Abstract
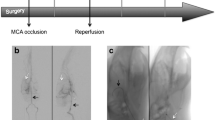
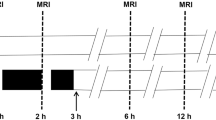
A stroke model in rats with photochemically induced thrombosis (PIT) of proximal cerebral middle artery (MCA) is introduced for magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) study. Thirty-seven rats subjected to surgical and optical procedures for inducing the PIT models were scanned using a 1.5-T scanner with T1-weighted imaging (T1WI), T2-weighted imaging (T2WI), diffusion-weighted imaging (DWI), and contrast-enhanced perfusion-weighted imaging (PWI) at 1 h and 24 h after MCA occlusion. The penumbra evolution and PWI-derived parameters including relative cerebral blood volume (rCBV) and relative cerebral blood flow (rCBF) were monitored; and the relative lesion size (RLS) was compared with the final RLS on the gold standard triphenyl tetrazolium chloride (TTC) staining at 24 h. The results showed that the focal cerebral ischemic lesions were detectable in all rats with different MR approaches. The lesion on PWI at 1 h and on all MR images at 24 h was matched well with that seen on TTC staining; the peri-infarct area decreased from 6.2 ± 7.2% of the brain volume at 1 h to 0.3 ± 5.6% at 24 h. Compared to that in the contralateral hemisphere, rCBV in ischemic region was 52.6 ± 21.4 and 40.0 ± 15.8% (p > 0.05), and rCBF was 64.6 ± 11.2 and 47.3 ± 11.1% (p < 0.05) at 1 h and 24 h respectively. The present PIT model in rats has been successfully adopted for MRI research, which might be feasible for certain stroke studies and should be beneficial for the evaluation on effects of potential diagnostic and therapeutic approaches.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ahmed SH, Shaikh AY, Shaikh Z, Hsu CY (2000) What animal models have taught us about the treatment of acute stroke and brain protection. Curr Atheroscler Rep 2:167–180
Traystman RJ (2003) Animal models of focal and global cerebral ischemia. Ilar J 44:85–95
Hoehn M, Nicolay K, Franke C, van der Sanden B (2001) Application of magnetic resonance to animal models of cerebral ischemia. J Magn Reson Imaging 14:491–509
Lee VM, Burdett NG, Carpenter A et al. (1996) Evolution of photochemically induced focal cerebral ischemia in the rat. Magnetic resonance imaging and histology. Stroke 27:2110–2118
Lanens D, Spanoghe M, Van Audekerke J, Oksendal A, Van der Linden A, Dommisse R (1995) Complementary use of T2-weighted and postcontrast T1- and T2*-weighted imaging to distinguish sites of reversible and irreversible brain damage in focal ischemic lesions in the rat brain. Magn Reson Imaging 13:185–192
Yao H, Ibayashi S, Sugimori H, Fujii K, Fujishima M (1996) Simplified model of krypton laser-induced thrombotic distal middle cerebral artery occlusion in spontaneously hypertensive rats. Stroke 27:333–336
Watson BD, Dietrich WD, Busto R, Wachtel MS, Ginsberg MD (1985) Induction of reproducible brain infarction by photochemically initiated thrombosis. Ann Neurol 17:497–504
Takamatsu H, Tsukada H, Kakiuchi T, Tatsumi M, Umemura K (2000) Changes in local cerebral blood flow in photochemically induced thrombotic occlusion model in rats. Eur J Pharmacol 398:375–379
Suzuki Y, Takagi Y, Nakamura R, Hashimoto K, Umemura K (2003) Ability of NMDA and non-NMDA receptor antagonists to inhibit cerebral ischemic damage in aged rats. Brain Res 964:116–120
Umemura K, Wada K, Uematsu T, Nakashima M (1993) Evaluation of the combination of a tissue-type plasminogen activator, SUN9216, and a thromboxane A2 receptor antagonist, vapiprost, in a rat middle cerebral artery thrombosis model. Stroke 24:1077–1081
Takamatsu H, Kondo K, Ikeda Y, Umemura K (1998) Neuroprotective effects depend on the model of focal ischemia following middle cerebral artery occlusion. Eur J Pharmacol 362:137–142
Li F, Silva MD, Sotak CH, Fisher M (2000) Temporal evolution of ischemic injury evaluated with diffusion-, perfusion-, and T2-weighted MRI. Neurology 54:689–696
Kastrup A, Engelhorn T, Beaulieu C, de Crespigny A, Moseley ME (1999) Dynamics of cerebral injury, perfusion, and blood-brain barrier changes after temporary and permanent middle cerebral artery occlusion in the rat. J Neurol Sci 166:91–99
Giles AR (1987) Guidelines for the use of animals in biomedical research. Thromb Haemost 58:1078–1084
Bederson JB, Pitts LH, Tsuji M, Nishimura MC, Davis RL, Bartkowski H (1986) Rat middle cerebral artery occlusion: Evaluation of the model and development of a neurologic examination. Stroke 17:472–476
Schlaug G, Benfield A, Baird AE, et al. (1999) The ischemic penumbra: Operationally defined by diffusion and perfusion MRI. Neurology 53:1528–1537
Gu WG, Brannstrom T, Jiang W, Wester P (1999) A photothrombotic ring stroke model in rats with remarkable morphological tissue recovery in the region at risk. Exp Brain Res 125:171–183
Fiehler J, von Bezold M, Kucinski T et al. (2002) Cerebral blood flow predicts lesion growth in acute stroke patients. Stroke 33:2421–2425
Grandin CB, Duprez TP, Smith AM et al. (2002) Which MR-derived perfusion parameters are the best predictors of infarct growth in hyperacute stroke? Comparative study between relative and quantitative measurements. Radiology 223:361–370
Griswold MA, Jakob PM, Heidemann RM et al. (2002) Generalized autocalibrating partially parallel acquisitions (GRAPPA). Magn Reson Med 47:1202–1210
Jespers L, Vanwetswinkel S, Lijnen HR et al. (1999) Structural and functional basis of plasminogen activation by staphylokinase. Thromb Haemost 81:479–485
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Chen, F., Suzuki, Y., Nagai, N. et al. Rat cerebral ischemia induced with photochemical occlusion of proximal middle cerebral artery: a stroke model for MR imaging research. MAGMA 17, 103–108 (2004). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10334-004-0061-9
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10334-004-0061-9