Abstract
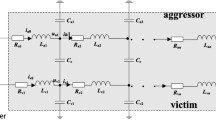
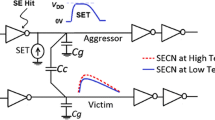
Due to scaling effects, integrated circuits are becoming more sensitive to transient pulses and delay effects caused by single event (SE) particles. In addition, cross-coupling effects among wires can cause SE transients to spread other paths of the circuit which may increase the SE vulnerability of CMOS circuits. The coupling effects among interconnects need to be considered in single event modeling and analysis of CMOS logic gates due to technology scaling effects that increase both SE vulnerability and crosstalk effects. This work studies the effect of SE coupling on circuit delays and proposes a worst-case delay estimation method for use in design automation tools for the first time to our knowledge. The SE coupling delay expressions derived show very good results in comparison to HSPICE results. Results show an average error of about 6.3 % for worst-case delay while allowing for very fast analysis in comparison to HSPICE.
















Similar content being viewed by others
References
Dodd, P. E., & Massengill, L. W. (2003). Basic mechanisms and modeling of single-event upset in digital microelectronics. IEEE Transactions on Nuclear Science, 50(3), 583–602.
Mitra, S., Karnik, T., Seifert, N., & Zhang, M. (2000). Logic soft errors in sub-65 nm technologies design and CAD challenges. In Proceedings on DAC, 2005 (pp. 2–3).
Normand, E. (1996). Single-event effects in avionics. IEEE Transactions on Nuclear Science, 43(2), 461–474.
Bradley, P. D., & Normand, E. (2004). Single event upset in implantable cardioverter defibrillators. IEEE Transactions on Nuclear Science, 45(6), 2929–2940.
Balasubramanian, A., Sternberg, A. L., Bhuva, B. L., & Massengill, L. W. (2006). Crosstalk effects caused by single event hits in deep sub-micron CMOS technologies. IEEE Transactions on Nuclear Science, 53(6), 3306–3311.
Sayil, S., Akkur, A. B., & Gaspard, N. (2009). Single event crosstalk shielding for CMOS logic. Microelectronics Journal, 40(6), 1000–1006.
Sayil, S., Wang, J., & Yeddula, S. R. (2013). Single event coupling soft errors in nanoscale CMOS circuits. IEEE Design & Test, 30, 89–96.
Heydari, P., & Pedram, M. (2005). Capacitive coupling noise in high-speed VLSI circuits. IEEE Transactions on Computer Aided Design, 24(3), 478–488.
Becer, M. R., Blaauw, D., Zolotov, V., Panda, R., & Hajj, I. N. (2002). Analysis of noise avoidance techniques in DSM interconnects using a complete crosstalk noise model. In Proceedings of 2002 design, automation and test in Europe conference (pp. 456–464).
Sayil, S., & Borra, U. K. (2009). A multiline model for time-efficient estimation of crosstalk. Analog Integrated Circuits and Signal Processing, 59(1), 65–75.
Balasubramanian, A., Amusan, O. A., Bhuva, B. L., Reed, R. A., Sternberg, A. L., Andrew, L., et al. (2008). Measurement and analysis of interconnect crosstalk due to single events in a 90 nm CMOS technology. IEEE Transactions on Nuclear Science, 55(4), 2079–2084.
Sayil, S., & Akkur, A. B. (2010). Mitigation for single event coupling delay. International Journal of Electronics, 97(1), 17–29.
Sayil, S., Boorla, V. K., & Yeddula, S. R. (2011). Modeling single event crosstalk in nanometer technologies. IEEE Transactions on Nuclear Science, 57(5), 2493–2502.
Liu, B., Cai, L., & Zhu, J. (2012). Accurate analytical model for single event (SE) crosstalk. IEEE Transactions on Nuclear Science, 59(4), 1621–1627.
Kawaguchi, H. & Sakurai, T. (1998). Delay and noise formulas for capacitively coupled distributed RC lines. In Proceedings of Asian South Pacific design automatic conference (pp. 35–38).
Predictive Technology Model (PTM). (2013). http://www.eas.asu.edu/~ptm.
Kahng, A. B., Muddu, S., & Sarto, E. (2000). On switch factor based analysis of coupled RC interconnects. In Proceedings on ACM/IEEE design automation conference (pp. 79–84).
Rajappan, V. & Sapatnekar, S. S. (2003). An efficient algorithm for calculating the worst-case delay due to crosstalk. In Proceedings of 21st international conference on computer design (pp. 76–81).
Dartu, F. & Pileggi, L. T. (1997). Calculating worst-case gate delays due to dominant capacitance coupling. In Proceedings on ACM/IEEE design automation conference (pp. 46–51).
Kauppila, J. S., Sternberg, A. L., Alles, M. L., Francis, A. M., Holmes, J., Amusan, O. A., & Massengill, L. W. (2009). A bias dependent single-event compact model implemented into BSIM4 and a 90 nm CMOS process design kit. IEEE Transactions on Nuclear Science, 56(6), 3152–3157.
DasGupta, S., Witulski, A. F., Bhuva, B., Alles, M., Massengill, L. W., Amusan, O. A., et al. (2007). Effect of well and substrate potential modulation on single event pulse shape in deep submicron CMOS. IEEE Transactions on Nuclear Science, 54(6), 2407–2412.
Garg, R. & Khatri, S. (2009). 3D simulation and analysis of the radiation tolerance of voltage scaled digital circuits. Presented at the 2009 IEEE workshop on silicon errors in logic—System effects, Stanford, CA.
Naseer, R., Draper, J., Boulghassoul, Y., DasGupta, S., & Witulski, A. (2007). Critical charge and set pulse widths for combinational logic in commercial 90 nm CMOS technology. In Proceedings of the 17th Great Lakes symposiums on VLSI (pp. 227–230).
Uznanski, S., Gasiot, G., Roche, P., Autran, J. L., & Tavernier, C. (2010). Single event upset and multiple cell upset modeling in commercial bulk 65 nm CMOS SRAMs and flip-flops. IEEE Transactions on Nuclear Science, 57(4), 1876–1883.
Levy, R., Blaauw, D., Braca, G., Dasgupta, A., Grinshpon, A., Oh, C., Orshav, B., Sirichotiyakul, S., & Zolotov, V. (2002). Clarinet: A noise analysis tool for deep submicron design. In Proceedings of international conference on C.A.D. (pp. 587–594).
Choudhury, M. R., Zhou, Q., & Mohanram, K. (2006). Design optimization for single-event upset robustness using simultaneous dual-VDD and sizing techniques. In Proceedings of the 2006 IEEE/ACM international conference on C.A.D. (pp. 204–209).
Wirth, G., Vierira, M., & Kastensmidt, F. L. (2007). Accurate and computer efficient modelling of single event transients in CMOS circuits. IET Circuits, Devices and Systems, 1(2), 137–142.
Qian, J., Pullela, S., & Pillage, L. T. (1994). Modeling the effective capacitance for the RC interconnect of CMOS gates. IEEE Transactions on Comput-Aided Design, 13(12), 1526–1535.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
This work was supported in part by the Research Enhancement Grant (#420224) from Lamar University.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Sayil, S., Yao, Y. Single event coupling delay estimation in nanometer technologies. Analog Integr Circ Sig Process 86, 215–225 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10470-015-0670-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10470-015-0670-4