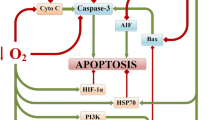
We compared the intensity of apoptosis in the peri-infarction area of the brain after isolated and combined exposure to hypoxia and hypercapnia prior to focal ischemic stroke modeling. Hypoxia and hypercapnia reduced the number of TUNEL-positive cells in the peri-infarction area, and their combination was most effective in comparison with effects of isolated exposures. The maximum neuroprotective effect of combined exposure to hypoxia and hypercapnia in comparison with isolated exposures was determined by inhibition of apoptosis in the peri-infarction zone.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Kulikov VP, Tregub PP, Bespalov AG, Vvedenskiy AJ. Comparative efficacy of hypoxia, hypercapnia and hypercapnic hypoxia increases body resistance to acute hypoxia in rats. Patol. Fiziol. Eksp. Ter. 2013;(3):59-61. Russian.
Tregub PP, Kulikov VP, Rucheikin NY, Belova EV, Motin YG. Proliferative and synthetic activity of nerve cells after combined or individual exposure to hypoxia and hypercapnia. Bull. Exp. Biol. Med. 2015;159(3):334-336.
Broughton BR, Reutens DC, Sobey CG. Apoptotic mechanisms after cerebral ischemia. Stroke. 2009;40(5):e331-e339.
Cantagrel S, Krier C, Ducrocq S, Bodard S, Payen V, Laugier J, Guilloteau D, Chalon S. Hypoxic preconditioning reduces apoptosis in a rat model of immature brain hypoxia-ischaemia. Neurosci. Lett. 2003;347(2):106-110.
Chen F, Suzuki Y, Nagai N, Peeters R, Sun X, Coudyzer W, Marchal G, Ni Y. Rat cerebral ischemia induced with photochemical occlusion of proximal middle cerebral artery: a stroke model for MR imaging research. MAGMA. 2004;17(3-6):103-108.
Gao X, Chang C, Duan D, Ru L, Yin G. Effect of hypoxic preconditioning on neural cell apoptosis and expression of Bcl-2 and Bax in cerebral ischemia-reperfusion in rats. J. Huazhong Univ. Sci. Technolog. Med. Sci. 2006;26(1):17-20.
Gold R, Schmied M, Giegerich G, Breitschopf H, Hartung HP, Toyka KV, Lassmann H. Differentiation between cellular apoptosis and necrosis by the combined use of in situ tailing and nick translation techniques. Lab. Invest. 1994;71(2):219-225.
Pevsner PH, Eichenbaum JW, Miller DC, Pivawer G, Eichenbaum KD, Stern A, Zakian KL, Koutcher JA. A photothrombotic model of small early ischemic infarcts in the rat brain with histologic and MRI correlation. J. Pharmacol. Toxicol. Methods. 2001;45(3):227-233.
Rybnikova E, Gluschenko T, Tulkova E, Churilova A, Jaroshevich O, Baranova K, Samoilov M. Preconditioning induces prolonged expression of transcription factors pCREB and NF-kappa B in the neocortex of rats before and following severe hypobaric hypoxia. J. Neurochem. 2008;106(3):1450-1458.
Tao T, Liu Y, Zhang J, Xu Y, Li W, Zhao M. Therapeutic hypercapnia improves functional recovery and attenuates injury via antiapoptotic mechanisms in a rat focal cerebral ischemia/reperfusion model. Brain Res. 2013;1533:52-62.
Tregub P, Kulikov V, Motin Y, Bespalov A, Osipov I. Combined exposure to hypercapnia and hypoxia provides its maximum neuroprotective effect during focal ischemic injury in the brain. J. Stroke Cerebrovasc. Dis. 2015;24(2):381-387.
Zhan L, Wang T, Li W, Xu ZC, Sun W, Xu E. Activation of Akt/FoxO signaling pathway contributes to induction of neuroprotection against transient global cerebral ischemia by hypoxic pre-conditioning in adult rats. J. Neurochem. 2010; 114(3):897-908.
Zhang YB, Lu GW, Yang MF, Niu JZ, Sun BL. Changes in Bcl-2 and Caspase-3 expressions in cortex of hypoxic preconditioning mice. Sheng Li Xue Bao. 2008;60(2):249-253.
Zhou Q, Cao B, Niu L, Cui X, Yu H, Liu J, Li H, Li W. Effects of permissive hypercapnia on transient global cerebral ischemia–reperfusion injury in rats. Anesthesiology. 2010; 112(2):288-297.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Translated from Byulleten’ Eksperimental’noi Biologii i Meditsiny, Vol. 161, No. 5, pp. 606-609, May, 2016
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Tregub, P.P., Malinovskaya, N.A., Kulikov, V.P. et al. Inhibition of Apoptosis is a Potential Way to Improving Ischemic Brain Tolerance in Combined Exposure to Hypercapnia and Hypoxia. Bull Exp Biol Med 161, 666–669 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10517-016-3481-4
Received:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10517-016-3481-4