Abstract
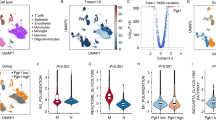
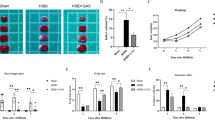
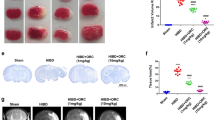
Promoting the M2 phenotype polarization of microglia is of great significance in alleviating hypoxic-ischemic encephalopathy (HIE). The umbilical artery blood sample was collected to evaluate the expression of cGAS, and the aberrant expressed cGAS was verified in the oxygen glucose deprivation (OGD) microglia which was established to mimic HIE in vitro. Then the regulating role of cGAS on the transformation of microglia M2 phenotype polarization and glycolysis was investigated. Moreover, the lactylation of cGAS in OGD treated microglia was evaluated by western blot. cGAS was found to be highly expressed in umbilical artery blood of HIE group, and OGD treated microglia. OGD interference activated microglia into M1 phenotype by enhancing CD86 and suppressing CD206 levels; meanwhile, the microglia in OGD group highly expressed IL-1β, iNOS and TNF-α, and lowly expressed IL-4, IL-10, and Arg-1. Inhibition of cGAS promotes the transformation of microglia from M1 to M2 phenotype. Meanwhile, OGD increased ECAR and decreased OCR to regulate glycolysis, cGAS deficiency inhibits glycolysis in OGD treated microglia. Moreover, the pan lysine lactylation (Pan-Kla) levels and lactated cGAS levels in microglia were upregulated in the OGD group. Lactate reversed the effects of cGAS knockdown on microglia polarization and glycolysis. The present study reveals that the cGAS-mediated neuron injury is associated with high level of cGAS lactylation. Inhibition of cGAS promotes the M2 phenotype polarization of microglia and suppress glycolysis. Thereby, targeting cGAS provides a new strategy for the development of therapeutic agents against HIE.





Similar content being viewed by others
Data Availability
All data included in this study are available upon request by contact with the corresponding author.
References
Al MA, Yu H, Sharmeen R, McCullough LD, Liu F (2021) IRF5 signaling in phagocytes is detrimental to neonatal hypoxic ischemic encephalopathy. Transl Stroke Res 12:602–614
Arvin KL, Han BH, Du Y et al (2002) Minocycline markedly protects the neonatal brain against hypoxic-ischemic injury. Ann Neurol 52:54–61
Augusto-Oliveira M, Arrifano GP, Delage CI et al (2022) Plasticity Microglia Biol Rev 97:217–250
Cao DJ, Schiattarella GG, Villalobos E et al (2018) Cytosolic DNA sensing promotes macrophage transformation and governs myocardial ischemic injury. Circulation 137:2613–2634
Chen AN, Luo Y, Yang YH et al (2021) Lactylation, a novel metabolic reprogramming code: current status and prospects. Front Immunol 12:688910
Chen L, Huang L, Gu Y et al (2022) Lactate-lactylation hands between metabolic reprogramming and immunosuppression. Int J Mol Sci 23:11943
Deng Q, Wu C, Liu TC, Duan R, Yang L (2023) Exogenous lactate administration: a potential novel therapeutic approach for neonatal hypoxia-ischemia. Exp Neurol 367:114450
[Diagnostic criteria for neonatal hypoxic-ischemic encephalopathy]. Zhonghua Er Ke Za Zhi 2005;43:584
Du X, Xu Y, Chen S, Fang M (2020) Inhibited CSF1R alleviates ischemia injury via inhibition of microglia M1 polarization and NLRP3 pathway. Neural Plast 2020:8825954
Gamdzyk M, Doycheva DM, Araujo C et al (2020) cGAS/STING pathway activation contributes to delayed neurodegeneration in neonatal hypoxia-ischemia rat model: possible involvement of LINE-1. Mol Neurobiol 57:2600–2619
Greco P, Nencini G, Piva I et al (2020) Pathophysiology of hypoxic–ischemic encephalopathy: a review of the past and a view on the future. Acta Neurol Belg 120:277–288
Guo Y, Dai W, Zheng Y et al (2022) Mechanism and regulation of microglia polarization in intracerebral hemorrhage. Molecules 27:7080
Hammad IA, Blue NR, Allshouse AA et al (2020) Umbilical cord abnormalities and stillbirth. Obstet Gynecol 135:644–652
Han M, Zhang Z, Liu Z et al (2023) Three-dimensional-cultured MSC-derived exosome with hydrogel for cerebral ischemia repair. Biomater. Adv. 149:213396
Hao Y, Kacal M, Ouchida AT et al (2019) Targetome analysis of chaperone-mediated autophagy in cancer cells. Autophagy 15:1558–1571
Herz J, Köster C, Reinboth BS et al (2018) Interaction between hypothermia and delayed mesenchymal stem cell therapy in neonatal hypoxic-ischemic brain injury. Brain Behav Immun 70:118–130
Hu S, Gao Y, Gao R et al (2022) The selective STING inhibitor H-151 preserves myocardial function and ameliorates cardiac fibrosis in murine myocardial infarction. Int Immunopharmacol 107:108658
Jiang GL, Yang XL, Zhou HJ et al (2021) cGAS knockdown promotes microglial M2 polarization to alleviate neuroinflammation by inhibiting cGAS-STING signaling pathway in cerebral ischemic stroke. Brain Res Bull 171:183–195
Kennedy L, Glesaaen ER, Palibrk V et al (2022) Lactate receptor HCAR1 regulates neurogenesis and microglia activation after neonatal hypoxia-ischemia. eLife. https://doi.org/10.7554/eLife.76451
Kofler J, Wiley CA (2011) Microglia: key innate immune cells of the brain. SAGE Publications, Los Angeles, CA, pp 103–114
Kumagai S, Koyama S, Itahashi K et al (2022) Lactic acid promotes PD-1 expression in regulatory T cells in highly glycolytic tumor microenvironments. Cancer Cell 40:201–218
Le K, Song Z, Deng J et al (2020) Quercetin alleviates neonatal hypoxic-ischemic brain injury by inhibiting microglia-derived oxidative stress and TLR4-mediated inflammation. Inflamm Res 69:1201–1213
Li J, Chen L, Qin Q et al (2022b) Upregulated hexokinase 2 expression induces the apoptosis of dopaminergic neurons by promoting lactate production in Parkinson’s disease. Neurobiol Dis 163:105605
Li B, Dasgupta C, Huang L, Meng X, Zhang L (2020) MiRNA-210 induces microglial activation and regulates microglia-mediated neuroinflammation in neonatal hypoxic-ischemic encephalopathy. Cell Mol Immunol 17:976–991
Li Y, Lu B, Sheng L et al (2018) Hexokinase 2-dependent hyperglycolysis driving microglial activation contributes to ischemic brain injury. J Neurochem 144:186–200
Li X, Yang Y, Zhang B et al (2022a) Lactate metabolism in human health and disease. Signal Transduct Tar 7:305
Liao Y, Cheng J, Kong X et al (2020) HDAC3 inhibition ameliorates ischemia/reperfusion-induced brain injury by regulating the microglial cGAS-STING pathway. Theranostics 10:9644–9662
Liu G, Li M, Qian S et al (2022) Interleukin-35 exhibits protective effects in a rat model of hypoxic-ischemic encephalopathy through the inhibition of microglia-mediated inflammation. Transl Pediatr 11:651–662
Locatelli A, Lambicchi L, Incerti M et al (2020) Is perinatal asphyxia predictable? BMC Pregnancy Childb 20:186
Min X, Zhang X, Li Y et al (2020) HSPA12A unstabilizes CD147 to inhibit lactate export and migration in human renal cell carcinoma. Theranostics 10:8573–8590
Orihuela R, McPherson CA, Harry GJ (2016) Microglial M1/M2 polarization and metabolic states. Brit J Pharmacol 173:649–665
Pan RY, He L, Zhang J et al (2022) Positive feedback regulation of microglial glucose metabolism by histone H4 lysine 12 lactylation in Alzheimer’s disease. Cell Metab 34:634–648
Shaik S, Eyal F, Zayek M, Gulati R (2023) 663—Therapeutic hypothermia in preterm neonates with hypoxic ischemic encephalopathy. Am J Med Sci 365:S363–S364
Shu J, Jiang L, Wang M et al (2022) Human bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells-derived exosomes protect against nerve injury via regulating immune microenvironment in neonatal hypoxic-ischemic brain damage model. Immunobiology 227:152178
Tsai CF, Chen GW, Chen YC et al (2021) Regulatory Effects of quercetin on M1/M2 macrophage polarization and oxidative/antioxidative balance. Nutrients 14:67
Wang L, Pavlou S, Du X et al (2019) Glucose transporter 1 critically controls microglial activation through facilitating glycolysis. Mol Neurodegener 14:2
Wang C, Wang Q, Lou Y et al (2018) Salidroside attenuates neuroinflammation and improves functional recovery after spinal cord injury through microglia polarization regulation. J Cell Mol Med 22:1148–1166
Wu Z, Miao X, Jiang Y et al (2023) Cardiomyocytic cyclic GMP-AMP synthase is critical for the induction of experimental cardiac graft rejection. J Thoracic and Cardiovasc Surg. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jtcvs.2023.03.005
Xia DY, Yuan JL, Jiang XC et al (2021) SIRT1 promotes M2 microglia polarization via reducing ROS-mediated NLRP3 inflammasome signaling after subarachnoid hemorrhage. Front Immunol 12:770744
Yang X, Xu S, Qian Y, Xiao Q (2017) Resveratrol regulates microglia M1/M2 polarization via PGC-1α in conditions of neuroinflammatory injury. Brain Behav Immun 64:162–172
Yıldız EP, Ekici B, Tatlı B (2017) Neonatal hypoxic ischemic encephalopathy: an update on disease pathogenesis and treatment. Expert Rev Neurother 17:449–459
Yu S, Doycheva DM, Gamdzyk M et al (2021) Activation of MC1R with BMS-470539 attenuates neuroinflammation via cAMP/PKA/Nurr1 pathway after neonatal hypoxic-ischemic brain injury in rats. J Neuroinflamm 18:26
Zhang D, Tang Z, Huang H et al (2019) Metabolic regulation of gene expression by histone lactylation. Nature (London) 574:575–580
Zhang G, Ye M, Li M (2020) Deregulated miR-384 serves as a biomarker in neonatal hypoxic-ischemic encephalopathy and alleviates microglia-mediated neuroinflammation. Mol Biol Rep 47:5411–5420
Zhang SS, Zhu L, Peng Y et al (2022) Long-term running exercise improves cognitive function and promotes microglial glucose metabolism and morphological plasticity in the hippocampus of APP/PS1 mice. J Neuroinflamm 19:34
Zhao M, Yao Y, Du J et al (2021) 6-gingerol alleviates neonatal hypoxic-ischemic cerebral and white matter injury and contributes to functional recovery. Front Pharmacol 12:707772
Zhou D, Ji L, Chen Y (2020) TSPO modulates IL-4-induced microglia/macrophage M2 polarization via PPAR-gamma pathway. J Mol Neurosci 70:542–549
Zhou Y, Yang L, Liu X, Wang H (2022) Lactylation may be a novel posttranslational modification in inflammation in neonatal hypoxic-ischemic encephalopathy. Front Pharmacol 13:926802
Acknowledgements
Not applicable.
Funding
This study was supported by Medical Research Project of Yancheng Municipal Health Commission (No. YK2023113).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
All authors contributed to the study conception and design. Material preparation, data collection and analysis were performed by QG and CX. The first draft of the manuscript was written by LW and ZC, LW and ZC contribute equally as co first authors. All authors commented on previous versions of the manuscript. All authors read and approved the final manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors have no relevant financial or non-financial interests to disclose.
Ethical Approval
The study was approved by the Ethics Committee of Funing County People’s Hospital. A statement to confirm that all methods were carried out in accordance with relevant guidelines and regulations.
Consent to Participate
Written informed consent was obtained from their legal guardians.
Consent for publication
Not applicable.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
10528_2023_10631_MOESM1_ESM.jpg
Supplementary file1 (JPG 368 KB)—(A) The mRNA expression and (B) protein levels of cGAS in BV2 microglia under the OGD treatment increased in a time-dependent way.
10528_2023_10631_MOESM2_ESM.jpg
Supplementary file2 (JPG 1763 KB)—Lactylation of cGAS at lysine 162 site downregulates the cGAS protein levels to promote the transformation of microglia from M1 to M2.(A) The cGAS protein levels in microglia were measured by western blot with wild type (WT) or cGAS mutants (K162R). (B–I) Secretion of IL-1β, iNOS, TNF-α, IL-4, IL-10, and Arg-1 in microglia cells of each group. ***p<0.001
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Wang, L., Cai, Z., Gu, Q. et al. cGAS Deficiency Regulates the Phenotypic Polarization and Glycolysis of Microglia Through Lactylation in Hypoxic-Ischemic Encephalopathy Cell Model. Biochem Genet (2024). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10528-023-10631-2
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10528-023-10631-2