Abstract
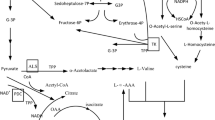
Cephalosporin C (CPC) productivity of Acremonium chrysogenum has been improved significantly through classical strain improvement programs. Here, we used transcription and metabolite profiling to address mechanisms underlying CPC production in a high yield (HY) strain. Transcription and metabolite profiling indicated that enzymes involved in amino acid production are higher in abundance in the HY strain. Moreover, results indicate a higher flow of precursors from the glycolysis and gluconeogenesis pathways to serine synthesis at the late stage of fermentation in the HY strain. In addition, less pyruvate would enter the TCA cycle thus favoring valine synthesis. Amino acid production would also benefit from a more active pentose phosphate pathway and γ-amino butyric acid shunt both generating NADPH. Moreover the glyoxylate pathway seems to be more active in the HY strain. These results may provide new leads for CPC strain improvement in industry.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Cao J, Barbosa JM, Singh NK, Locy RD (2013) GABA shunt mediates thermotolerance in Saccharomyces cerevisiae by reducing reactive oxygen production. Yeast 30:129–144
Chaudhary AK, Dhakal D, Sohng JK (2013) An insight into the "-Omics" based engineering of Streptomycetes for secondary metabolite overproduction. Biomed Res Int 13:1–15
Demain AL (1983) Biosynthesis ofβ-lactam antibiotics. In: Demain AL, Solomon NA (eds) Antibiotics containing the β-lactam structure. Springer-Verlag, New York, pp 189–228
Demain AL, Zhang J (1998) Cephalosporin C production by Cephalosporium acremonium: the methionine story. Crit Rev Biotechnol 18:283–294
Drew SW, Demain AL (1975) Production of cephalosporin C by single and double sulfur auxotrophic mutants of Cephalosporium acremonium. Antimicrob Agents Chemother 8:5–10
Gunnarsson N, Eliasson A, Nielsen J (2004) Control of fluxes towards antibiotics and the role of primary metabolism in production of antibiotics. Adv Biochem Engin/Biotechnol 88:137–178
Hijarrubia MJ, Aparicio JF, Martin JF (2002) Nitrate regulation of alpha-aminoadipate reductase formation and lysine inhibition of its activity in Penicillium chrysogenum and Acremonium chrysogenum. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 59:270–277
Karaffa L, Sandor E, Kozma J, Kubicek CP, Szentirmai A (1999) The role of the alternative respiratory pathway in the stimulation of cephalosporin C formation by soybean oil in Acremonium chrysogenum. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 51:633–638
Karaffa L, Sandor E, Fekete E, Kozma J, Szentirmai A, Pocsi I (2003) Stimulation of the cyanide-resistant alternative respiratory pathway by oxygen in Acremonium chrysogenum correlates with the size of the intracellular peroxide pool. Can J Microbiol 49:216–220
Kern A, Tilley E, Hunter IS, Legisa M, Glieder A (2007) Engineering primary metabolic pathways of industrial micro-organisms. J Biotechnol 129:6–29
Kleijn RJ, van Winden WA, Ras C, van Gulik WM, Schipper D, Heijnen JJ (2006) 13C-labeled gluconate tracing as a direct and accurate method for determining the pentose phosphate pathway split ration in Penicillium chrysogenum. Appl Environ Biotechnol 72:4743–4754
Kozma J, Karaffa L (1996) Effect of oxygen on the respiratory system and cephalosporin-C production in Acremonium chrysogenum. J Biotechnol 48:59–66
Li J, Yang Y, Chu J, Huang M, Li L, Zhang X et al (2010) Quantitative metabolic flux analysis revealed uneconomical utilization of ATP and NADPH in Acremonium chrysogenum fed with soybean oil. Bioprocess Biosyst Eng 33:1119–1129
Litzka O, Bergh KT, Brulle JV, Steidl S, Brakhage AA (1999) Transcriptional control of expression of fungal ß-lactam biosynthesis genes. Antonie Van Leeuwenhoek 75:95–105
Liu Y, Gong G, Xie L, Yuan N, Zhu C et al (2010) Improvement of cephalosporin C production by recombinant DNA integration in Acremonium chrysogenum. Mol Biotechnol 44:101–109
Liu Y, Xie L, Gong G, Zhang W, Zhu B, Hu Y (2014) De novo comparative transcriptome analysis of Acremonium chrysogenum: high-yield and wild-type strains of cephalosporin C producer. PLoS ONE 9:1–13
Martín JF, Demain AL (2002) Unraveling the methionine-cephalosporin puzzle in Acremonium chrysogenum. Trends Biotechnol 20:502–507
Nasution U, van Gulik WM, Ras C, Proell A, Heijnen JJ (2008) A metabolome study of the steady-state relation between central metabolism, amino acid biosynthesis and penicillin production in Penicillium chrysogenum. Metab Eng 10:10–23
Nelson DL, Cox MM (2008) Lehninger Principles of Biochemistry, 5th edn. W. H. Freeman and Company, New York
Nielsen J, Jorgensen H (1995) Metabolic control analysis of the penicillin biosynthesis pathway in a high-yielding strain of P. chrysogenum. Biotechnol Prog 11:299–305
Novodvorska M, Hayer K, Pullan ST, Wilson R, Blythe MJ, Stam H et al (2013) Trancriptional landscape of Aspergillus niger at breaking of conidial dormancy revealed by RNA-sequencing. BMC Genom 14:1–18
Schmitt EK, Hoff B, Kück U (2004) Regulation of cephalosporin biosynthesis. Adv Biochem Engin/Biotechnol 88:1–43
Telesnina GN, Bartoshevish YE, Krakhmaleva IN, Petyushenko RM, Sazykin YO, Navashin SM (1990) Bioenergetic parameters of Acremonium chrysogenum. J Basic Microbiol 30:273–278
Terfehr D, Dahlmann TA, Specht T, Zadra I, Kürnsteiner H, Kück U (2014) Genome sequence and annotation of Acremonium chrysogenum, producer of the beta-Lactam antibiotic cephalosporin C. Genome Announc 2:1–2
van Gulik WM, De Laat WTAM, Vinke JL, Heijnen JJ (2000) Application of metabolic flux analysis for the identification of metabolic bottlenecks in the biosynthesis of penicillin-G. Biotechnol Bioeng 68:602–618
Xu H, Andi B, Qian J, West AH, Cook PF (2006) The α-aminoadipate pathway for lysine biosynthesis in fungi. Cell Biochem Biophys 46:43–64
Yang Y, Lu H, Ding MZ, Jiang J, Chen Y, Yuan YJ (2012) Comparative analysis of intracellular metabolites of Cephalosporium acremonium in pilot and industrial fermentation processes. Biotechnol Appl Biochem 59:228–237
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by Ministry of Science and Technology of the People’s Republic of China (Grant No: 2011ZX09203-001-06) and Shanghai Municipal Science and Technology Commission (Grant No: 13431900204 and 11ZR1435200).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Han, S., Liu, Y., Xie, L. et al. Comparative expression profiling of genes involved in primary metabolism in high-yield and wild-type strains of Acremonium chrysogenum . Antonie van Leeuwenhoek 109, 357–369 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10482-015-0638-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10482-015-0638-5