Abstract
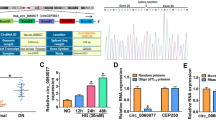
Patients suffering from terminal-stage diabetic nephropathy (DN) are commonly diagnosed with kidney failure. The condition of DN patients gets generally improved by long-chain noncoding RNA (LncRNA) since it regulates microRNA (miR). The current study analyzes the role played by NEAT2/miR-206 upon cell death of renal tubular epithelial cells (RTECs), high glucose (HG)-induced inflammation and oxidative stress in diabetic nephropathy (DN). The researcher used high glucose (HG) to treat HK-2 cells in in vitro conditions to establish the DN cell model. qRT-PCR was used to confirm the transfection effect whereas the researcher also tested NEAT2, nucleotide-binding oligomerization domain, leucine-rich repeat and pyrin domain containing (NLRP3), caspase-1, interleukin IL-1β, gasdermin D (GSMDD)-N, and miR-206. To analyze the proteins in caspase-1, IL-1β, GSMDD-N, and NLRP3, Western blot technique was performed. The technique is also used to observe the pyroptosis. To identify TNF-α, IL-6, MCP-9, NEAT2, miR‐206, and NLRP3, dual‐luciferase reporter assay was conducted through ELISA kit to emphasize the correlation that exists among the above-mentioned factors. NEAT2 has been confirmed to have bound with miR-206 through double luciferase report experiments as well as RNA immunoprecipitation (RIP). NEAT2, present in HK-2 cells, was induced by HG. So, if NEAT2 is knocked down, it would mitigate TNF-α, IL-6, and MCP-9 as well. Among the HK-2 cells intervened with HG, the overexpressed miR-206 that was transfected into cells was in alignment with the modifications introduced in inflammatory factors and cytokines after NEAT2 is knocked down. The current study concludes that if NEAT2 is upregulated, it has the potential to retreat the inhibition of miR-206 on inflammatory response as well pyroptosis. Further, by targeting miR-206, NEAT2 has the potential to enhance HG-induced HK-2 pyroptosis. This miR-206 is predicted to be a latent target in the clinical treatment of DN.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abdel Ghafar MT, Shalaby KH, Okda HI et al (2020) Assessment of two novel renal tubular proteins in type 2 diabetic patients with nephropathy. J Investig Med 68:748–755
Azizi S, Andohjerdi RB, Mohajerani H (2020) Evaluation of two types of vitamin D receptor gene morphism in patients with type 2 diabetes and obesity. Int J Adv Biol Biomed Res 8(1):86–91
Bhan A, Soleimani M, Mandal SS (2017) Long noncoding RNA and cancer: a new paradigm. Cancer Res 77:3965–3981
He Y, Hara H, Nunez G (2016) Mechanism and regulation of NLRP3 inflammasome activation. Trends Biochem Sci 41:1012–1021
Hughes MM, O’Neill LAJ (2018) Metabolic regulation of NLRP3. Immunol Rev 281:88–98
Ioannou K (2017) Diabetic nephropathy: is it always there? Assumptions, weaknesses and pitfalls in the diagnosis. Hormones (athens) 16:351–361
Kanwar YS, Sun L, Xie P, Liu FY, Chen S (2011) A glimpse of various pathogenetic mechanisms of diabetic nephropathy. Annu Rev Pathol 6:395–423
Khajeh H, Bahari A, Rashki A (2021) TCF7L2 polymorphisms in type 2 diabetes, insight from HRM and ARMS techniques. Int J Adv Biol Biomed Res 9(3):204–214
Kitada M, Koya D (2017) Diabetic nephropathy. Nihon Jinzo Gakkai Shi 59:38–42
Kor NM, Didarshetaban MB, Pour HRS (2013) Fenugreek (Trigonella foenum-graecum L.) as a valuable medicinal plant. Int J Adv Biol Biomed Res 1(8):922–931
Li JH, Liu S, Zhou H, Qu LH, Yang JH (2014) starBase v2.0: decoding miRNA-ceRNA, miRNA-ncRNA and protein-RNA interaction networks from large-scale CLIP-Seq data. Nucleic Acids Res 42:D92-97
Li S, Geng J, Xu X, Huang X, Leng D, Jiang D, Liang J, Wang C, Jiang D, Dai H (2016) miR-130b-3p modulates epithelial-mesenchymal crosstalk in lung fibrosis by targeting IGF-1. PLoS ONE 11:e0150418
Liu SX, Zheng F, Xie KL, Xie MR, Jiang LJ, Cai Y (2019) Exercise reduces insulin resistance in type 2 diabetes mellitus via mediating the LncRNA MALAT1/MicroRNA-382-3p/Resistin axis. Mol Ther Nucleic Acids 18:34–44
Liu B, Qiang L, Wang GD, Duan Q, Liu J (2019) LncRNA MALAT1 facilities high glucose induced endothelial to mesenchymal transition and fibrosis via targeting miR-145/ZEB2 axis. Eur Rev Med Pharmacol Sci 23(8):3478–3486
Liu SX, Zheng F, Xie KL, Xie MR, Jiang LJ, Cai Y (2019a) Exercise reduces insulin resistance in type 2 diabetes mellitus via mediating the LncRNA MALAT1/MicroRNA-382-3p/resistin axis. Mol Ther Nucleic Acids 18:34–44
Livak KJ, Schmittgen TD (2001) Analysis of relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and the 2(-Delta Delta C(T)) method. Methods 25:402–408
López-Campos JL, Arellano E, Calero C, Delgado A, Márquez E, Cejudo P, Ortega F, Rodríguez-Panadero F, Montes-Worboys A (2012) Determination of inflammatory biomarkers in patients with COPD: a comparison of different assays. BMC Med Res Methodol 31(12):40. https://doi.org/10.1186/1471-2288-12-40
Magee C, Grieve DJ, Watson CJ, Brazil DP (2017) Diabetic nephropathy: a tangled web to unweave. Cardiovasc Drugs Ther 31:579–592
Salmena L, Poliseno L, Tay Y, Kats L, Pandolfi PP (2011) A ceRNA hypothesis: the Rosetta Stone of a hidden RNA language? Cell 146:353–358
Samaeekia R, Adorno-Cruz V, Bockhorn J, Chang YF, Huang S, Prat A, Ha N, Kibria G, Huo D, Zheng H, Dalton R, Wang Y, Moskalenko GY, Liu H (2017) miR-206 inhibits stemness and metastasis of breast cancer by targeting MKL1/IL11 pathway. Clin Cancer Res 23:1091–1103
Song J, Su ZZ, Shen QM (2020) Long non-coding RNA MALAT1 regulates proliferation, apoptosis, migration and invasion via miR-374b-5p/SRSF7 axis in non-small cell lung cancer. Eur Rev Med Pharmacol Sci 24:1853–1862
St Laurent G, Wahlestedt C, Kapranov P (2015) The Landscape of long noncoding RNA classification. Trends Genet 31:239–251
Vande Walle L, Lamkanfi M (2016) Pyroptosis. Curr Biol 26:R568–R572
Wang F, Gao X, Zhang R, Zhao P, Sun Y, Li C (2019a) LncRNA TUG1 ameliorates diabetic nephropathy by inhibiting miR-21 to promote TIMP3-expression. Int J Clin Exp Pathol 12:717–729
Wang T, Zhang Q, Liu M, Lu H, Lu H, Zhu J, Yuan Z, Li J (2019b) suPAR as a marker of diabetic nephropathy in patients with type 2 diabetes. Int J Clin Exp Med 12:4218–4225
Wang W, Jia Y-J, Yang Y-L, Xue M, Zheng Z-J, Wang L, Xue Y-M (2020) LncRNA GAS5 exacerbates renal tubular epithelial fibrosis by acting as a competing endogenous RNA of miR-96–5p. Biomed Pharmacotherapy. 121:109411
Wu K, Li J, Qi Y, Zhang C, Zhu D, Liu D, Zhao S (2019) SNHG14 confers gefitinib resistance in non-small cell lung cancer by up-regulating ABCB1 via sponging miR-206–3p. Biomed Pharmacother 116:108995
Yan Q, Tian Y, Hao F (2018a) Downregulation of LncRNA UCA1 inhibits proliferation and invasion of cervical cancer cells through miR-206 expression. Oncol Res. https://doi.org/10.3727/096504018X15185714083446
Yan Q, Tian Y, Hao F (2018b) Downregulation of LncRNA UCA1 inhibits proliferation and invasion of cervical cancer cells through miR-206 expression. Oncol Res 9:1
Yunqiao L, Vanke H, Jun X, Tangmeng G (2014) MicroRNA-206, down-regulated in hepatocellular carcinoma, suppresses cell proliferation and promotes apoptosis. Hepatogastroenterology 61:1302–1307
Zarei M, Ghafaryan H (2020) Alfa-Glucosidase inhibitory and antioxidant activity of hexane extract of flowers, leave and stems of Haplophyllum acutifolium DC. and Ferula haussknechtii Wolff ex Rech. Int J Adv Biol Biomed Res 8(2):153–164
Zhang J, Jiang T, Liang X, Shu S, Xiang X, Zhang W, Guo T, Xie W, Deng W, Tang X (2019) LncRNA MALAT1 mediated high glucose-induced HK-2 cell epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition and injury. J Physiol Biochem 75:443–452
Zhang Z, Li M, Zhang Z (2020) LncRNA MALAT1 modulates oxaliplatin resistance of gastric cancer via sponging miR-22-3p. Onco Targets Ther 13:1343–1354
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
El-Lateef, A.E.A., El-Shemi, A.G.A., Alhammady, M.S. et al. LncRNA NEAT2 Modulates Pyroptosis of Renal Tubular Cells Induced by High Glucose in Diabetic Nephropathy (DN) by via miR-206 Regulation. Biochem Genet 60, 1733–1747 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10528-021-10164-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10528-021-10164-6