Abstract
Objectives
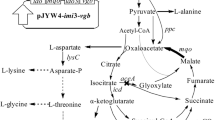
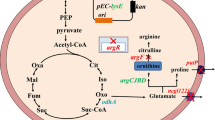
To explore an l-isoleucine (Ile)-induced biosensor for down-regulation of Ile synthesis pathway and enhancement of 4-hydroxyisoleucine (4-HIL) production in Corynebacterium glutamicum SN01.
Results
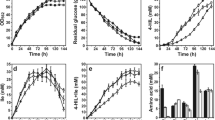
Four Ile-induced riboswitches (IleRSN) with different strength were screened from mutation library based on TPP riboswitch. Firstly, IleRSN were integrated into the chromosome of strain SN01 immediately upstream of ilvA gene. The 4-HIL titer of strains carrying PtacM-driven IleRS1 or IleRS3 (14.09 ± 1.07, 15.20 ± 0.93 g 4-HIL L−1) were similar with control strain S-D5I (15.73 ± 2.66 g 4-HIL L−1). Then, another copy of IleRS3-ilvA was integrated downstream of the chromosomal cg0963 gene in SN01-derived strain D-RS with down-regulated l-lysine (Lys) biosynthesis. The Ile supply and 4-HIL titer increased in ilvA two-copy strains KIRSA-3-D5I and KIRSA-3-9I, and Ile concentration was maintained less than 35 mmol L−1 under the control of IleRS3 during fermentation. The resulting strain KIRSA-3-9I produced 22.46 ± 0.96 g 4-HIL L−1.
Conclusion
The screened IleRS was effective in the dynamic down-regulation of Ile synthesis pathway in C. glutamicum, and IleRSN with different strength can be applied in various conditions.







Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
The data used to support the findings of this study are available from the corresponding author upon request.
References
Barrick JE, Corbino KA, Winkler WC, Nahvi A et al (2004) New RNA motifs suggest an expanded scope for riboswitches in bacterial genetic control. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 101(17):6421–6426. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.0308014101
Bédard ASV, Hien EDM, Lafontaine DA (2020) Riboswitch regulation mechanisms: RNA, metabolites and regulatory proteins. Biochim Biophys Acta Gene Regul Mech 1863(3):194501. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bbagrm.2020.194501
Broca C, Breil V, Cruciani-Guglielmacci C, Manteghetti M, Rouault C, Derouet M, Rizkalla S, Pau B, Petit P, Ribes G (2004) Insulinotropic agent ID-1001 (4-hydroxyisoleucine) activates insulin signaling in rat. Am J Physiol Endocrinol Metab 287(3):E463–E471. https://doi.org/10.1152/ajpendo.00163.2003
Chen Y, Liao Y, Kong W, Wang S (2020) ATP dynamic regeneration strategy for enhancing co-production of glutathione and S-adenosylmethionine in Escherichia coli. Biotechnol Lett 42(12):2581–2587. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10529-020-02989-9
Du P, Yan S, Qian X, Pan J, Zhang Z, Yu H, Xu J (2020) Engineering Bacillus subtilis isoleucine dioxygenase for efficient synthesis of (2S,3R,4S)-4-hydroxyisoleucine. J Agric Food Chem 68(49):14555–14563. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.jafc.0c06544
Fang Y, Zhang S, Wang J, Yin L, Zhang H, Wang Z, Song J, Hu X, Wang X (2021) Metabolic detoxification of 2-oxobutyrate by remodeling Escherichia coli acetate bypass. Metabolites 11(1):30. https://doi.org/10.3390/metabo11010030
Fowden L, Pratt HM, Smith A (1973) 4-Hydroxyisoleucine from seed of Trigonella foenum-graecum. Phytochemistry 12(7):1707–1711. https://doi.org/10.1016/0031-9422(73)80391-7
Fu M, Nie Y, Mu X, Xu Y, Xiao R (2014) A novel isoleucine dioxygenase and its expression in recombinant Escherichia coli for synthesis of 4-hydroxyisoleucine. Chem Ind Eng Prog 33(11):3037−3044. 1000-6613(2014)33:11<3037:XXYLAS>2.0.TX;2-1
Hallberg ZF, Su Y, Kitto RZ, Hammond MC (2017) Engineering and in vivo applications of riboswitches. Annu Rev Biochem 86:515–539. https://doi.org/10.1146/annurev-biochem-060815-014628
Hibi M, Kawashima T, Kedera T, Smirnov SV, Sokolov PM, Sugiyama M, Shimizu S, Yokozeki K, Ogawa J (2011) Characterization of Bacillus thuringiensis l-isoleucine dioxygenase for production of useful amino acids. Appl Environ Microbiol 77(19):6926–6930. https://doi.org/10.1128/aem.05035-11
Hong K, Zhang J, Jin B, Chen T, Wang Z (2022) Development and characterization of a glycine biosensor system for fine-tuned metabolic regulation in Escherichia coli. Microb Cell Fact 21(1):56. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12934-022-01779-4
Hu J, Tan Y, Li Y, Hu X, Xu D, Wang X (2013) Construction and application of an efficient multiple-gene-deletion system in Corynebacterium glutamicum. Plasmid 70(3):303–313. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.plasmid.2013.07.001
International Diabetes Federation (2021) IDF Diabetes Atlas, 10th edn. International Diabetes Federation, Brussels
Jang S, Jang S, Yang J, Seo SW, Jung GY (2018) RNA-based dynamic genetic controllers: development strategies and applications. Curr Opin Biotechnol 53:1–11. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.copbio.2017.10.005
Kamiura R, Toya Y, Matsuda F, Shimizu H (2019) Theophylline-induced riboswitch accurately regulates protein expression at low level in Escherichia coli. Biotechnol Lett 41(6–7):743–751. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10529-019-02672-8
Kivero AD, Novikova AE, Smirnov SV (2012) Modification of E. coli central metabolism to optimize the biotransformation of l-isoleucine into 4-hydroxyisoleucine by enzymatic hydroxylation. Appl Biochem Microbiol 48(7):639–644. https://doi.org/10.1134/S0003683812070034
Kodera T, Smirnov SV, Samsonova NN, Kozlov YI, Koyama R, Hibi M, Ogawa J, Yokozeki K, Shimuzu S (2009) A novel l-isoleucine hydroxylating enzyme, l-isoleucine dioxygenase from Bacillus thuringiensis, produces (2S,3R,4S)-4-hydroxyisoleucine. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 390(3):506–510. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bbrc.2009.09.126
Lai W, Shi F, Tan S, Liu H, Li Y, Xiang Y (2022) Dynamic control of 4-hydroxyisoleucine biosynthesis by multi-biosensor in Corynebacterium glutamicum. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 106:5105–5121. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00253-022-12034-6
Muranaka N, Sharma V, Nomura Y, Yokobayashi Y (2009) An efficient platform for genetic selection and screening of gene switches in Escherichia coli. Nucleic Acids Res 37(5):e39. https://doi.org/10.1093/nar/gkp039
Nomura Y, Yokobayashi Y (2007) Dual selection of a genetic switch by a single selection marker. Biosystems 90(1):115–120. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biosystems.2006.07.006
Ogawa J, Yamanaka H, Mano J, Doi Y, Horinouchi N, Kodera T, Nio N, Smirnov SV, Samsonova NN (2007) Synthesis of 4-hydroxyisoleucine by the aldolase-transaminase coupling reaction and basic characterization of the aldolase from Arthrobacter simplex AKU 626. Biosci Biotechnol Biochem 71(7):1607–1615. https://doi.org/10.1271/bbb.60655
Page K, Shaffer J, Lin S, Zhang M, Liu JM (2018) Engineering riboswitches in vivo using dual genetic selection and fluorescence-activated cell sorting. ACS Synth Biol 7(9):2000–2006. https://doi.org/10.1021/acssynbio.8b00099
Pang Q, Han H, Liu X, Wang Z, Liang Q, Hou J, Qi Q, Wang Q (2020) In vivo evolutionary engineering of riboswitch with high-threshold for N-acetylneuraminic acid production. Metab Eng 59:36–43. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ymben.2020.01.002
Pavlova N, Kaloudas D, Penchovsky R (2019) Riboswitch distribution, structure, and function in bacteria. Gene 708:38–48. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.gene.2019.05.036
Qian S, Cirino PC (2016) Using metabolite-responsive gene regulators to improve microbial biosynthesis. Curr Opin Chem Eng 52:190–214. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.coche.2016.08.020
Sauvaire Y, Petit P, Broca C, Manteghetti M, Baissac Y, Fernandez-Alvarez J, Gross R, Roye M, Leconte A, Gomis R (1998) 4-Hydroxyisoleucine: a novel amino acid potentiator of insulin secretion. Diabetes 47(2):206–210. https://doi.org/10.2337/diab.47.2.206
Schäfer A, Tauch A, Jäger W, Kalinowski J, Thierbach G, Pühler A (1994) Small mobilizable multi-purpose cloning vectors derived from the Escherichia coli plasmids pK18 and pK19: selection of defined deletions in the chromosome of Corynebacterium glutamicum. Gene 145(1):69–73. https://doi.org/10.1016/0378-1119(94)90324-7
Shi F, Niu T, Fang H (2015) 4-Hydroxyisoleucine production of recombinant Corynebacterium glutamicum ssp. lactofermentum under optimal corn steep liquor limitation. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 99(9):3851–3863. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00253-015-6481-9
Shi F, Zhang S, Li Y, Lu Z (2019) Enhancement of substrate supply and ido expression to improve 4-hydroxyisoleucine production in recombinant Corynebacterium glutamicum ssp. lactofermentum. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 103(10):4113–4124. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00253-019-09791-2
Smirnov SV, Samsonava NN, Novikova AE, Matrosov NG, Rushkevich NY, Kodera T, Ogawa J, Yamanaka H, Shimizu S (2007) A novel strategy for enzymatic synthesis of 4-hydroxyisoleucine: identification of an enzyme possessing HMKP (4-hydroxy-3-methyl-2-keto-pentanoate) aldolase activity. FEMS Microbiol Lett 273(1):70–77. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1574-6968.2007.00783.x
Tan S, Shi F, Liu H, Yu X, Wei S, Fan Z, Li Y (2020) Dynamic control of 4-hydroxyisoleucine biosynthesis by modified l-isoleucine biosensor in recombinant Corynebacterium glutamicum. ACS Synth Biol 9:2378–2389. https://doi.org/10.1021/acssynbio.0c00127
Wang Q, Ouazzani J, Sasaki NA, Potier P (2002) A practical synthesis of (2S,3R,4S)-4-hydroxyisoleucine, a potent insulinotropic α-amino acid from fenugreek. Eur J Org Chem 5:834–839. https://doi.org/10.1002/1099-0690(200203)2002:5%3c834::AID-EJOC834%3e3.0.CO;2-6
Wei M, Li G, Xie H, Yang W et al (2022) Sustainable production of 4-hydroxyisoleucine with minimised carbon loss by simultaneously utilising glucose and xylose in engineered Escherichia coli. Bioresour Technol 354:127196. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biortech.2022.127196
Winkler WC, Breaker RR (2003) Genetic control by metabolite-binding riboswitches. ChemBioChem 4(10):1024–1032. https://doi.org/10.1002/cbic.200300685
Winkler W, Nahvi A, Breaker RR (2002) Thiamine derivatives bind messenger RNAs directly to regulate bacterial gene expression. Nature 419(6910):952–956. https://doi.org/10.1038/nature01145
Wu Y, Zhu L, Li S, Chu H, Wang X, Xu W (2023) High content design of riboswitch biosensors: all-around rational module-by-module design. Biosens Bioelectron 220:114887. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bios.2022.114887
Zhang C, Li Y, Ma J, Liu Y et al (2018) High production of 4-hydroxyisoleucine in Corynebacterium glutamicum by multistep metabolic engineering. Metab Eng 49:287–298. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ymben.2018.09.008
Zhou L, Zeng A (2015) Exploring lysine riboswitch for metabolic flux control and improvement of l-lysine synthesis in Corynebacterium glutamicum. ACS Synth Biol 4(6):729–734. https://doi.org/10.1021/sb500332c
Funding
This work was supported by the program of State Key Laboratory of Food Science and Technology (SKLF-ZZA-201904).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
FS conceived and designed research. YX, RC and WL conducted experiments. YX and FS analyzed data. YX and FS wrote the manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Ethical approval
This article does not contain any studies with human participants or animals performed by any of the authors.
Consent to publication
All authors have read the manuscript and agreed to publish.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Xiang, Y., Chen, R., Shi, F. et al. Exploring l-isoleucine riboswitches for enhancing 4-hydroxyisoleucine production in Corynebacterium glutamicum. Biotechnol Lett 45, 1169–1181 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10529-023-03407-6
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10529-023-03407-6