Abstract
Objectives
To improve target protein production by manipulating expression levels of alanine racemase in Bacillus licheniformis.
Results
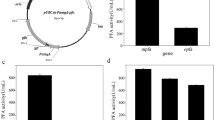
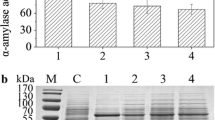
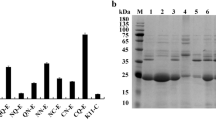
The gene of dal was identified to be responsible for alanine racemase function. Based on the selection marker of dal, a food-grade expression system was constructed in B. licheniformis, and effects of different dal expression levels mediated by promoters on α-amylase production were investigated. The highest α-amylase activity (155 U/ml) was obtained in BL10D/pP43SAT-PtetDal, increased by 27% compared with that of the control strain BL10/pP43SAT in tetracycline-based system (123 U/ml). Moreover, the dal transcriptional level was not correlated positively with that of amyL.
Conclusions
A food-grade system for high-level production of α-amylase was constructed in B. licheniformis, revealing that expression levels of selection marker significantly affected target protein production.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Cai D, Wei X, Qiu Y, Chen Y, Chen J, Wen Z, Chen S (2016) High-level expression of nattokinase in Bacillus licheniformis by manipulating signal peptide and signal peptidase. J Appl Microbiol 121:704–712
Cai D, He P, Lu X, Zhu C, Zhu J, Zhan Y, Wang Q, Wen Z, Chen S (2017a) A novel approach to improve poly-gamma-glutamic acid production by NADPH regeneration in Bacillus licheniformis WX-02. Sci Rep 7:43404
Cai D, Wang H, He P, Zhu C, Wang Q, Wei X, Nomura CT, Chen S (2017b) A novel strategy to improve protein secretion via overexpression of the SppA signal peptide peptidase in Bacillus licheniformis. Microb Cell Fact 16:70
Chen J, Fu G, Gai Y, Zheng P, Zhang D, Wen J (2015a) Combinatorial Sec pathway analysis for improved heterologous protein secretion in Bacillus subtilis: identification of bottlenecks by systematic gene overexpression. Microb Cell Fact 14:92
Chen J, Gai Y, Fu G, Zhou W, Zhang D, Wen J (2015b) Enhanced extracellular production of alpha-amylase in Bacillus subtilis by optimization of regulatory elements and over-expression of PrsA lipoprotein. Biotechnol Lett 37:899–906
Chen J, Jin Z, Gai Y, Sun J, Zhang D (2017) A food-grade expression system for d-psicose 3-epimerase production in Bacillus subtilis using an alanine racemase-encoding selection marker. Bioresour Bioprocess 4:9
Cheng J, Guan C, Cui W, Zhou L, Liu Z, Li W, Zhou Z (2016) Enhancement of a high efficient autoinducible expression system in Bacillus subtilis by promoter engineering. Protein Expr Purif 127:81–87
He W, Mu W, Jiang B, Yan X, Zhang T (2016) Construction of a food grade recombinant Bacillus subtilis based on replicative plasmids with an auxotrophic marker for biotransformation of d-fructose to d-allulose. J Agric Food Chem 64:3243–3250
Kang Z, Yang S, Du G, Chen J (2014) Molecular engineering of secretory machinery components for high-level secretion of proteins in Bacillus species. J Ind Microbiol Biotechnol 41:1599–1607
Pfleger BF, Pitera DJ, Smolke CD, Keasling JD (2006) Combinatorial engineering of intergenic regions in operons tunes expression of multiple genes. Nat Biotechnol 24:1027–1032
Sasaki Y, Ito Y, Sasaki T (2004) ThyA as a selection marker in construction of food-grade host-vector and integration systems for Streptococcus thermophilus. Appl Environ Microbiol 70:1858–1864
Sokarda Slavic M, Pesic M, Vujcic Z, Bozic N (2016) Overcoming hydrolysis of raw corn starch under industrial conditions with Bacillus licheniformis ATCC 9945a alpha-amylase. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 100:2709–2719
Wei X, Zhou Y, Chen J, Cai D, Wang D, Qi G, Chen S (2015) Efficient expression of nattokinase in Bacillus licheniformis: host strain construction and signal peptide optimization. J Ind Microbiol Biotechnol 42:287–295
Xia Y, Chen W, Zhao J, Tian F, Zhang H, Ding X (2007) Construction of a new food-grade expression system for Bacillus subtilis based on theta replication plasmids and auxotrophic complementation. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 76:643–650
Yang S, Kang Z, Cao W, Du G, Chen J (2016) Construction of a novel, stable, food-grade expression system by engineering the endogenous toxin-antitoxin system in Bacillus subtilis. J Biotechnol 219:40–47
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by the National Science & Technology Pillar Program during the twelfth five-year plan period (2013AA102801-52), the Science and Technology Program of Wuhan (20160201010086).
Supporting information
Supplementary Table 1—The strains and plasmids used in this study.
Supplementary Table 2—The primers used in this research.
Supplementary Fig. 1—Confirmation of gene deficient strains by PCR amplification.
Supplementary Fig. 2—Effects of dal or alrB deficiency on the cell growth in the medium with or without d-alanine.
Supplementary Fig. 3—The flow chart for construction of the co-expression vectors.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
He, P., Zhang, Z., Cai, D. et al. High-level production of α-amylase by manipulating the expression of alanine racamase in Bacillus licheniformis . Biotechnol Lett 39, 1389–1394 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10529-017-2359-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10529-017-2359-5