Abstract
Objectives
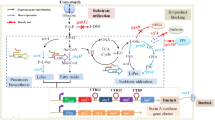
To investigate the role of maltose stearic acid ester (MSAE) for improving raw-starch-digesting glucoamylase (RSDG) production by Aspergillus niger F-01 and its regulatory mechanism.
Results
RSDG activity was enhanced 8.3-fold by adding 5 g MSAE to 1 l basal medium at the beginning of the culture. RSDG biosynthesis nearly ceased by adding 100 μg actinomycin D/ml or 50 μg cycloheximide/ml in a 48 h culture in the basal medium. RSDG biosynthesis was restarted by adding MSAE in the culture repressed by actinomycin D. No revival of RSDG synthesis was observed by adding MSAE in the culture repressed by cycloheximide.
Conclusions
MSAE improved RSDG production in A. niger by inducing the transcription of RSDG.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abe J, Bergmann FW, Obata K, Hizukuri S (1988) Production of the raw-starch digesting amylase of Aspergillus sp. K-27. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 27:447–450
Biely P, Kratki Z, Vrsanska M, Urmanicova D (1980) Induction and inducers of endo-1,4-β-xylanase in the yeast Cryptococcus albidus. Eur J Biochem 108:323–329
Cinelli BA, Castilho LR, Freire DMG, Castro AM (2015) A brief review on the emerging technology of ethanol production by cold. Fuel 150:721–729
Favaro L, Viktor MJ, Rose SH, Viljoen-Bloom M, van Zyl WH, Basaglia M, Cagnin L, Casella S (2015) Consolidated bioprocessing of starchy substrates into ethanol by industrial Saccharomyces cerevisiae strains secreting fungal amylases. Biotechnol Bioeng 112:1751–1760
Hidalgo-Lara ME, Amelia GS, Montes-Horcasitas MC (2005) β-Methyl-xyloside: positive effect on xylanase induction in Cellulomonas flavigena. J Ind Microbiol Biotechnol 32:345–348
Kurasawa T, Yachi M, Suto M, Kamagata Y, Takao S, Tomita F (1992) Induction of cellulase by gentiobiose and its sulfur-containing analog in Penicillium purpurogenum. Appl Environ Microbiol 58:106–110
Moshi AP, Hosea KMM, Emrode E, Gashaw M, Önnby L, Nges IA (2016) Production of raw starch-degrading enzyme by Aspergillus sp. and its use in conversion of inedible wild cassava flour to bioethanol. J Biosci Bioeng 121:457–463
Pou-Llinas J, Driguez H (1987) d-Xylose as inducer of the xylan-degrading enzyme system in the yeast Pullularia pullulans. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 27:134–138
Rajoka MI, Yasmeen A (2005) Induction and production studies of a novel glucoamylase of Aspergillus niger. World J Microbiol Biotechnol 21:179–187
Sun H, Zhao P, Ge X, Xia Y, Hao Z, Liu J, Peng M (2010) Recent advances in microbial raw starch degrading enzymes. Appl Biochem Biotech 160:988–1003
Wang S, Liu G, Yu J, Tian S, Huang B, Xing M (2013) RNA interference with carbon catabolite repression in Trichoderma koningii for enhancing cellulase production. Enzyme Microb Technol 53:104–109
Waterschoot J, Gomand SV, Fierens E, Delcour JA (2015) Production, structure, physicochemical and functional properties of maize, cassava, wheat, potato and rice starches. Starch 67:14–29
Acknowledgements
This study was supported by National Nonprofit Institute Research Grant (CATAS-ITBB 2015RC06) and National Natural Science Fund of China (31000029).
Supporting information
Supplementary Table 1—Primers used for qPCR.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Sun, H., Peng, M. Improvement of glucoamylase production for raw-starch digestion in Aspergillus niger F-01 by maltose stearic acid ester. Biotechnol Lett 39, 561–566 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10529-016-2277-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10529-016-2277-y