Abstract
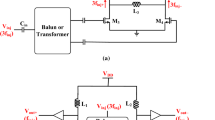
A low power and wide locking-range W-band (75–110 GHz) divide-by-2 direct injection-locked frequency-divider (DILFD) using standard 90 nm CMOS technology is reported. To enhance the operation frequency, distributed LC network is used as the load of the crossed-coupled transistors. To improve the input sensitivity, a power matching network is included at the injection terminal of the switch transistor. In addition, to enhance the frequency locking range, body bias technique (i.e. a body resistor in conjunction with a zero body-source bias) is adopted in the switch transistor to reduce its threshold voltage. The result shows that a wide locking-range of 23.5 GHz [from 69.5 to 93 GHz (28.9%)], covering the 77–81-GHz-band for short range automotive radar system and 81–86-GHz-band for high-speed point-to-point wireless communication access system, was achieved. The DILFD can be operated at a low input power of − 35 dBm, one of the best input sensitivity ever reported for a W-band CMOS divider. The power consumption of the DILFD was only 3 mW from a 0.7 V power supply. The chip area was only 0.76 × 0.66 mm2 excluding the test pads.









Similar content being viewed by others
References
Hwang, Y. J., Wang, H., & Chu, T. H. (2004). A W-band subharmonically pumped monolithic GaAas-based HEMT gate mixer. IEEE Microwave and Wireless Components Letters, 14(7), 313–315.
Jain, V., Tzeng, F., Zhou, L., & Heydari, P. (2009). A single-chip dual-band 22–29-GHz/77–81-GHz BiCMOS transceiver for automotive radars. IEEE Journal of Solid-State Circuits, 44(12), 3469–3485.
Chen, A. Y. K., Baeyens, Y., Chen, Y. K., & Lin, J. (2010). A low-power linear SiGe BiCMOS low-noise amplifier for millimeter-wave active imaging. IEEE Microwave and Wireless Components Letters, 20(2), 103–105.
Kallfass, I., Antes, J., Schneider, T., Kurz, F., Lopez-Diaz, D., Diebold, S., et al. (2011). All active MMIC-based wireless communication at 220 GHz. IEEE Transactions on Terahertz Science and Technology, 1(2), 477–487.
Chang, J. F., & Lin, Y. S. (2011). a high-performance distributed amplifier using multiple noise suppression techniques. IEEE Microwave and Wireless Components Letters, 21(9), 495–497.
Lin, Y. S., Chang, J. F., & Lu, S. S. (2011). Analysis and design of CMOS distributed amplifier using inductively-peaking cascaded gain cell for UWB systems. IEEE Transactions on Microwave Theory and Techniques, 59(10), 2513–2524.
Lin, Y. S., Chen, C. Z., Yang, H. Y., Chen, C. C., Lee, J. H., Huang, G. W., et al. (2010). Analysis and design of a CMOS UWB LNA with dual-RLC-branch wideband input matching network. IEEE Transactions on Microwave Theory and Techniques, 58(2), 287–296.
Chang, J. F., & Lin, Y. S. (2009). A 3–10 GHz low-power, low-noise CMOS distributed amplifier using splitting-load inductive peaking and noise-suppression techniques. IET Electronics Letters, 45(20), 1033–1035.
Chen, C. Z., Wang, C. C., Lin, Y. S., & Huang, G. W. (2011). CMOS (2.28 mW, 67.28–80.78 GHz) divide-by-4 direct injection-locked frequency divider using tunable LC source-degeneration. Microwave and Optical Technology Letters, 53(12), 2776–2781.
Lin, Y. S., Lee, J. H., Huang, S. L., Wang, C. H., Wang, C. C., & Lu, S. S. (2012). Design and analysis of a 21 ~ 29 GHz ultra-wideband receiver front-end in 0.18 μm CMOS technology. IEEE Microwave Theory and Techniques, 60(8), 2590–2604.
Lin, Y. S., Lan, K. S., Wang, C. C., & Li, G. H. (2017). Design and implementation of a 94 GHz CMOS down-conversion mixer with integrated miniature planar baluns for image radar sensors. Analog Integrated Circuits and Signal Processing, 91(3), 353–365.
Lin, Y. S., & Nguyen, V. K. (2017). 94 GHz CMOS power amplifiers using miniature dual Y-shaped combiner with RL load. IEEE Transactions on Circuits and Systems-I: Regular Papers (accepted for publication).
Lin, Y. S., Lan, K. S., Wang, C. C., Chi, C. C., & Lu, S. S. (2016). 6.3 mW 94 GHz CMOS down-conversion mixer with 11.6 dB gain and 54 dB LO-RF isolation. IEEE Microwave and Wireless Components Letters, 26(8), 604–606.
Lin, Y. S., Wen, W. C., & Wang, C. C. (2014). 13.6 mW 79 GHz CMOS up-conversion mixer with 2.1 dB gain and 35.9 dB LO-RF isolation. IEEE Microwave and Wireless Components Letters, 24(2), 126–128.
Wang, K. J., Rylyakov, A., & Yang, C. K. (2005). A broadband 44-GHz frequency divider in 90 nm CMOS. In IEEE compound semiconductor integrated circuits symposium (pp. 196–199).
Choi, W., Kim, K., & Kwon, Y. (2010). Ultra-low-power series-feedback frequency divider using 0.15 µm GaAs pHEMT’s at W-Band. Microwave and Wireless Components Letters, IEEE, 20, 634–636.
Wang, C. C., Chen, C. Z., & Lin, Y. S. (2011). CMOS direct injection-locked frequency divider (3.55 mW 80 GHz) with 26.3% locking range using distributed LC tank and body bias techniques. Microwave and Optical Technology Letters, 53(11), 2694–2697.
Tsai, K. H., Cho, L. C., Wu, J. H., & Liu, S. I. (2008). 3.5 mW W-band frequency divider with wide locking range in 90 nm CMOS technology. In IEEE international solid-state circuits conference (pp. 466–467).
Yun, J., Kim, H., Seo, H., & Rieh, J. S. (2012). A 140 GHz single-ended injection locked frequency divider with inductive feedback in SiGe HBT technology. In IEEE topical meeting on silicon monolithic integrated circuits in RF systems (pp. 61–64).
Chao, Y., & Luong, H. C. (2013). Analysis and design of a 2.9-mW 53.4–79.4-GHz frequency-tracking injection-locked frequency divider in 65-nm CMOS. IEEE Journal of Solid-State Circuits, 48(10), 2403–2418.
Gu, Q., Xu, Z., & Chang, M. C. F. (2007). A wide locking range and low power V-band frequency divider in 90 nm CMOS. In IEEE symposium on VLSI circuits (pp. 266–267).
Fu, H., Fei, W., Yu, H., & Ren, J. (2014). 60.8–67 GHz and 6.3 mW injection-locked frequency divider with switching-inductor loaded transformer in 65 nm CMOS. In IEEE MTT-S international microwave symposium (pp. 1–4).
Chen, Y. T., Li, M. W., Huang, T. H., & Chuang, H. R. (2010). A V-band CMOS direct injection-locked frequency divider using forward body bias technology. IEEE Microwave and Wireless Components Letters, 20, 396–398.
Kazuno, M., Motoyoshi, M., Kameda, S., & Suematsu, N. (2017). A 18.6 GHz locking range, 60 GHz band varactor-tuned injection locked frequency divider in 65 nm CMOS. In Global symposium on millimeter-waves (pp. 146–148).
Zhang, J., Liu, H., Wu, Y., Zhao, C., & Kang, K. (2017). A 27.9–53.5 GHz transformer-based injection-locked frequency divider with 62.9% locking range. In IEEE radio frequency integrated circuits symposium (pp. 324–327).
Imani, A., & Hashemi, H. (2017). Distributed injection-locked frequency dividers. IEEE Journal of Solid-State Circuits, 52(8), 2083–2093.
Mazzanti, A., Uggetti, P., & Svelto, F. (2004). Analysis and design of injection-locked LC dividers for quadrature generation. IEEE Journal of Solid-State Circuits, 39(9), 1425–1433.
Chang, J. F., & Lin, Y. S. (2010). Miniature 1.87-dB insertion-loss V-band CMOS bandpass filter with two enhanced finite transmission zeros. Microwave and Optical Technology Letters, 52(8), 1830–1836.
Pozar, D. M. (2005). Microwave engineering (3rd ed.). New York: Wiley.
Lin, Y. S., Chang, J. F., Liang, H. B., Wang, T., & Lu, S. S. (2007). High-performance transmission-line inductors for 30–60 GHz RFIC applications. IEEE Transactions on Electron Devices, 54(9), 2512–2519.
Acknowledgements
This work is supported by the Ministry of Science and Technology (MOST) of the R.O.C. under Contracts MOST103-2221-E-260-027-MY3 and MOST105-2221-E-260-025-MY3. The authors are very grateful for the supports from the National Chip Implementation Center (CIC), Taiwan, for chip fabrication, and National Nano-Device Laboratory (NDL), Taiwan, for measurements.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Lin, YS., Lan, KS. & Lin, HC. W-band CMOS direct injection-locked frequency divider with 23.5-GHz locking range using distributed LC network and power matching and body bias techniques. Analog Integr Circ Sig Process 99, 707–721 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10470-019-01427-9
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10470-019-01427-9