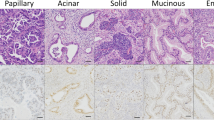
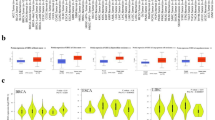
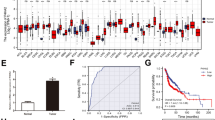
Abstract
Fibrinogen-like protein 1 (FGL1) is a proliferation- and metabolism-related factor secreted by the liver that is aberrantly expressed and functionally abnormal in human malignancies. However, the role of FGL1 in head and neck squamous cell carcinoma (HNSCC) remains unknown. We analysed FGL1 expression in HNSCC and its impact on patient survival using the TCGA database. The role of FGL1 in HNSCC cells was investigated by Cell Counting Kit-8, colony formation, and Transwell assays. In addition, we conducted in vivo experiments to assess the effect of FGL1 knockdown on tumour growth. We found that FGL1 was highly expressed in HNSCC and correlated with a poor prognosis. Downregulation of FGL1 expression inhibited the proliferation and invasion of HNSCC cells. Furthermore, mechanistic analysis revealed that FGL1 induced an epithelial-mesenchymal transition (EMT) phenotype and, thus, the malignant progression of HNSCC cells. Finally, xenograft models showed that FGL1 knockdown significantly inhibited EMT in HNSCC in vivo. Our study revealed that FGL1, an oncogene, promotes the malignant progression of HNSCC, providing new perspective on and potential therapeutic target for the treatment of HNSCC.





Similar content being viewed by others
Data Availability
The data that support the findings of this study are available from the corresponding author upon reasonable request.
References
Banyard J, Bielenberg DR (2015) The role of EMT and MET in cancer dissemination. Connect Tissue Res 56:403–413
Bie F, Wang G, Qu X, Wang Y, Huang C, Wang Y et al (2019) Loss of FGL1 induces epithelial–mesenchymal transition and angiogenesis in LKB1 mutant lung adenocarcinoma. Int J Oncol 55:697–707
Castilho RM, Squarize CH, Almeida LO (2017) Epigenetic modifications and Head and Neck Cancer: implications for Tumor Progression and Resistance to Therapy. Int J Mol Sci, 18
Gao M, Zhan YQ, Yu M, Ge CH, Li CY, Zhang JH et al (2014) Hepassocin activates the EGFR/ERK cascade and induces proliferation of L02 cells through the src-dependent pathway. Cell Signal 26:2161–2166
Greenberg AS, Coleman RA, Kraemer FB, McManaman JL, Obin MS, Puri V et al (2011) The role of lipid droplets in metabolic disease in rodents and humans. J Clin Invest 121:2102–2110
Liu Z, Ukomadu C (2008) Fibrinogen-like protein 1, a hepatocyte derived protein is an acute phase reactant. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 365:729–734
Lv Z, Cui B, Huang X, Feng HY, Wang T, Wang HF et al (2021) FGL1 as a Novel Mediator and Biomarker of Malignant Progression in Clear Cell Renal Cell Carcinoma. Front Oncol 11:756843
Michalopoulos GK, Bhushan B (2021) Liver regeneration: biological and pathological mechanisms and implications. Nat Rev Gastroenterol Hepatol 18:40–55
Mikheeva SA, Mikheev AM, Petit A, Beyer R, Oxford RG, Khorasani L et al (2010) TWIST1 promotes invasion through mesenchymal change in human glioblastoma. Mol Cancer 9:194
Mittal V (2018) Epithelial mesenchymal transition in Tumor Metastasis. Annu Rev Pathol 13:395–412
Mody MD, Rocco JW, Yom SS, Haddad RI, Saba NF (2021) Head and neck cancer. Lancet 398:2289–2299
Qian W, Zhao M, Wang R, Li H (2021) Fibrinogen-like protein 1 (FGL1): the next immune checkpoint target. J Hematol Oncol 14:147
Sun C, Gao W, Liu J, Cheng H, Hao J (2020) FGL1 regulates acquired resistance to Gefitinib by inhibiting apoptosis in non-small cell lung cancer. Respir Res 21:210
Sung H, Ferlay J, Siegel RL, Laversanne M, Soerjomataram I, Jemal A et al (2021) Global Cancer Statistics 2020: GLOBOCAN estimates of incidence and Mortality Worldwide for 36 cancers in 185 countries. CA Cancer J Clin 71:209–249
Tang XY, Xiong YL, Shi AP, Sun Y, Han Q, Lv Y et al (2022) The downregulation of fibrinogen-like protein 1 inhibits the proliferation of lung adenocarcinoma via regulating MYC-target genes. Transl Lung Cancer Res 11:404–419
Wang J, Sanmamed MF, Datar I, Su TT, Ji L, Sun J et al (2019) Fibrinogen-like protein 1 is a major Immune Inhibitory ligand of LAG-3. Cell 176:334–347
Wicki A, Lehembre F, Wick N, Hantusch B, Kerjaschki D, Christofori G (2006) Tumor invasion in the absence of epithelial-mesenchymal transition: podoplanin-mediated remodeling of the actin cytoskeleton. Cancer Cell 9:261–272
Woo SR, Turnis ME, Goldberg MV, Bankoti J, Selby M, Nirschl CJ et al (2012) Immune inhibitory molecules LAG-3 and PD-1 synergistically regulate T-cell function to promote tumoral immune escape. Cancer Res 72:917–927
Yan Q, Lin HM, Zhu K, Cao Y, Xu XL, Zhou ZY et al (2022) Immune Checkpoint FGL1 expression of circulating Tumor cells is Associated with Poor Survival in Curatively Resected Hepatocellular Carcinoma. Front Oncol 12:810269
Zhang Y, Qiao HX, Zhou YT, Hong L, Chen JH (2018) Fibrinogen–like–protein 1 promotes the invasion and metastasis of gastric cancer and is associated with poor prognosis. Mol Med Rep 18:1465–1472
Zhou L, Xu N, Shibata H, Saloura V, Uppaluri R (2021) Epigenetic modulation of immunotherapy and implications in head and neck cancer. Cancer Metastasis Rev 40:141–152
Funding
This study was funded by Natural Science Foundation of Fujian Province (2021J011373).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Zhiyong Pan and Linwei Mao and developed methods, interpreted results, and wrote the manuscript, Weiqun Hu revised the manuscript, Pingping Wang and Zhicong Zheng prepared Figs. 1, 2, 3, 4 and 5 and Enrun Lin and Jinqiao Huang prepared Table 1, and 2. All authors reviewed and approved the manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Ethics Approval
Our research has obtained permission from the Institutional Ethics Committee of Affiliated Hospital of Putian University.
Competing interests
The authors declare that they have no known competing financial interests or personal relationships that could have appeared to influence the work reported in this paper.
Additional information
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Pan, Z., Hu, W., Huang, J. et al. Increased FGL1 Expression Predicts Poor Prognosis and Promotes EMT in Head and Neck Squamous Cell Carcinoma. Biochem Genet (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10528-023-10545-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10528-023-10545-z