Abstract
Objectives
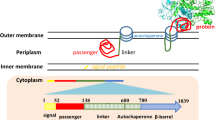
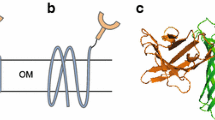
An efficient bacterial surface display system based on the anchoring motif derived from Escherichia coli (E. coli) outer membrane protease OmpT was developed in this study.
Results
Referring to the classical Lpp-OmpA (LOA) display system, the signal peptide and nine amino acids of mature Lpp were fused to the transmembrane domain comprising five β-strands of truncated OmpT to generate a novel Lpp-OmpT (LOT) display system. The C-terminal fusion strategy was used to fuse a small peptide (His tag) and red fluorescent protein (mCherry) to the C-terminus of LOT. Cell surface exposure of His tag and mCherry were compared between the LOA and LOT display systems. E. coli expressing LOT-His tag adsorbed more Cu2+ than E. coli expressing LOA-His tag. E. coli expressing both LOT-mCherry-His tag and LOA-mCherry-His tag adhered to Cu2+ chelating sepharose beads, and adhered cells could be dissociated from the beads after excess Cu2+ treatment. More importantly, compared with the LOA system, a higher amount of LOT-mCherry-His tag hybrid protein was demonstrated to be localized at the outer membrane by both fluorescence spectrophotometric determination of cell fractions and cell-surface immunofluorescence assay.
Conclusions
These results suggest that genetically modified OmpT can be used as a potential anchoring motif to efficiently and stably display polypeptides and proteins, and that the LOT system could be used in a variety of biotechnological and industrial processes.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Baek JH, Han MJ, Lee SH, Lee SY (2010) Enhanced display of lipase on the Escherichia coli cell surface, based on transcriptome analysis. Appl Environ Microbiol 76:971–973. https://doi.org/10.1128/AEM.02463-09
Daugherty PS, Chen G, Olsen MJ, Iverson BL, Georgiou G (1998) Antibody affinity maturation using bacterial surface display. Protein Eng 11:825–832
Fleetwood F, Andersson KG, Stahl S, Lofblom J (2014) An engineered autotransporter-based surface expression vector enables efficient display of Affibody molecules on OmpT-negative E. coli as well as protease-mediated secretion in OmpT-positive strains. Microb Cell Fact 13:179. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12934-014-0179-z
Francisco JA, Earhart CF, Georgiou G (1992) Transport and anchoring of beta-lactamase to the external surface of Escherichia coli. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 89:2713–2717
Georgiou G, Stephens DL, Stathopoulos C, Poetschke HL, Mendenhall J, Earhart CF (1996) Display of beta-lactamase on the Escherichia coli surface: outer membrane phenotypes conferred by Lpp’-OmpA’-beta-lactamase fusions. Protein Eng 9:239–247
Han MJ, Lee SH (2015) An efficient bacterial surface display system based on a novel outer membrane anchoring element from the Escherichia coli protein YiaT. FEMS Microbiol Lett 362:1–7. https://doi.org/10.1093/femsle/fnu002
Han MJ, Lee SY, Hong SH (2012) Comparative analysis of envelope proteomes in Escherichia coli B and K-12 strains. J Microbiol Biotechnol 22:470–478
Han L, Zhao Y, Cui S, Liang B (2018) Redesigning of microbial cell surface and its application to whole-cell biocatalysis and biosensors. Appl Biochem Biotechnol 185:396–418. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12010-017-2662-6
Hritonenko V, Stathopoulos C (2007) Omptin proteins: an expanding family of outer membrane proteases in Gram-negative Enterobacteriaceae. Mol Membr Biol 24:395–406. https://doi.org/10.1080/09687680701443822
Hu S, Kong J, Sun Z, Han L, Kong W, Yang P (2011) Heterologous protein display on the cell surface of lactic acid bacteria mediated by the s-layer protein. Microb Cell Fact 10:86. https://doi.org/10.1186/1475-2859-10-86
Hui CY, Guo Y, He QS, Peng L, Wu SC, Cao H, Huang SH (2010) Escherichia coli outer membrane protease OmpT confers resistance to urinary cationic peptides. Microbiol Immunol 54:452–459. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1348-0421.2010.00238.x
Hui C et al (2018a) Surface display of PbrR on Escherichia coli and evaluation of the bioavailability of lead associated with engineered cells in mice. Sci Rep 8:5685. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-018-24134-3
Hui CY, Guo Y, Yang XQ, Zhang W, Huang XQ (2018b) Surface display of metal binding domain derived from PbrR on Escherichia coli specifically increases lead(II) adsorption. Biotechnol Lett 40:837–845. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10529-018-2533-4
Hui CY, Guo Y, Zhang W, Huang XQ (2018c) Rapid monitoring of the target protein expression with a fluorescent signal based on a dicistronic construct in Escherichia coli. AMB Express 8:81. https://doi.org/10.1186/s13568-018-0612-5
Ko KC, Lee B, Cheong DE, Han Y, Choi JH, Song JJ (2015) Bacterial cell surface display of a nultifunctional cellulolytic enzyme screened from a bovine rumen metagenomic resource. J Microbiol Biotechnol 25:1835–1841. https://doi.org/10.4014/jmb.1507.07030
Kojima M, Akahoshi T, Okamoto K, Yanase H (2012) Expression and surface display of Cellulomonas endoglucanase in the ethanologenic bacterium Zymobacter palmae. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 96:1093–1104. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00253-012-4424-2
Lee H et al (2013) Expression of a lipase on the cell-surface of Escherichia coli using the OmpW anchoring motif and its application to enantioselective reactions. Biotechnol Lett 35:1677–1683. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10529-013-1260-0
Maruthamuthu MK, Selvamani V, Nadarajan SP, Yun H, Oh YK, Eom GT, Hong SH (2018) Manganese and cobalt recovery by surface display of metal binding peptide on various loops of OmpC in Escherichia coli. J Ind Microbiol Biotechnol 45:31–41. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10295-017-1989-x
Michon C, Langella P, Eijsink VG, Mathiesen G, Chatel JM (2016) Display of recombinant proteins at the surface of lactic acid bacteria: strategies and applications. Microb Cell Fact 15:70. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12934-016-0468-9
Mrabet NT (1992) One-step purification of Actinoplanes missouriensis D-xylose isomerase by high-performance immobilized copper-affinity chromatography: functional analysis of surface histidine residues by site-directed mutagenesis. Biochemistry 31:2690–2702
Park TJ, Heo NS, Yim SS, Park JH, Jeong KJ, Lee SY (2013) Surface display of recombinant proteins on Escherichia coli by BclA exosporium of Bacillus anthracis. Microb Cell Fact 12:81. https://doi.org/10.1186/1475-2859-12-81
Rutherford N, Mourez M (2006) Surface display of proteins by gram-negative bacterial autotransporters. Microb Cell Fact 5:22. https://doi.org/10.1186/1475-2859-5-22
Salema V, Fernandez LA (2017) Escherichia coli surface display for the selection of nanobodies. Microb Biotechnol 10:1468–1484. https://doi.org/10.1111/1751-7915.12819
Schuurmann J, Quehl P, Festel G, Jose J (2014) Bacterial whole-cell biocatalysts by surface display of enzymes: toward industrial application. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 98:8031–8046. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00253-014-5897-y
Shao X, Jiang M, Yu Z, Cai H, Li L (2009) Surface display of heterologous proteins in Bacillus thuringiensis using a peptidoglycan hydrolase anchor. Microb Cell Fact 8:48. https://doi.org/10.1186/1475-2859-8-48
Shimazu M, Mulchandani A, Chen W (2001) Cell surface display of organophosphorus hydrolase using ice nucleation protein. Biotechnol Prog 17:76–80. https://doi.org/10.1021/bp0001563
Sousa C, Cebolla A, de Lorenzo V (1996) Enhanced metalloadsorption of bacterial cells displaying poly-His peptides. Nat Biotechnol 14:1017–1020. https://doi.org/10.1038/nbt0896-1017
Stathopoulos C, Georgiou G, Earhart CF (1996) Characterization of Escherichia coli expressing an Lpp’OmpA(46-159)-PhoA fusion protein localized in the outer membrane. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 45:112–119
Tabor S, Richardson CC (1985) A bacteriophage T7 RNA polymerase/promoter system for controlled exclusive expression of specific genes. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 82:1074–1078
Thulasingam M, Damodharan S, Madhana Vigneshwari G, Pandaranayaka PJE, Elizabeth Hanna L, Usha R, Krishnaswamy S (2017) Characterization of Salmonella typhi OmpC and OmpF porins engineered with HIV-gp41 epitope on the surface loops. Proteins 85:657–664. https://doi.org/10.1002/prot.25246
Timari S, Kallay C, Osz K, Sovago I, Varnagy K (2009) Transition metal complexes of short multihistidine peptides. Dalton Trans 11:1962–1971. https://doi.org/10.1039/b816498c
van Bloois E, Winter RT, Kolmar H, Fraaije MW (2011) Decorating microbes: surface display of proteins on Escherichia coli. Trends Biotechnol 29:79–86. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tibtech.2010.11.003
Van Deventer JA, Wittrup KD (2014) Yeast surface display for antibody isolation: library construction, library screening, and affinity maturation. Methods Mol Biol 1131:151–181. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-1-62703-992-5_10
Vandeputte-Rutten L, Kramer RA, Kroon J, Dekker N, Egmond MR, Gros P (2001) Crystal structure of the outer membrane protease OmpT from Escherichia coli suggests a novel catalytic site. EMBO J 20:5033–5039. https://doi.org/10.1093/emboj/20.18.5033
Verhoeven GS, Alexeeva S, Dogterom M, den Blaauwen T (2009) Differential bacterial surface display of peptides by the transmembrane domain of OmpA. PLoS ONE 4:e6739. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0006739
Xu Z, Lee SY (1999) Display of polyhistidine peptides on the Escherichia coli cell surface by using outer membrane protein C as an anchoring motif. Appl Environ Microbiol 65:5142–5147
Yang Z, Liu Q, Wang Q, Zhang Y (2008) Novel bacterial surface display systems based on outer membrane anchoring elements from the marine bacterium Vibrio anguillarum. Appl Environ Microbiol 74:4359–4365. https://doi.org/10.1128/AEM.02499-07
Yim SS, An SJ, Han MJ, Choi JW, Jeong KJ (2013) Isolation of a potential anchoring motif based on proteome analysis of Escherichia coli and its use for cell surface display. Appl Biochem Biotechnol 170:787–804. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12010-013-0236-9
Yoon SH et al (2012) Comparative multi-omics systems analysis of Escherichia coli strains B and K-12. Genome Biol 13:R37. https://doi.org/10.1186/gb-2012-13-5-r37
Acknowledgements
This research was supported by Natural Science Foundation of Guangdong Province (2015A030313838), Science and Technology Program of Shenzhen (JCYJ20180306170237563).
Supporting information
Supplementary Fig. 1—The cloning/expression region of pLT (A), pLA (B), pLTR (C), pLAR (D), plac-LTR (E), and plac-LAR (F).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Hui, Cy., Guo, Y., Liu, L. et al. Development of a novel bacterial surface display system using truncated OmpT as an anchoring motif. Biotechnol Lett 41, 763–777 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10529-019-02676-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10529-019-02676-4