of ASCs and EPCs promotes vascularized bone regeneration in critical-sized bone defects of cranial bone in rats. Stem Cell Res Ther 11(1):1–12. https://doi.org/10.1186/s13287-020-01858-6
Hodge J, Quint C (2019) The improvement of cell infiltration in an electrospun scaffold with multiple synthetic biodegradable polymers using sacrificial PEO microparticles. J Biomed Mater Res A 107(9):1954–1964. https://doi.org/10.1002/jbm.a.36706
Janaszak M, Wolfe R, Ahsan T (2016) Biomechanics in stem cell manufacturing. In: Stem cell manufacturing. Elsevier, Amsterdam, pp 27–42
Jia Y, Zhang C, Zheng X, Gao M (2021) Co-cultivation of progenitor cells enhanced osteogenic gene expression and angiogenesis potential in vitro. J Int Med Res 49(4):03000605211004024. https://doi.org/10.1177/03000605211004024
Kang H, Zeng Y, Varghese S (2018) Functionally graded multilayer scaffolds for in vivo osteochondral tissue engineering. Acta Biomater 78:365–377. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.actbio.2018.07.039
Karkan SF, Rahbarghazi R, Davaran S, Kaleybar LS, Khoshfetrat AB, Heidarzadeh M, Zolali E, Akbarzadeh A (2021) Electrospun polyurethane/poly (ɛ-caprolactone) nanofibers promoted the attachment and growth of human endothelial cells in static and dynamic culture conditions. Microvasc Res 133:104073. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.mvr.2020.104073
Kwak S, Haider A, Gupta KC, Kim S, Kang I-K (2016) Micro/nano multilayered scaffolds of PLGA and collagen by alternately electrospinning for bone tissue engineering. Nanoscale Res Lett 11(1):1–16. https://doi.org/10.1186/s11671-016-1532-4
Lai Y, Li Y, Cao H, Long J, Wang X, Li L, Li C, Jia Q, Teng B, Tang T (2019) Osteogenic magnesium incorporated into PLGA/TCP porous scaffold by 3D printing for repairing challenging bone defect. Biomaterials 197:207–219. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biomaterials.2019.01.013
Lee Y-U, Hayman D, Sprague EA, Han H-C (2010) Effects of axial stretch on cell proliferation and intimal thickness in arteries in organ culture. Cell Mol Bioeng 3(3):286–295. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12195-010-0128-9
Lee SJ, Kim ME, Nah H, Seok JM, Jeong MH, Park K, Kwon IK, Lee JS, Park SA (2019) Vascular endothelial growth factor immobilized on mussel-inspired three-dimensional bilayered scaffold for artificial vascular graft application: In vitro and in vivo evaluations. J Colloid Interface Sci 537:333–344. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jcis.2018.11.039
Li N, Zhou L, Xie W, Zeng D, Cai D, Wang H, Zhou C, Wang J, Li L (2019) Alkaline phosphatase enzyme-induced biomineralization of chitosan scaffolds with enhanced osteogenesis for bone tissue engineering. Chem Eng J 371:618–630
Lin X, Patil S, Gao Y-G, Qian A (2020) The bone extracellular matrix in bone formation and regeneration. Front Pharmacol 11:757. https://doi.org/10.3389/fphar.2020.00757
Liu X-W, Ma B, Zi Y, Xiang L-B, Han T-Y (2021) Effects of rutin on osteoblast MC3T3-E1 differentiation, ALP activity and Runx2 protein expression. Eur J Histochem. https://doi.org/10.4081/ejh.2021.3195
McCoy RJ, Jungreuthmayer C, O’Brien FJ (2012) Influence of flow rate and scaffold pore size on cell behavior during mechanical stimulation in a flow perfusion bioreactor. Biotechnol Bioeng 109(6):1583–1594. https://doi.org/10.1002/bit.24424
Mitra D, Whitehead J, Yasui OW, Leach JK (2017) Bioreactor culture duration of engineered constructs influences bone formation by mesenchymal stem cells. Biomaterials 146:29–39. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biomaterials.2017.08.044
Moghadam Deymeh S, Hashemi-Najafabadi S, Baghaban-Eslaminejad M, Bagheri F (2022) Use of gelatin as a sacrificial agent in combination with ultrasonication to improve cell infiltration and osteogenesis of nanofibrous PCL-nHA scaffolds for bone tissue engineering. Iran J Biotechnol 20(4):1–12. https://doi.org/10.30498/IJB.2022.305258.3154
Mokhtari-Jafari F, Amoabediny G, Dehghan MM, Abbasi Ravasjani S, Jabbari Fakhr M, Zamani Y (2021) Osteogenic and angiogenic synergy of human adipose stem cells and human umbilical vein endothelial cells cocultured in a modified perfusion bioreactor. Organogenesis. https://doi.org/10.1080/15476278.2021.1954769
Najdanović JG, Cvetković VJ, Stojanović ST, Vukelić-Nikolić MĐ, Živković JM, Najman SJ (2021) Vascularization and osteogenesis in ectopically implanted bone tissue-engineered constructs with endothelial and osteogenic differentiated adipose-derived stem cells. World J Stem Cells 13(1):91. https://doi.org/10.4252/wjsc.v13.i1.91
Nguyen BNB, Moriarty RA, Kamalitdinov T, Etheridge JM, Fisher JP (2017) Collagen hydrogel scaffold promotes mesenchymal stem cell and endothelial cell coculture for bone tissue engineering. J Biomed Mater Res A 105(4):1123–1131. https://doi.org/10.1002/jbm.a.36008
Nokhbatolfoghahaei H, Bohlouli M, Paknejad Z, Rad MR, Amirabad LM, Salehi-Nik N, Khani MM, Shahriari S, Nadjmi N, Ebrahimpour A (2020) Bioreactor cultivation condition for engineered bone tissue: effect of various bioreactor designs on extra cellular matrix synthesis. J Biomed Mater Res A 108(8):1662–1672. https://doi.org/10.1002/jbm.a.36932
Parham S, Kharazi AZ, Bakhsheshi-Rad HR, Ghayour H, Ismail AF, Nur H, Berto F (2020) Electrospun nano-fibers for biomedical and tissue engineering applications: a comprehensive review. Materials 13(9):2153. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma13092153
Peach CJ, Mignone VW, Arruda MA, Alcobia DC, Hill SJ, Kilpatrick LE, Woolard J (2018) Molecular pharmacology of VEGF-A isoforms: binding and signalling at VEGFR2. Int J Mol Sci 19(4):1264. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms19041264
Pedrini F, Hausen M, Gomes R, Duek E (2020) Enhancement of cartilage extracellular matrix synthesis in poly (PCL–TMC) urethane scaffolds: a study of oriented dynamic flow in bioreactor. Biotechnol Lett 42(12):2721–2734. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10529-020-02983-1
Perez-Puyana V, Villanueva P, Jiménez-Rosado M, de la Portilla F, Romero A (2021) Incorporation of elastin to improve polycaprolactone-based scaffolds for skeletal muscle via electrospinning. Polymers 13(9):1501. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym13091501
Rahmani A, Hashemi-Najafabadi S, Eslaminejad MB, Bagheri F, Sayahpour FA (2019) The effect of modified electrospun PCL-nHA-nZnO scaffolds on osteogenesis and angiogenesis. J Biomed Mater Res A 107(9):2040–2052. https://doi.org/10.1002/jbm.a.36717
Ramírez-Rodríguez GB, Pereira AR, Herrmann M, Hansmann J, Delgado-López JM, Sprio S, Tampieri A, Sandri M (2021) Biomimetic mineralization promotes viability and differentiation of human mesenchymal stem cells in a perfusion bioreactor. Int J Mol Sci 22(3):1447. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms22031447
Rauh J, Milan F, Günther K-P, Stiehler M (2011) Bioreactor systems for bone tissue engineering. Tissue Eng B 17(4):263–280. https://doi.org/10.1089/ten.TEB.2010.0612
Rego EB, Inubushi T, Kawazoe A, Miyauchi M, Tanaka E, Takata T, Tanne K (2011) Effect of PGE2 induced by compressive and tensile stresses on cementoblast differentiation in vitro. Arch Oral Biol 56(11):1238–1246. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.archoralbio.2011.05.007
Riehl BD, Lim JY (2015) Mechanical and physical regulation of cell behavior. In: Stem cell biology and tissue engineering in dental sciences. Elsevier, Amsterdam, pp 99–115
Salifu A, Lekakou C, Labeed F (2017) Multilayer cellular stacks of gelatin-hydroxyapatite fiber scaffolds for bone tissue engineering. J Biomed Mater Res A 105(3):779–789. https://doi.org/10.1002/jbm.a.35954
Sawyer SW, Zhang K, Horton JA, Soman P (2020) Perfusion-based co-culture model system for bone tissue engineering. AIMS Bioeng 7(2):91. https://doi.org/10.3934/bioeng.2020009
Schott NG, Friend NE, Stegemann JP (2021) Coupling osteogenesis and vasculogenesis in engineered orthopedic tissues. Tissue Eng B 27(3):199–214. https://doi.org/10.1089/ten.TEB.2020.0132
Sharma U, Pal D, Prasad R (2014) Alkaline phosphatase: an overview. Indian J Clin Biochem 29(3):269–278. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12291-013-0408-y
Shi F, Xiao D, Zhang C, Zhi W, Liu Y, Weng J (2021a) The effect of macropore size of hydroxyapatite scaffold on the osteogenic differentiation of bone mesenchymal stem cells under perfusion culture. Regener Biomater 8(6):rbab050. https://doi.org/10.1093/rb/rbab050
Shi H, Zhou Z, Li W, Fan Y, Li Z, Wei J (2021b) Hydroxyapatite based materials for bone tissue engineering: a brief and comprehensive introduction. Crystals 11(2):149. https://doi.org/10.3390/cryst11020149
Stewart S, Darwood A, Masouros S, Higgins C, Ramasamy A (2020) Mechanotransduction in osteogenesis. Bone Joint Res 9(1):1–14. https://doi.org/10.1302/2046-3758.91.BJR-2019-0043.R2
Tang Y, Hu M, Xu Y, Chen F, Chen S, Chen M, Qi Y, Shen M, Wang C, Lu Y (2020) Megakaryocytes promote bone formation through coupling osteogenesis with angiogenesis by secreting TGF-β1. Theranostics 10(5):2229. https://doi.org/10.7150/thno.40559
Tsai H-H, Yang K-C, Wu M-H, Chen J-C, Tseng C-L (2019) The effects of different dynamic culture systems on cell proliferation and osteogenic differentiation in human mesenchymal stem cells. Int J Mol Sci 20(16):4024. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms20164024
Udomluck N, Koh W-G, Lim D-J, Park H (2020) Recent developments in nanofiber fabrication and modification for bone tissue engineering. Int J Mol Sci 21(1):99. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms21010099
Vining KH, Mooney DJ (2017) Mechanical forces direct stem cell behaviour in development and regeneration. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol 18(12):728–742. https://doi.org/10.1038/nrm.2017.108
Wang JH, Li B (2010) Mechanics rules cell biology. BMC Sports Sci Med Rehabil 2(1):1–7. https://doi.org/10.1186/1758-2555-2-16
Yaghoobi M, Hashemi-Najafabadi S, Soleimani M, Vasheghani-Farahani E, Mousavi SM (2016) Osteogenic differentiation and mineralization on compact multilayer nHA-PCL electrospun scaffolds in a perfusion bioreactor. Iran J Biotechnol 14(2):41. https://doi.org/10.15171/ijb.1382
Yaghoobi M, Hashemi-Najafabadi S, Soleimani M, Vasheghani-Farahani E (2019) Osteogenic induction of human mesenchymal stem cells in multilayered electrospun scaffolds at different flow rates and configurations in a perfusion bioreactor. J Biosci Bioeng 128(4):495–503. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jbiosc.2019.03.015
Yamada S, Yassin MA, Schwarz T, Hansmann J, Mustafa K (2021) Induction of osteogenic differentiation of bone marrow stromal cells on 3D polyester-based scaffolds solely by subphysiological fluidic stimulation in a laminar flow bioreactor. J Tissue Eng 12:20417314211019376. https://doi.org/10.1177/20417314211019375
Yong KW, Choi JR, Choi JY, Cowie AC (2020) Recent advances in mechanically loaded human mesenchymal stem cells for bone tissue engineering. Int J Mol Sci 21(16):5816. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms21165816
Yu V, Damek-Poprawa M, Nicoll S, Akintoye SO (2009) Dynamic hydrostatic pressure promotes differentiation of human dental pulp stem cells. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 386(4):661–665. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bbrc.2009.06.106
Zhao F, Van Rietbergen B, Ito K, Hofmann S (2020) Fluid flow-induced cell stimulation in bone tissue engineering changes due to interstitial tissue formation in vitro. Int J Numer Methods Biomed Eng 36(6):e3342. https://doi.org/10.1002/cnm.3342
Acknowledgements
The authors would like to express their gratitude to Tarbiat Modares University and Royan Institute for their financial support of this study. Special appreciation is extended to Mohammad Jafari Atrabi (Center for Reproductive Medicine, Goettingen, Germany) and Mahmood Alipour (Royan institute, Iran) for their assistance with IHC tests.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Dr. SMD had the most contribution in this study that is the researches related to his PhD thesis. Drs. SH-N and FB are academic staff in Tarbiat Modares University at the field of Tissue Engineering. MB-E is academic staff in Royan Institute at the field of Tissue Engineering.
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Ethical approval
Yes.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Deymeh, S.M., Hashemi-Najafabadi, S., Baghaban-Eslaminejad, M. et al. Investigation of osteogenesis and angiogenesis in perfusion bioreactors using improved multi-layer PCL-nHA-nZnO electrospun scaffolds. Biotechnol Lett 45, 1223–1243 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10529-023-03411-w
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10529-023-03411-w