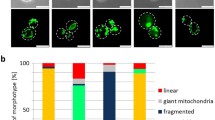
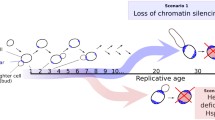
Abstract
The replicative lifespan of the yeast Saccharomyces cerevisiae models the aging of stem cells. Age asymmetry between the mother and daughter cells is established during each cell division, such that the daughter retains the capacity for self-renewal while this ability is diminished in the mother. The segregation of fully-functional mitochondria to daughter cells is one mechanism that underlies this age asymmetry. In this study, we have examined the role of mitochondrial dynamics in this phenomenon. Mitochondrial dynamics involve the processes of fission and fusion. Out of the three fusion and three fission genes tested, we have found that only FZO1 is required for the segregation of fully-functional mitochondria to daughter cells and in the maintenance of age asymmetry as manifested in the potential of daughters for a full replicative lifespan despite its deterioration in their mothers. The quality of mitochondria is determined by their turnover, and we have also discovered that deletion of FZO1 reduces mitophagy. Mitochondrial dysfunction elicits a compensatory retrograde response that extends replicative lifespan. Typically, the dysfunction that triggers this response encompasses energy production. The disruption of mitochondrial dynamics by deletion of FZO1 also activates the retrograde response to extend replicative lifespan. We call this novel pathway the mitochondrial dynamics-associated retrograde response (MDARR) because it is distinct in the signal proximal to the mitochondrion that initiates it. Furthermore, the MDARR engages the mitophagy receptor Atg32 on the mitochondrial surface, and we propose that this is due to the accumulation of Atg32-Atg11-Dnm1 complexes on the mitochondrion in the absence of Fzo1 activity. MDARR can be masked by the operation of the ‘classic’ retrograde response.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Amberg DC, Burke DJ, Strathern JN (2006) Yeast vital stains: calcofluor staining of chitin and bud scars. CSH Protoc. https://doi.org/10.1101/pdb.prot4166
Bernhardt D, Muller M, Reichert AS, Osiewacz HD (2015) Simultaneous impairment of mitochondrial fission and fusion reduces mitophagy and shortens replicative lifespan. Sci Rep 5:7885. https://doi.org/10.1038/srep07885
Borghouts C, Benguria A, Wawryn J, Jazwinski SM (2004) Rtg2 protein links metabolism and genome stability in yeast longevity. Genetics 166:765–777
Brunet A, Rando TA (2017) Interaction between epigenetic and metabolism in aging stem cells. Curr Opin Cell Biol 45:1–7. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ceb.2016.12.009
Chistiakov DA, Sobenin IA, Revin VV, Orekhov AN, Bobryshev YV (2014) Mitochondrial aging and age-related dysfunction of mitochondria. Biomed Res Int 2014:238463. https://doi.org/10.1155/2014/238463
Denoth Lippuner A, Julou T, Barral Y (2014) Budding yeast as a model organism to study the effects of age. FEMS Microbiol Rev 38:300–325. https://doi.org/10.1111/1574-6976.12060
Egilmez NK, Jazwinski SM (1989) Evidence for the involvement of a cytoplasmic factor in the aging of the yeast Saccharomyces cerevisiae. J Bacteriol 171:37–42
Epstein CB et al (2001) Genome-wide responses to mitochondrial dysfunction. Mol Biol Cell 12:297–308
Hayflick L, Moorhead PS (1961) The serial cultivation of human diploid cell strains. Exp Cell Res 25:585–621
Heeren G et al (2009) The mitochondrial ribosomal protein of the large subunit, Afo1p, determines cellular longevity through mitochondrial back-signaling via TOR1. Aging (Albany NY) 1:622–636
Higuchi-Sanabria R et al (2016) Mitochondrial anchorage and fusion contribute to mitochondrial inheritance and quality control in the budding yeast Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Mol Biol Cell 27:776–787. https://doi.org/10.1091/mbc.E15-07-0455
Jazwinski SM (1990) Aging and senescence of the budding yeast Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Mol Microbiol 4:337–343
Jazwinski SM (1993) The genetics of aging in the yeast Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Genetica 91:35–51
Jazwinski SM (2015) Mitochondria to nucleus signaling and the role of ceramide in its integration into the suite of cell quality control processes during aging. Ageing Res Rev 23:67–74. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.arr.2014.12.007
Jazwinski SM, Egilmez NK, Chen JB (1989) Replication control and cellular life span. Exp Gerontol 24:423–436
Jiang JC, Stumpferl SW, Tiwari A, Qin Q, Rodriguez-Quinones JF, Jazwinski SM (2016) Identification of the target of the retrograde response that mediates replicative lifespan extension in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Genetics 204:659–673. https://doi.org/10.1534/genetics.116.188086
Journo D, Mor A, Abeliovich H (2009) Aup1-mediated regulation of Rtg3 during mitophagy. J Biol Chem 284:35885–35895. https://doi.org/10.1074/jbc.M109.048140
Kanki T et al (2009a) A genomic screen for yeast mutants defective in selective mitochondria autophagy. Mol Biol Cell 20:4730–4738. https://doi.org/10.1091/mbc.E09-03-0225
Kanki T, Wang K, Cao Y, Baba M, Klionsky DJ (2009b) Atg32 is a mitochondrial protein that confers selectivity during mitophagy. Dev Cell 17:98–109. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.devcel.2009.06.014
Katajisto P et al (2015) Asymmetric apportioning of aged mitochondria between daughter cells is required for stemness. Science 348:340–343. https://doi.org/10.1126/science.1260384
Kennedy BK, Austriaco NR Jr, Guarente L (1994) Daughter cells of Saccharomyces cerevisiae from old mothers display a reduced life span. J Cell Biol 127:1985–1993
Kennedy BK, Austriaco NR, Zhang J, Guarente L (1995) Mutation in the silencing gene SIR4 can delay aging in S. cerevisiae. Cell 80:485–496
Kirchman PA, Kim S, Lai CY, Jazwinski SM (1999) Interorganelle signaling is a determinant of longevity in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Genetics 152:179–190
Kirchman PA, Miceli MV, West RL, Jiang JC, Kim S, Jazwinski SM (2003) Prohibitins and Ras2 protein cooperate in the maintenance of mitochondrial function during yeast aging. Acta Biochim Pol 50:1039–1056
Kissova I, Deffieu M, Manon S, Camougrand N (2004) Uth1p is involved in the autophagic degradation of mitochondria. J Biol Chem 279:39068–39074. https://doi.org/10.1074/jbc.M406960200
Klinger H et al (2010) Quantitation of (a)symmetric inheritance of functional and of oxidatively damaged mitochondrial aconitase in the cell division of old yeast mother cells. Exp Gerontol 45:533–542. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.exger.2010.03.016
Knuppertz L, Osiewacz HD (2016) Orchestrating the network of molecular pathways affecting aging: role of nonselective autophagy and mitophagy. Mech Ageing Dev 153:30–40. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.mad.2016.01.003
Lai CY, Jaruga E, Borghouts C, Jazwinski SM (2002) A mutation in the ATP2 gene abrogates the age asymmetry between mother and daughter cells of the yeast Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Genetics 162:73–87
Lam YT, Aung-Htut MT, Lim YL, Yang H, Dawes IW (2011) Changes in reactive oxygen species begin early during replicative aging of Saccharomyces cerevisiae cells. Free Radic Biol Med 50:963–970. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.freeradbiomed.2011.01.013
Laun P et al (2001) Aged mother cells of Saccharomyces cerevisiae show markers of oxidative stress and apoptosis. Mol Microbiol 39:1166–1173
Liu Z, Butow RA (2006) Mitochondrial retrograde signaling. Annu Rev Genet 40:159–185. https://doi.org/10.1146/annurev.genet.40.110405.090613
Mao K, Wang K, Liu X, Klionsky DJ (2013) The scaffold protein Atg11 recruits fission machinery to drive selective mitochondria degradation by autophagy. Dev Cell 26:9–18. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.devcel.2013.05.024
McFaline-Figueroa JR et al (2011) Mitochondrial quality control during inheritance is associated with lifespan and mother-daughter age asymmetry in budding yeast. Aging Cell 10:885–895. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1474-9726.2011.00731.x
Miceli MV, Jiang JC, Tiwari A, Rodriguez-Quinones JF, Jazwinski SM (2011) Loss of mitochondrial membrane potential triggers the retrograde response extending yeast replicative lifespan. Front Genet 2:102. https://doi.org/10.3389/fgene.2011.00102
Mijaljica D, Prescott M, Devenish RJ (2011) A fluorescence microscopy assay for monitoring mitophagy in the yeast Saccharomyces cerevisiae. J Vis Exp. https://doi.org/10.3791/2779
Minois N, Frajnt M, Wilson C, Vaupel JW (2005) Advances in measuring lifespan in the yeast Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 102:402–406. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.0408332102
Molon M, Panek A, Molestak E, Skoneczny M, Tchorzewski M, Wnuk M (2018) Daughters of the budding yeast from old mothers have shorter replicative lifespans but not total lifespans. Are DNA damage and rDNA instability the factors that determine longevity? Cell Cycle 17:1173–1187. https://doi.org/10.1080/15384101.2018.1464846
Morrison SJ, Kimble J (2006) Asymmetric and symmetric stem-cell divisions in development and cancer. Nature 441:1068–1074. https://doi.org/10.1038/nature04956
Mortimer RK, Johnston JR (1959) Life span of individual yeast cells. Nature 183:1751–1752
Oh J, Lee YD, Wagers AJ (2014) Stem cell aging: mechanisms, regulators and therapeutic opportunities. Nat Med 20:870–880. https://doi.org/10.1038/nm.3651
Okamoto K, Kondo-Okamoto N, Ohsumi Y (2009) Mitochondria-anchored receptor Atg32 mediates degradation of mitochondria via selective autophagy. Dev Cell 17:87–97. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.devcel.2009.06.013
Park PU, McVey M, Guarente L (2002) Separation of mother and daughter cells. Methods Enzymol 351:468–477
Piper PW, Jones GW, Bringloe D, Harris N, MacLean M, Mollapour M (2002) The shortened replicative life span of prohibitin mutants of yeast appears to be due to defective mitochondrial segregation in old mother cells. Aging Cell 1:149–157
Rafelski SM et al (2012) Mitochondrial network size scaling in budding yeast. Science 338:822–824. https://doi.org/10.1126/science.1225720
Roman H (1956) Studies of gene mutation in Saccharomyces. Cold Spring Harb Symp Quant Biol 21:175–185
Scheckhuber CQ, Erjavec N, Tinazli A, Hamann A, Nystrom T, Osiewacz HD (2007) Reducing mitochondrial fission results in increased life span and fitness of two fungal ageing models. Nat Cell Biol 9:99–105. https://doi.org/10.1038/ncb1524
Schleit J et al (2013) Molecular mechanisms underlying genotype-dependent responses to dietary restriction. Aging Cell 12:1050–1061. https://doi.org/10.1111/acel.12130
Seo JG, Lai CY, Miceli MV, Jazwinski SM (2007) A novel role of peroxin PEX6: suppression of aging defects in mitochondria. Aging Cell 6:405–413. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1474-9726.2007.00291.x
Shai N et al (2018) Systematic mapping of contact sites reveals tethers and a function for the peroxisome-mitochondria contact. Nat Commun 9:1761. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41467-018-03957-8
Sherman F (1991) Getting started with yeast. Methods Enzymol 194:3–21
Tacutu R et al (2018) Human ageing genomic resources: new and updated databases. Nucleic Acids Res 46:D1083–d1090. https://doi.org/10.1093/nar/gkx1042
Tanaka A, Cleland MM, Xu S, Narendra DP, Suen DF, Karbowski M, Youle RJ (2010) Proteasome and p97 mediate mitophagy and degradation of mitofusins induced by Parkin. J Cell Biol 191:1367–1380. https://doi.org/10.1083/jcb.201007013
Twig G et al (2008) Fission and selective fusion govern mitochondrial segregation and elimination by autophagy. EMBO J 27:433–446. https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.emboj.7601963
Westermann B (2014) Mitochondrial inheritance in yeast. Biochim Biophys Acta 1837:1039–1046. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bbabio.2013.10.005
Yanai H, Budovsky A, Barzilay T, Tacutu R, Fraifeld VE (2017) Wide-scale comparative analysis of longevity genes and interventions. Aging Cell 16:1267–1275. https://doi.org/10.1111/acel.12659
Zhang H, Singh KK (2014) Global genetic determinants of mitochondrial DNA copy number. PLoS ONE 9:e105242. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0105242
Acknowledgements
We are grateful to Rodney J. Devenish for the gift of pAS1NB::mt-Rosella. We thank Jennifer Wyckoff for DNA sequencing and for assistance with microscopy, which were carried out in the Genomics, Biostatistics, and Bioinformatics Core, supported by Grant P20GM103629 from the National Institutes of Health (NIH). This research was supported by Grant AG006168 from the NIH.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no competing interest.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Jiang, J.C., Stumpferl, S.W. & Jazwinski, S.M. Dual roles of mitochondrial fusion gene FZO1 in yeast age asymmetry and in longevity mediated by a novel ATG32-dependent retrograde response. Biogerontology 20, 93–107 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10522-018-9779-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10522-018-9779-z