Abstract
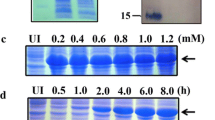
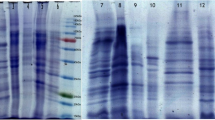
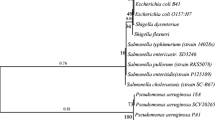
The outer membrane protein (ExbB) of Pseudomonas fluorescens present in the outermost layer may possess immune functions and potential applications in subunit vaccines. ExbB bioinformatic analysis elucidated that the relationship among Pseudomonas species was closer than others, and anti-ExbB serum might provide cross-protective ability to resist Pseudomonas bacterial infection in animals. ExbB was obtained via molecular cloning, prokaryotic expression, and purification. The optimal expression conditions were a strain OD600 value of 1.0 and IPTG concentration of 0.3 mmol/L, inducing time of 3 h, and inducing temperature of 32℃. Mice immunized to ExbB could significantly increase (p < 0.05) the spleen index and leukocyte phagocytosis parameters such as phagocytic percentage (PP) and phagocytic index (PI). The specific antiserum titer (1:12,800) was obtained, which had an in vitro immune recognition effect on both P. fluorescens and Aeromonas hydrophila. Passive immunization results for anti-ExbB mouse serum to Carassius auratus showed that ExbB serum could significantly enhance PP (p < 0.05) and PI (p < 0.05). Moreover, the passive protective rate of anti-ExbB serum against P. fluorescens infection was 54% (p < 0.05), and the passive cross-protective rate against A. hydrophila was 38.4% (p < 0.05). Furthermore, the expression of immune-related genes such as IL-6, IL-8, IL-1β, and TNF-α was significantly decreased (p < 0.05) in kidneys and gills after challenging with P. fluorescens, while the downward trend was not obvious after challenging with A. hydrophila. The trend changes of antioxidant-related factors such as malondialdehyde (MDA), superoxide dismutase (SOD), glutathione peroxidase (GSH-Px), and catalase (CAT) were not obvious after bacterial challenge. Interestingly, there was a significant reduction in the histopathological lesions in the kidney, spleen, and intestine of C. auratus challenged by P. fluorescens and A. hydrophila. Altogether, the results suggest that ExbB has an immune function in passive protection against P. fluorescens and passive cross-protection against A. hydrophila and can boost resistance to infection against the most dangerous bacterial pathogens infecting freshwater fish.








Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
The data used to support the findings of this study are included in the article.
Code availability
Not applicable, no code developed.
Abbreviations
- GAPDH:
-
Glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate dehydrogenase
- IL-1β:
-
Interleukin-1β
- IL-6:
-
Interleukin-6
- IL-8:
-
Interleukin-8
- TNF-α:
-
Tumor necrosis factor-α
References
Abdel-Latif HMR, Dawood MAO, Menanteau-Ledouble S, El-Matbouli M (2020) The nature and consequences of co-infections in tilapia: a review. J Fish Dis 6:651–664. https://doi.org/10.1111/jfd.13164
Abdel-Latif HMR, Khafaga AF (2020) Natural co-infection of cultured Nile tilapia Oreochromis niloticus with Aeromonas hydrophila and Gyrodactylus cichlidarum experiencing high mortality during summer. Aquac Res 5:1880–1892. https://doi.org/10.1111/are.14538
Abd El-Kader MF, Fath El-Bab AF, Abd-Elghany MF, Abdel-Warith AA, Younis EM, Dawood MAO (2021) Selenium nanoparticles act potentially on the growth performance, hemato-biochemical indices, antioxidative, and immune-related genes of European seabass (Dicentrarchus labrax). Biol Trace Elem Res 8:3126–3134. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12011-020-02431-1
Ali MG, Zhang Z, Gao Q, Pan M, Rowan EG, Zhang J (2020) Recent advances in therapeutic applications of neutralizing antibodies for virus infections: an overview. Immunol Res 6:325–339. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12026-020-09159-z
Ascoli CA, Aggeler B (2018) Overlooked benefits of using polyclonal antibodies. Biotechniques 3:127–136. https://doi.org/10.2144/btn-2018-0065
Awan F, Dong Y, Wang N, Liu J, Ma K, Liu Y (2018) The fight for invincibility: environmental stress response mechanisms and Aeromonas hydrophila. Microb Pathog 116:135–145. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.micpath.2018.01.023
Bandeira Junior G, de Freitas SC, Descovi SN, Antoniazzi A, Cargnelutti JF, Baldisserotto B (2019) Aeromonas hydrophila infection in silver catfish causes hyperlocomotion related to stress. Microb Pathog 132:261–265. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.micpath.2019.05.017
Celia H, Botos I, Ni X, Fox T, De Val N, Lloubes R, Jiang J, Buchanan SK (2019) Cryo-EM structure of the bacterial Ton motor subcomplex ExbB-ExbD provides information on structure and stoichiometry. Commun Biol 2:358. https://doi.org/10.1038/s42003-019-0604-2
Chen C, Kang C, Rong N, Wu NN, Chen CL, Wu SQ, Zhang XY, Liu X (2019) Evaluation of immunogenicity, protective immunity on aquaculture pathogenic Vibrio and fermentation of Vibrio alginolyticus flagellin FlaC protein. Iranian J Biotech 3:e2628. https://doi.org/10.29252/ijb.2628
Chen C, Wu NN, Rong N, Kang C, Chen CL, Wu SQ, Liu X, Zhang XY (2020) Immunoprotective evaluation of Escherichia coli outer membrane protein A against the main pathogens of animal mastitis. J Pharm Res 1:155–162. https://doi.org/10.4314/tjpr.v19i1.23
Dawood MAO, Gewaily MS, Soliman AA, Shukry M, Amer AA, Younis EM, Abdel-Warith AA, Van Doan H, Saad AH, Aboubakr M, Abdel-Latif HMR, Fadl SE (2020) Marine-Derived chitosan nanoparticles improved the intestinal histo-morphometrical features in association with the health and immune response of grey mullet (Liza ramada). Mar Drugs 12:611. https://doi.org/10.3390/md18120611
De Mot R, Schoofs G, Roelandt A, Declerck P, Proost P, Van Damme J, Vanderleyden J (1994) Molecular characterization of the major outer-membrane protein OprF from plant root-colonizing Pseudomonas fluorescens. Microbiology (reading) 6:1377–1387. https://doi.org/10.1099/00221287-140-6-1377
Diao J, Li L, Fan Y, Wang S, Gai C, Wang Y, Yu X, Wang X, Xu L, Liu H, Ye H (2020) Recombinant outer membrane protein C of Aeromonas salmonicida subsp. masoucida, a potential vaccine candidate for rainbow trout (Oncorhynchus mykiss). Microb Pathog 145:104211. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.micpath.2020.104211
Egan AJF (2018) Bacterial outer membrane constriction. Mol Microbiol 6:676–687. https://doi.org/10.1111/mmi.13908
El-Son MAM, Nofal MI, Abdel-Latif HMR (2021) Co-infection of Aeromonas hydrophila and Vibrio parahaemolyticus isolated from diseased farmed striped mullet (Mugil cephalus) in Manzala. Egypt-A Case Report Aquaculture 530:735738. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.aquaculture.2020.735738
Garcia D, Lima D, da Silva DGH, de Almeida EA (2020) Decreased malondialdehyde levels in fish (Astyanax altiparanae) exposed to diesel: evidence of metabolism by aldehyde dehydrogenase in the liver and excretion in water. Ecotoxicol Environ Saf 190:110107. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ecoenv.2019.110107
Griboff J, Carrizo JC, Bonansea RI, Valdés ME, Wunderlin DA, Amé MV (2020) Multiantibiotic residues in commercial fish from Argentina. The presence of mixtures of antibiotics in edible fish, a challenge to health risk assessment. Food Chem 332:127380. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.foodchem.2020.127380
Gudla R, Konduru GV, Nagarajaram HA, Siddavattam D (2019) Organophosphate hydrolase interacts with Ton components and is targeted to the membrane only in the presence of the ExbB/ExbD complex. FEBS Lett 6:581–593. https://doi.org/10.1002/1873-3468.13345
Hoseinifar SH, Shakouri M, Yousefi S, Van Doan H, Shafiei S, Yousefi M, Mazandarani M, Torfi Mozanzadeh M, Tulino MG, Faggio C (2020) Humoral and skin mucosal immune parameters, intestinal immune related genes expressing and antioxidant defense in rainbow trout (Oncorhynchus mykiss) fed olive (Olea europea L.) waste. Fish Shellfish Immunol 100:171–178. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.fsi.2020.02.067
Huo HJ, Chen SN, Li L, Nie P (2019) Functional characterization of IL-10 and its receptor subunits in a perciform fish, the mandarin fish, Siniperca chuatsi. Dev Comp Immunol 97:64–75. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.dci.2019.03.017
Lee SH, Lee SY, Park BC (2005) Cell surface display of lipase in Pseudomonas putida KT2442 using OprF as an anchoring motif and its biocatalytic applications. Appl Environ Microbiol 12:8581–8586. 10. 1128/AEM.71.12.8581–8586.2005
Liao H, Cheng X, Zhu D, Wang M, Jia R, Chen S, Chen X, Biville F, Liu M, Cheng A (2015) TonB energy transduction systems of Riemerella anatipestifer are required foriron and hemin utilization. PLoS ONE 5:e0127506. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0127506
Li H, Ye MZ, Peng B, Wu HK, Xu CX, Xiong XP, Wang C, Wang SY, Peng XX (2010) Immunoproteomic identification of polyvalent vaccine candidates from Vibrio parahaemolyticus outer membrane proteins. J Proteome Res 5:2573–2583. https://doi.org/10.1021/pr1000219
Liu X, Chen C, Zhang XY (2020) Drug-drug interaction of acetaminophen and roxithromycin with the cocktail of cytochrome P450 and hepatotoxicity in rats. Int J Med Sci 3:414–421. https://doi.org/10.7150/ijms.38527
Liu X, Sun W, Wu NN, Rong N, Kang C, Jian SJ, Chen CL, Chen C, Zhang XY (2021) Synthesis of Escherichia coli OmpA oral nanoparticles and evaluation of immune functions against the major etiologic agent of cow mastitis. Vaccines (basel) 3:304. https://doi.org/10.3390/vaccines9030304
Liu X, Yang MJ, Wang SN, Xu D, Li H, Peng XX (2018) Differential antibody responses to outer membrane proteins contribute to differential immune protections between live and inactivated Vibrio parahemolyticus. J Proteome Res 9:2987–2994. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.jproteome.8b00176
Livak KJ, Schmittgen TD (2001) Analysis of relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and the 2(-Delta Delta C(T)) method. Methods 4:402–408. https://doi.org/10.1006/meth.2001.1262
Lovy J, Dicarlo-Emery D, Hutcheson JM (2017) A bacterium with close genetic identity to Pseudomonas mandelii associated with spring fish kills in wild bluegill Lepomis macrochirus Rafinesque and pumpkinseed sunfish Lepomis gibbosus (Linnaeus). J Fish Dis 12:1757–1764. https://doi.org/10.1111/jfd.12642
Maiti B, Dubey S, Munang’andu HM, Karunasagar I, Karunasagar I, Evensen Ø (2020) Application of outer membrane protein-based vaccines against major bacterial fish pathogens in India. Front Immunol 11:1362. https://doi.org/10.3389/fimmu.20201362
Meehan TL, Yalonetskaya A, Joudi TF, McCall K (2015) Detection of cell death and phagocytosis in the drosophila ovary. Methods Mol Biol 1328:191–206. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-1-4939-2851-4_14
Nayak SK (2020) Current prospects and challenges in fish vaccine development in India with special reference to Aeromonas hydrophila vaccine. Fish Shellfish Immunol 100:283–299. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.fsi.2020.01.064
Peng B, Lin XP, Wang SN, Yang MJ, Peng XX, Li H (2018) Polyvalent protective immunogens identified from outer membrane proteins of Vibrio parahaemolyticus and their induced innate immune response. Fish Shellfish Immunol 72:104–110. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.fsi.2017.10.046
Peng B, Ye JZ, Han Y, Zeng L, Zhang JY, Li H (2016) Identification of polyvalent protective immunogens from outer membrane proteins in Vibrio parahaemolyticus to protect fish against bacterial infection. Fish Shellfish Immunol 54:204–210. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.fsi.2016.04.012
Pore D, Chakrabarti MK (2013) Outer membrane protein A (OmpA) from Shigella flexneri 2a: a promising subunit vaccine candidate. Vaccine 336:3644–3650. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.vaccine.2013.05.100
Pramanik A, Hauf W, Hoffmann J, Cernescu M, Brutschy B, Braun V (2011) Oligomeric structure of ExbB and ExbB-ExbD isolated from Escherichia coli as revealed by LILBID mass spectrometry. Biochemistry 41:8950–8956. https://doi.org/10.1021/bi2008195
Silva YRO, Contreras-Martel C, Macheboeuf P, Dessen A (2020) Bacterial secretins: mechanisms of assembly and membrane targeting. Protein Sci 4:893–904. https://doi.org/10.1002/pro.3835
Solana JC, Ramírez L, Cook EC, Hernández-García E, Sacristán S, Martín ME (2020) Subcutaneous immunization of Leishmania HSP70-II null mutant line reduces the severity of the experimental visceral leishmaniasis in BALB/c mice. Vaccines (basel) 1:141. https://doi.org/10.3390/vaccines8010141
Stockinger Z, Grabo D, Benov A, Tien H, Seery J, Humphries A (2018) Blunt abdominal trauma, splenectomy, and post-splenectomy vaccination. Mil Med 2:98–100. https://doi.org/10.1093/milmed/usy095
Tang R, Zhu J, Feng L, Li J, Liu X (2019) Characterization of LuxI/LuxR and their regulation involved in biofilm formation and stress resistance in fish spoilers Pseudomonas fluorescens. Int J Food Microbiol 297:60–71. 10. 1016/j.ijfoodmicro.2018.12.011
Ukidve A, Zhao Z, Fehnel A, Krishnan V, Pan DC, Gao Y, Mandal A, Muzykantov V, Mitragotri S (2020) Erythrocyte-driven immunization via biomimicry of their natural antigen-presenting function. Proc Natl Acad Sci 30:17727–17736. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.2002880117
Vaca DJ, Thibau A, Schütz M, Kraiczy P, Happonen L, Malmström J, Kempf VAJ (2020) Interaction with the host: the role of fibronectin and extracellular matrix proteins in the adhesion of Gram-negative bacteria. Med Microbiol Immunol 3:277–299. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00430-019-00644-3
Wang Y, Hong X, Liu J, Zhu J, Chen J (2020) Interactions between fish isolates Pseudomonas fluorescens and Staphylococcus aureus in dual-species biofilms and sensitivity to carvacrol. Food Microbiol 91:103506. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.fm.2020.103506
Wootla B, Denic A, Rodriguez M (2014) Polyclonal and monoclonal antibodies in clinic. Methods Mol Biol 1060:79–110. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-1-62703-586-6_5
Xu C, Soyfoo DM, Wu Y, Xu S (2020) Virulence of Helicobacter pylori outer membrane proteins: an updated review. Eur J Clin Microbiol Infect Dis 10:1821–1830. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10096-020-03948-y
Yun S, Lee SJ, Giri SS, Kim HJ, Kim SG, Kim SW, Han SJ, Kwon J, Oh WT, Chang Park S (2020) Vaccination of fish against Aeromonas hydrophila infections using the novel approach of transcutaneous immunization with dissolving microneedle patches in aquaculture. Fish Shellfish Immunol 97:34–40. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.fsi.2019.12.026
Funding
This work was supported by the Key Research and Development Program of Shaanxi (2020LSFP2-38) and Project of Shaanxi University of Technology (SLGQD1803), Innovation and Entrepreneurship Training Program for college students in Shaanxi Province (S201910720027), China.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Xiang Liu and Chen Chen are responsible for the design of the research and the writing of the paper. Wei Sun, Na Rong, and Sijie Jian are responsible for the completion of the entire process of the experiment and data analysis. Chunlin Chen and Rui Ding are responsible for the guidance of the experimental process and revision of the paper. Rui Chen and Chao Kang are helpful to assist the experiment.
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Ethics approval
The authors followed all ethical policies of the journal in all methods and actions. Specifically, all animal procedures were performed in accordance with the guidelines prescribed in the Guide for the Care and Use of Laboratory Animals and were approved by the Institutional Animal Ethics Committee, Shaanxi University of Technology, China (No. 2020–03).
Consent to participate
Not applicable.
Consent for publication
Not applicable.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher's note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Sun, W., Rong, N., Jian, S. et al. Immune responses and protective efficacy of outer membrane protein ExbB of Pseudomonas fluorescens against Aeromonas hydrophila and Pseudomonas fluorescens affecting Carassius auratus. Aquacult Int 29, 2823–2840 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10499-021-00784-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10499-021-00784-5