Abstract
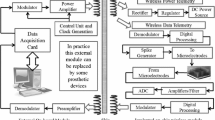
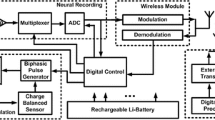
Here we present a low-power 16 channel neural signal measurement and stimulation system. The gain and high-pass corner frequency are programmable from 100 to 5000 and from 0.5 to 900 Hz, respectively. All channels can also be configured as outputs to electrically stimulate neurons by bipolar current pulses. The amplifying stage consists of 16 pre-amplifiers, a multiplexer and two broadband post-amplifiers. The measured signal is digitized with a 10-bit SAR A/D converter. The circuit contains a control logic for buffering the measured results and sending them into an SPI bus that is used to stream the data to a PC at 3.5 Mbps. The logic can also control the circuit’s bias currents, high-pass corner frequency, post-amplifier gains and stimulation current strengths. The mixed-signal circuit is manufactured with a low-cost 0.35 µm 4M2P IC process. The circuit consumes 1.29–1.59 mW power, depending on the amplifying gain.

















Similar content being viewed by others
References
Du, J., et al. (2009). High-resolution three-dimensional extracellular recording of neuronal activity with microfabricated electrode arrays. Journal of Neurophysiology, 101(3), 1671–1678.
Jochum, T., Denison, T., & Wolf, P. (2009). Integrated circuit amplifiers for multi-electrode intracortical recording. Journal of Neural Engineering, 6(1), 1–26.
Avestruz, A.-T., Santa, W., Carlson, D., Jensen, R., Stanslaski, S., Helfenstine, A., & Denison, T. (2008). A 5 µW/channel spectral analysis IC for chronic bidirectional brain-machine interfaces. IEEE Journal of Solid-State Circuits, 43(12), 3006–3024.
Aziz, J., Abdelhalim, K., Shulyzki, R., Genov, R., Bardakjian, B., Derchansky, M., et al. (2009). 256-channel neural recording and delta compression microsystem with 3D electrodes. IEEE Journal of Solid-State Circuits, 44(3), 995–1005.
Chae, M. S., Yang, Z., Yuce, M., Hoang, L., & Liu, W. (2009). A 128-channel 6 mW wireless neural recording IC with spike feature extraction and UWB transmitter. IEEE Transactions on Neural Systems and Rehabilitation Engineering, 17(4), 312–321.
Harrison, R. R., Watkins, P. T., Kier, R. J., Lovejoy, R. O., Black, D. J., Greger, B., & Solzbacher, F. (2007). A low-power integrated circuit for a wireless 100-electrode neural recording system. IEEE Journal of Solid-State Circuits, 42(1), 123–133.
Mollazadeh, M., Murari, K., Cauwenberghs, G., & Thakor, N. (2009). Micropower CMOS integrated low-noise amplification, filtering, and digitization of multimodal neuropotentials. IEEE Transactions on Biomedical Circuits and Systems, 3(1), 1–10.
Muller, R., Gambini, S., & Rabaey, J. (2012). A 0.013 mm2, 5 µW, DC-coupled neural signal acquisition IC with 0.5 V supply. IEEE Journal of Solid-State Circuits, 47(1), 232–243.
Olsson, R., Buhl, D., Sirota, A., Buzsaki, G., & Wise, K. (2005). Band tunable and multiplexed integrated circuits for simultaneous recording and stimulation with microelectrode arrays. IEEE Transactions on Biomedical Engineering, 52(7), 1303–1311.
Perelman, Y., & Ginosar, R. (2007). An integrated system for multichannel neuronal recording with spike/LFP separation, integrated A/D conversion and threshold detection. IEEE Transactions on Biomedical Engineering, 54(1), 130–137.
Shahrokhi, F., Abdelhalim, K., Serletis, D., Carlen, P. L., & Genov, R. (2010). The 128-channel fully differential digital integrated neural recording and stimulation interface. IEEE Transactions on Biomedical Circuits and Systems, 4(3), 149–161.
Sodagar, A., Perlin, G., Yao, Y., Najafi, K., & Wise, K. (2009). An implantable 64-channel wireless microsystem for single-unit neural recording. IEEE Journal of Solid-State Circuits, 44(9), 2591–2604.
Zou, X., Xu, X., Yao, L., & Lian, Y. (2010). A 1-V 450-nW fully integrated programmable biomedical sensor interface chip. IEEE Journal of Solid-State Circuits, 44(4), 1067–1077.
Gosselin, B., Ayoub, A. E., Roy, J.-F., Sawan, M., Lepore, F., Chaudhuri, A., & Guitton, D. (2009). A mixed-signal multichip neural recording interface with bandwidth reduction. IEEE Transactions on Biomedical Circuits and Systems, 3, 129–141.
Kmon, P., & Grybos, P. (2013). Energy efficient low-noise multichannel neural amplifier in submicron CMOS process. IEEE Transactions on Circuits and Systems I: Regular Papers, 60(7), 1764–1775.
O. Kursu & T. Rahkonen. (2014). Integrated circuit for neural recording and stimulation. In Proceedings of 32nd Nordic Microelectronics Conference NORCHIP, Oct. 27–28, 2014, Tampere, Finland.
S.-M. Chin, C.-C. Hsieh, C.-F. Chiu, & H.-H. Tsai. (2010). A new rail-to-rail comparator with adaptive power control for low power SAR ADCs in biomedical application. In Proceedings of 2010 IEEE International Symposium on Circuits and Systems (ISCAS), pp. 1575–1578.
S. Lan, C. Yuan, Y. Lam, & L. Siek. (2011). An ultra-low-power rail-to-rail comparator for ADC designs. In Proceedings of IEEE 54th International Midwest Symposium on Circuits and Systems (MWSCAS), pp. 1–4.
Agnes, A., Bonizzoni, E., Malcovati, P., & Maloberti, F. (2010). An ultralow power successive approximation A/D converter with time-domain comparator. Analog Integrated Circuits and Signal Processing, 64(2), 183–190.
Steyaert, M. S. J., & Sansen, W. M. C. (1987). A micropower low-noise monolithic instrumentation amplifier for medical purposes. IEEE Journal of Solid-State Circuits, 22(6), 1163–1168.
Acknowledgments
The authors wish to thank Senior Technician Matti Polojärvi for chip bonding.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kursu, O., Vähäsöyrinki, M. & Rahkonen, T. Integrated 16-channel neural recording and stimulation circuit. Analog Integr Circ Sig Process 84, 363–372 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10470-015-0593-0
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10470-015-0593-0