Abstract
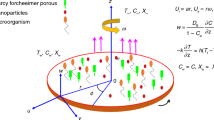
This paper discusses the natural convection boundary layer flow of a micropolar nanofluid over a vertical permeable cone with variable wall temperatures. Non-similar solutions are obtained. The nonlinearly coupled differential equations under the boundary layer approximations governing the flow are solved numerically using an efficient, iterative, tri-diagonal, implicit finite difference method. Different experimental correlations for both nanofluid effective viscosity and nanofluid thermal conductivity are considered. It is found that as the vortex-viscosity parameter increases, both the velocity profiles and the local Nusselt number decrease. Also, among all the nanoparticles considered in this investigation, Cu gives a good convection.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Choi, S. U. S. Enhancing thermal conductivity of fluids with nanoparticles. ASME Fluids Engineering Division, 231, 99–105 (1995)
Makinde, O. D. and Aziz, A. Boundary layer flow of a nanofluid past a stretching sheet with a convective boundary condition. International Journal of Thermal Sciences, 50, 1326–1332 (2011)
Cheng, C. Y. Free convection boundary layer flow over a horizontal cylinder of elliptic cross section in porous media saturated by a nanofluid. International Communications in Heat and Mass Transfer, 39, 931–936 (2012)
Mansour, M. A., Mohamed, R. A., Abd-Elaziz, M. M., and Ahmed, S. E. Numerical simulation of mixed convection flows in a square lid-driven cavity partially heated from below using nanofluid. International Communications in Heat and Mass Transfer, 37, 1504–1512 (2010)
Mahdy, A. and Ahmed, S. E. Laminar free convection over a vertical wavy surface embedded in a porous medium saturated with a nanofluid. Transport in Porous Media, 91, 423–435 (2012)
Mansour, M. A. and Ahmed, S. E. Mixed convection flows in a square lid-driven cavity with heat source at the bottom utilizing nanofluid. The Canadian Journal of Chemical Engineering, 90, 100–110 (2012)
Li, Y. Q., Wang, F. C., Liu, H., and Wu, H. A. Nanoparticle-tuned spreading behavior of nanofluid droplets on the solid substrate. Microfluid Nanofluid, 18, 111–120 (2015)
Wang, F. C. and Wu, H. A. Enhanced oil droplet detachment from solid surfaces in charged nanoparticle suspensions. Soft Matter, 9(33), 7974–7980 (2013)
Li, Y. Q., Wu, H. A., and Wang, F. C. Effect of a single nanoparticle on the contact line motion. Langmuir, 32(48), 12676–12685 (2016)
Eringen, A. Theory of micropolar fluids. Journal of Mathematics and Mechanics, 16, 1–18 (1966)
El-Aziz, A. M. Mixed convection flow of a micropolar fluid from an unsteady stretching surface with viscous dissipation. Journal of the Egyptian Mathematical Society, 21, 385–394 (2013)
Olajuwon, B. I., Oahimire, J. I., and Ferdow, M. Effect of thermal radiation and Hall current on heat and mass transfer of unsteady MHD flow of a viscoelastic micropolar fluid through a porous medium. Engineering Science and Technology, An International Journal, 17, 185–193 (2014)
Mansour, M. A., Mohamed, R. A., El-Aziz, A. M., and Ahmed, S. E. Steady axisymmetric flow and heat transfer of micropolar fluid over a vertical permeable slender cylinder in the presence of thermal radiation. International Journal of Applied Mechanics and Engineering, 15, 1185–1203 (2010)
Mansour, M. A., Mohamed, R. A., El-Aziz, A. M., and Ahmed, S. E. Thermal stratification and suction/injection effects on flow and heat transfer of micropolar fluid due to stretching cylinder. International Journal for Numerical Methods in Biomedical Engineering, 27, 1951–1963 (2011)
Ahmed, S. E. and Rashad, A. M. Natural convection of micropolar nanofluids in a rectangular enclosure saturated with anisotropic porous media. Journal of Porous Media, 19(8), 737–750 (2016)
Cheng, C. Y. Natural convection boundary layer flow of a micropolar fluid over a vertical permeable cone with variable wall temperature. International Communications in Heat and Mass Transfer, 38, 429–433 (2011)
Hossain, M. A. and Paul, C. S. Free convection from a vertical permeable circular cone with non-uniform surface heat flux. Heat and Mass Transfer, 37, 167–173 (2001)
Hossain, M. A. and Paul, C. S. Free convection from a vertical permeable circular cone with non-uniform surface temperature. Acta Mechanica, 151, 103–114 (2001)
Hering, R. G. and Grosh, R. J. Laminar free convection from a non-isothermal cone. International Journal of Heat and Mass Transfer, 5, 1059–1068 (1962)
Na, T. Y. and Chiou, J. P. Laminar natural convection over a frustum of a cone. Applied Scientific Research, 35, 409–421 (1979)
Yih, K. A. Effect of radiation on natural convection about a truncated cone. International Journal of Heat and Mass Transfer, 42, 4299–4305 (1999)
Pop, I. and Na, T. Y. Natural convection over a vertical wavy frustum of a cone. International Journal of Non-linear Mechanics, 34, 925–934 (1999)
Pop, I. and Na, T. Y. Coupled heat and mass transfer by natural convection about a truncated cone in the presence of magnetic field and radiation effects. Numerical Heat Transfer, Part A: Application, 39, 511–530 (2001)
Postelnicu, A. Free convection about a vertical frustum of a cone in a micropolar fluid. International Journal of Engineering Science, 44, 672–682 (2006)
Blottner, F. G. Finite-difference methods of solution of the boundary-layer equation. AIAA Journal, 8, 193–205 (1970)
Ahmadi, G. Self-similar solution of incompressible micropolar boundary layer flow over a semiinfinite flat plate. International Journal of Engineering Science, 14(7), 639–646 (1976)
Rees, D. A. S. and Pop, I. Free convection boundary-layer flow of a micropolar fluid from a vertical flat plate. IMA Journal of Applied Mathematics, 61(2), 179–197 (1998)
Pak, B. C. and Cho, Y. I. Hydrodynamic and heat transfer study of dispersed fluid with submicron metallic oxide particles. Experimental Heat Transfer, 11(2), 151–170 (1998)
Godson, L., Raja, B., Lal, D. M., and Wongwises, S. Experimental investigation on the thermal conductivity and viscosity of silver-deionized water nanofluid. Experimental Heat Transfer, 23(4), 317–332 (2010)
Aminossadati, S. M. and Ghasemi, B. Natural convection cooling of a localised heat source at the bottom of a nanofluid-filled enclosure. European Journal of Mechanics B/Fluids, 28(5), 630–640 (2009)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ahmed, S.E. Modeling natural convection boundary layer flow of micropolar nanofluid over vertical permeable cone with variable wall temperature. Appl. Math. Mech.-Engl. Ed. 38, 1171–1180 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10483-017-2231-9
Received:
Revised:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10483-017-2231-9