Abstract
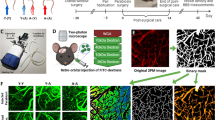
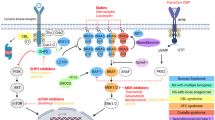
Current treatments of brain arteriovenous malformation (BAVM) are associated with considerable risks and at times incomplete efficacy. Therefore, a clinically consistent animal model of BAVM is urgently needed to investigate its underlying biological mechanisms and develop innovative treatment strategies. Notably, existing mouse models have limited utility due to heterogenous and untypical phenotypes of AVM lesions. Here we developed a novel mouse model of sporadic BAVM that is consistent with clinical manifestations in humans. Mice with BrafV600E mutations in brain ECs developed BAVM closely resembled that of human lesions. This strategy successfully induced BAVMs in mice across different age groups and within various brain regions. Pathological features of BAVM were primarily dilated blood vessels with reduced vascular wall stability, accompanied by spontaneous hemorrhage and neuroinflammation. Single-cell sequencing revealed differentially expressed genes that were related to the cytoskeleton, cell motility, and intercellular junctions. Early administration of Dabrafenib was found to be effective in slowing the progression of BAVMs; however, its efficacy in treating established BAVM lesions remained uncertain. Taken together, our proposed approach successfully induced BAVM that closely resembled human BAVM lesions in mice, rendering the model suitable for investigating the pathogenesis of BAVM and assessing potential therapeutic strategies.








Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
No datasets were generated or analysed during the current study.
References
Solomon RA, Connolly ES Jr (2017) Arteriovenous malformations of the brain. N Engl J Med 376(19):1859–1866. https://doi.org/10.1056/NEJMra1607407
Hong T, Yan Y, Li J, Radovanovic I, Ma X, Shao YW, Yu J, Ma Y, Zhang P, Ling F, Huang S, Zhang H, Wang Y (2019) High prevalence of KRAS/BRAF somatic mutations in brain and spinal cord arteriovenous malformations. Brain 142(1):23–34. https://doi.org/10.1093/brain/awy307
Stapf C, Labovitz DL, Sciacca RR, Mast H, Mohr JP, Sacco RL (2002) Incidence of adult brain arteriovenous malformation hemorrhage in a prospective population-based stroke survey. Cerebrovasc Dis 13(1):43–46. https://doi.org/10.1159/000047745
van Beijnum J, van der Worp HB, Buis DR, Al-Shahi Salman R, Kappelle LJ, Rinkel GJ, van der Sprenkel JW, Vandertop WP, Algra A, Klijn CJ (2011) Treatment of brain arteriovenous malformations: a systematic review and meta-analysis. JAMA 306(18):2011–2019. https://doi.org/10.1001/jama.2011.1632
Raper DMS, Winkler EA, Rutledge WC, Cooke DL, Abla AA (2020) An update on medications for brain arteriovenous malformations. Neurosurgery 87(5):871–878. https://doi.org/10.1093/neuros/nyaa192
Crist AM, Zhou X, Garai J, Lee AR, Thoele J, Ullmer C, Klein C, Zabaleta J, Meadows SM (2019) Angiopoietin-2 inhibition rescues arteriovenous malformation in a Smad4 Hereditary Hemorrhagic Telangiectasia Mouse Model. Circulation 139(17):2049–2063. https://doi.org/10.1161/CIRCULATIONAHA.118.036952
Han C, Lang MJ, Nguyen CL, Luna Melendez E, Mehta S, Turner GH, Lawton MT, Oh SP (2021) Novel experimental model of brain arteriovenous malformations using conditional Alk1 gene deletion in transgenic mice. J Neurosurg 1–12. https://doi.org/10.3171/2021.6.JNS21717
Ola R, Kunzel SH, Zhang F, Genet G, Chakraborty R, Pibouin-Fragner L, Martin K, Sessa W, Dubrac A, Eichmann A (2018) SMAD4 prevents Flow Induced Arteriovenous malformations by inhibiting casein kinase 2. Circulation 138(21):2379–2394. https://doi.org/10.1161/CIRCULATIONAHA.118.033842
Bharatha A, Faughnan ME, Kim H, Pourmohamad T, Krings T, Bayrak-Toydemir P, Pawlikowska L, McCulloch CE, Lawton MT, Dowd CF, Young WL, Terbrugge KG (2012) Brain arteriovenous malformation multiplicity predicts the diagnosis of hereditary hemorrhagic telangiectasia: quantitative assessment. Stroke 43(1):72–78. https://doi.org/10.1161/STROKEAHA.111.629865
Yang W, Liu A, Hung AL, Braileanu M, Wang JY, Caplan JM, Colby GP, Coon AL, Tamargo RJ, Ahn ES, Huang J (2016) Lower risk of intracranial arteriovenous malformation hemorrhage in patients with Hereditary Hemorrhagic Telangiectasia. Neurosurgery 78(5):684–693. https://doi.org/10.1227/NEU.0000000000001103
Al-Olabi L, Polubothu S, Dowsett K, Andrews KA, Stadnik P, Joseph AP, Knox R, Pittman A, Clark G, Baird W, Bulstrode N, Glover M, Gordon K, Hargrave D, Huson SM, Jacques TS, James G, Kondolf H, Kangesu L, Keppler-Noreuil KM, Khan A, Lindhurst MJ, Lipson M, Mansour S, O’Hara J, Mahon C, Mosica A, Moss C, Murthy A, Ong J, Parker VE, Riviere JB, Sapp JC, Sebire NJ, Shah R, Sivakumar B, Thomas A, Virasami A, Waelchli R, Zeng Z, Biesecker LG, Barnacle A, Topf M, Semple RK, Patton EE, Kinsler VA (2018) Mosaic RAS/MAPK variants cause sporadic vascular malformations which respond to targeted therapy. J Clin Invest 128(4):1496–1508. https://doi.org/10.1172/JCI98589
Nikolaev SI, Vetiska S, Bonilla X, Boudreau E, Jauhiainen S, Rezai Jahromi B, Khyzha N, DiStefano PV, Suutarinen S, Kiehl TR, Mendes Pereira V, Herman AM, Krings T, Andrade-Barazarte H, Tung T, Valiante T, Zadeh G, Tymianski M, Rauramaa T, Yla-Herttuala S, Wythe JD, Antonarakis SE, Frosen J, Fish JE, Radovanovic I (2018) Somatic activating KRAS mutations in arteriovenous malformations of the brain. N Engl J Med 378(3):250–261. https://doi.org/10.1056/NEJMoa1709449
Park ES, Kim S, Huang S, Yoo JY, Korbelin J, Lee TJ, Kaur B, Dash PK, Chen PR, Kim E (2021) Selective endothelial hyperactivation of oncogenic KRAS induces brain arteriovenous malformations in mice. Ann Neurol 89(5):926–941. https://doi.org/10.1002/ana.26059
Scherschinski L, Han C, Kim YH, Winkler EA, Catapano JS, Schriber TD, Vajkoczy P, Lawton MT, Oh SP (2023) Localized conditional induction of brain arteriovenous malformations in a mouse model of hereditary hemorrhagic telangiectasia. Angiogenesis. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10456-023-09881-w
Dankort D, Filenova E, Collado M, Serrano M, Jones K, McMahon M (2007) A new mouse model to explore the initiation, progression, and therapy of BRAFV600E-induced lung tumors. Genes Dev 21(4):379–384. https://doi.org/10.1101/gad.1516407
Fish JE, Flores Suarez CP, Boudreau E, Herman AM, Gutierrez MC, Gustafson D, DiStefano PV, Cui M, Chen Z, De Ruiz KB, Schexnayder TS, Ward CS, Radovanovic I, Wythe JD (2020) Somatic gain of KRAS function in the endothelium is sufficient to cause vascular malformations that require MEK but not PI3K signaling. Circ Res 127(6):727–743. https://doi.org/10.1161/CIRCRESAHA.119.316500
Ren AA, Snellings DA, Su YS, Hong CC, Castro M, Tang AT, Detter MR, Hobson N, Girard R, Romanos S, Lightle R, Moore T, Shenkar R, Benavides C, Beaman MM, Muller-Fielitz H, Chen M, Mericko P, Yang J, Sung DC, Lawton MT, Ruppert JM, Schwaninger M, Korbelin J, Potente M, Awad IA, Marchuk DA, Kahn ML (2021) PIK3CA and CCM mutations fuel cavernomas through a cancer-like mechanism. Nature 594(7862):271–276. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41586-021-03562-8
Qiu B, Zhao Z, Wang N, Feng Z, Chen XJ, Chen W, Sun W, Ge WP, Wang Y (2023) A systematic observation of vasodynamics from different segments along the cerebral vasculature in the penumbra zone of awake mice following cerebral ischemia and recanalization. J Cereb Blood Flow Metab 43(5):665–679. https://doi.org/10.1177/0271678X221146128
Ren J, Huang Y, Ren Y, Tu T, Qiu B, Ai D, Bi Z, Bai X, Li F, Li JL, Chen XJ, Feng Z, Guo Z, Lei J, Tian A, Cui Z, Lindner V, Adams RH, Wang Y, Zhao F, Korbelin J, Sun W, Wang Y, Zhang H, Hong T, Ge WP (2023) Somatic variants of MAP3K3 are sufficient to cause cerebral and spinal cord cavernous malformations. Brain. https://doi.org/10.1093/brain/awad104
Peng J, Pang J, Huang L, Enkhjargal B, Zhang T, Mo J, Wu P, Xu W, Zuo Y, Peng J, Zuo G, Chen L, Tang J, Zhang JH, Jiang Y (2019) LRP1 activation attenuates white matter injury by modulating microglial polarization through Shc1/PI3K/Akt pathway after subarachnoid hemorrhage in rats. Redox Biol 21:101121. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.redox.2019.101121
Smith LK, Parmenter T, Kleinschmidt M, Kusnadi EP, Kang J, Martin CA, Lau P, Patel R, Lorent J, Papadopoli D, Trigos A, Ward T, Rao AD, Lelliott EJ, Sheppard KE, Goode D, Hicks RJ, Tiganis T, Simpson KJ, Larsson O, Blythe B, Cullinane C, Wickramasinghe VO, Pearson RB, McArthur GA (2022) Adaptive translational reprogramming of metabolism limits the response to targeted therapy in BRAF(V600) melanoma. Nat Commun 13(1):1100. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41467-022-28705-x
Tu T, Yin S, Pang J, Zhang X, Zhang L, Zhang Y, Xie Y, Guo K, Chen L, Peng J, Jiang Y (2021) Irisin contributes to Neuroprotection by promoting mitochondrial Biogenesis after experimental subarachnoid hemorrhage. Front Aging Neurosci 13:640215. https://doi.org/10.3389/fnagi.2021.640215
Yang X, Dai Z, Gao C, Yin Y, Shi C, Liu R, Zhuge Q, Huang Y, Zhou B, Han Z, Zheng X (2022) Cerebral cavernous malformation development in chronic mouse models driven by dual recombinases induced gene deletion in brain endothelial cells. J Cereb Blood Flow Metab 42(12):2230–2244. https://doi.org/10.1177/0271678X221105995
Lu Y, Dai Y, Ou S, Miao Y, Wang Y, Liu Q, Wang Y, Wei P, Shan Y, Zhao G (2022) Using a bipolar electrode to create a temporal lobe Epilepsy Mouse Model by Electrical Kindling of the Amygdala. J Vis Exp 184. https://doi.org/10.3791/64113
Racine RJ (1972) Modification of seizure activity by electrical stimulation. II. Motor seizure. Electroencephalogr Clin Neurophysiol 32(3):281–294. https://doi.org/10.1016/0013-4694(72)90177-0
Liew JA, Yang W, Mashouf LA, Li S, Caplan JM, Tamargo RJ, Huang J (2020) Incidence of spontaneous obliteration in untreated brain arteriovenous malformations. Neurosurgery 86(1):139–149. https://doi.org/10.1093/neuros/nyz047
Chen CJ, Ding D, Derdeyn CP, Lanzino G, Friedlander RM, Southerland AM, Lawton MT, Sheehan JP (2020) Brain arteriovenous malformations: a review of natural history, pathobiology, and interventions. Neurology 95(20):917–927. https://doi.org/10.1212/WNL.0000000000010968
Sun Z, Kemp SS, Lin PK, Aguera KN, Davis GE (2022) Endothelial k-RasV12 expression induces Capillary Deficiency attributable to marked Tube Network expansion coupled to reduced pericytes and basement membranes. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol 42(2):205–222. https://doi.org/10.1161/ATVBAHA.121.316798
Zhang H, Peng H, Yan D, Wang K, Yuan K, Chen Y, Li Z, Li R, Li R, Lu J, Chen X, Ye X, Wang H, Zhao Y, Hao Q (2023) The micro-pathological characteristics in cerebral arteriovenous malformations(cAVMs). Microvasc Res 145:104452. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.mvr.2022.104452
Winkler EA, Birk H, Burkhardt JK, Chen X, Yue JK, Guo D, Rutledge WC, Lasker GF, Partow C, Tihan T, Chang EF, Su H, Kim H, Walcott BP, Lawton MT (2018) Reductions in brain pericytes are associated with arteriovenous malformation vascular instability. J Neurosurg 129(6):1464–1474. https://doi.org/10.3171/2017.6.JNS17860
Tu J, Stoodley MA, Morgan MK, Storer KP (2006) Ultrastructure of perinidal capillaries in cerebral arteriovenous malformations. Neurosurgery 58(5):961–970 discussion 961–970. https://doi.org/10.1227/01.NEU.0000210248.39504.B5
Rustenhoven J, Tanumihardja C, Kipnis J (2021) Cerebrovascular anomalies: perspectives from Immunology and Cerebrospinal Fluid Flow. Circ Res 129(1):174–194. https://doi.org/10.1161/CIRCRESAHA.121.318173
Winkler EA, Kim CN, Ross JM, Garcia JH, Gil E, Oh I, Chen LQ, Wu D, Catapano JS, Raygor K, Narsinh K, Kim H, Weinsheimer S, Cooke DL, Walcott BP, Lawton MT, Gupta N, Zlokovic BV, Chang EF, Abla AA, Lim DA, Nowakowski TJ (2022) A single-cell atlas of the normal and malformed human brain vasculature. Science 375(6584):eabi7377. https://doi.org/10.1126/science.abi7377
Kalucka J, de Rooij L, Goveia J, Rohlenova K, Dumas SJ, Meta E, Conchinha NV, Taverna F, Teuwen LA, Veys K, Garcia-Caballero M, Khan S, Geldhof V, Sokol L, Chen R, Treps L, Borri M, de Zeeuw P, Dubois C, Karakach TK, Falkenberg KD, Parys M, Yin X, Vinckier S, Du Y, Fenton RA, Schoonjans L, Dewerchin M, Eelen G, Thienpont B, Lin L, Bolund L, Li X, Luo Y, Carmeliet P (2020) Single-cell transcriptome atlas of murine endothelial cells. Cell 180(4):764–779e720. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cell.2020.01.015
Judith D, Versapuech M, Bejjani F, Palaric M, Verlhac P, Kuster A, Lepont L, Gallois-Montbrun S, Janvier K, Berlioz-Torrent C (2023) ATG5 selectively engages virus-tethered BST2/tetherin in an LC3C-associated pathway. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 120(20):e2217451120. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.2217451120
Kong N, Shan T, Wang H, Jiao Y, Zuo Y, Li L, Tong W, Yu L, Jiang Y, Zhou Y, Li G, Gao F, Yu H, Zheng H, Tong G (2020) BST2 suppresses porcine epidemic diarrhea virus replication by targeting and degrading virus nucleocapsid protein with selective autophagy. Autophagy 16(10):1737–1752. https://doi.org/10.1080/15548627.2019.1707487
Sun X, Zeng H, Kumar A, Belser JA, Maines TR, Tumpey TM (2016) Constitutively expressed IFITM3 protein in human endothelial cells poses an early infection block to human influenza viruses. J Virol 90(24):11157–11167. https://doi.org/10.1128/JVI.01254-16
Hur JY, Frost GR, Wu X, Crump C, Pan SJ, Wong E, Barros M, Li T, Nie P, Zhai Y, Wang JC, Tcw J, Guo L, McKenzie A, Ming C, Zhou X, Wang M, Sagi Y, Renton AE, Esposito BT, Kim Y, Sadleir KR, Trinh I, Rissman RA, Vassar R, Zhang B, Johnson DS, Masliah E, Greengard P, Goate A, Li YM (2020) The innate immunity protein IFITM3 modulates gamma-secretase in Alzheimer’s disease. Nature 586(7831):735–740. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41586-020-2681-2
Malik MNH, Waqas SF, Zeitvogel J, Cheng J, Geffers R, Gouda ZA, Elsaman AM, Radwan AR, Schefzyk M, Braubach P, Auber B, Olmer R, Musken M, Roesner LM, Gerold G, Schuchardt S, Merkert S, Martin U, Meissner F, Werfel T, Pessler F (2022) Congenital deficiency reveals critical role of ISG15 in skin homeostasis. J Clin Invest 132(3). https://doi.org/10.1172/JCI141573
Colonne PM, Sahni A, Sahni SK (2011) Rickettsia conorii infection stimulates the expression of ISG15 and ISG15 protease UBP43 in human microvascular endothelial cells. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 416(1–2):153–158. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bbrc.2011.11.015
Zhang W, Li Y, Xin S, Yang L, Jiang M, Xin Y, Wang Y, Cao P, Zhang S, Yang Y, Lu J (2023) The emerging roles of IFIT3 in antiviral innate immunity and cellular biology. J Med Virol 95(1):e28259. https://doi.org/10.1002/jmv.28259
Choi YJ, Bowman JW, Jung JU (2018) A talented duo: IFIT1 and IFIT3 Patrol viral RNA caps. Immunity 48(3):474–476. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.immuni.2018.03.001
Lupieri A, Smirnova NF, Solinhac R, Malet N, Benamar M, Saoudi A, Santos-Zas I, Zeboudj L, Ait-Oufella H, Hirsch E, Ohayon P, Lhermusier T, Carrie D, Arnal JF, Ramel D, Gayral S, Laffargue M (2020) Smooth muscle cells-derived CXCL10 prevents endothelial healing through PI3Kgamma-dependent T cells response. Cardiovasc Res 116(2):438–449. https://doi.org/10.1093/cvr/cvz122
Secchiero P, Corallini F, di Iasio MG, Gonelli A, Barbarotto E, Zauli G (2005) TRAIL counteracts the proadhesive activity of inflammatory cytokines in endothelial cells by down-modulating CCL8 and CXCL10 chemokine expression and release. Blood 105(9):3413–3419. https://doi.org/10.1182/blood-2004-10-4111
Pollard TD, Cooper JA (2009) Actin, a central player in cell shape and movement. Science 326(5957):1208–1212. https://doi.org/10.1126/science.1175862
Gudimchuk NB, McIntosh JR (2021) Regulation of microtubule dynamics, mechanics and function through the growing tip. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol 22(12):777–795. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41580-021-00399-x
Lechler T, Mapelli M (2021) Spindle positioning and its impact on vertebrate tissue architecture and cell fate. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol 22(10):691–708. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41580-021-00384-4
Niziol M, Zinczuk J, Zareba K, Guzinska-Ustymowicz K, Pryczynicz A (2021) Immunohistochemical analysis of the expression of adhesion proteins: TNS1, TNS2 and TNS3 in correlation with clinicopathological parameters in gastric Cancer. Biomolecules 11(5). https://doi.org/10.3390/biom11050640
Lee YJ, Yamada S, Lo SH (2023) Phase transition of tensin-1 during the focal adhesion disassembly and cell division. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 120(15):e2303037120. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.2303037120
Balbuena P, Li W, Ehrich M (2011) Assessments of tight junction proteins occludin, claudin 5 and scaffold proteins ZO1 and ZO2 in endothelial cells of the rat blood-brain barrier: cellular responses to neurotoxicants malathion and lead acetate. Neurotoxicology 32(1):58–67. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neuro.2010.10.004
Xu J, Kausalya PJ, Van Hul N, Caldez MJ, Xu S, Ong AGM, Woo WL, Mohamed Ali S, Kaldis P, Hunziker W (2021) Protective functions of ZO-2/Tjp2 expressed in Hepatocytes and Cholangiocytes Against Liver Injury and Cholestasis. Gastroenterology 160(6):2103–2118. https://doi.org/10.1053/j.gastro.2021.01.027
Kotelevets L, Chastre E (2021) A New Story of the three magi: scaffolding proteins and lncRNA suppressors of Cancer. Cancers (Basel) 13(17). https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers13174264
Tsukita S, Furuse M (1999) Occludin and claudins in tight-junction strands: leading or supporting players? Trends Cell Biol 9(7):268–273. https://doi.org/10.1016/s0962-8924(99)01578-0
Chen F, Ohashi N, Li W, Eckman C, Nguyen JH (2009) Disruptions of occludin and claudin-5 in brain endothelial cells in vitro and in brains of mice with acute liver failure. Hepatology 50(6):1914–1923. https://doi.org/10.1002/hep.23203
Jarvelin P, Wright R, Pekonen H, Keranen S, Rauramaa T, Frosen J (2020) Histopathology of brain AVMs part I: microhemorrhages and changes in the nidal vessels. Acta Neurochir (Wien) 162(7):1735–1740. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00701-020-04391-w
Wright R, Jarvelin P, Pekonen H, Keranen S, Rauramaa T, Frosen J (2020) Histopathology of brain AVMs part II: inflammation in arteriovenous malformation of the brain. Acta Neurochir (Wien) 162(7):1741–1747. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00701-020-04328-3
Sandalcioglu IE, Wende D, Eggert A, Muller D, Roggenbuck U, Gasser T, Wiedemayer H, Stolke D (2006) Vascular endothelial growth factor plasma levels are significantly elevated in patients with cerebral arteriovenous malformations. Cerebrovasc Dis 21(3):154–158. https://doi.org/10.1159/000090526
Kciuk M, Gielecinska A, Budzinska A, Mojzych M, Kontek R (2022) Metastasis and MAPK pathways. Int J Mol Sci 23(7). https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms23073847
Murphy PA, Kim TN, Huang L, Nielsen CM, Lawton MT, Adams RH, Schaffer CB, Wang RA (2014) Constitutively active Notch4 receptor elicits brain arteriovenous malformations through enlargement of capillary-like vessels. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 111(50):18007–18012. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.1415316111
Boon LM, Dekeuleneer V, Coulie J, Marot L, Bataille AC, Hammer F, Clapuyt P, Jeanjean A, Dompmartin A, Miikka Vikkula M Case report study of thalidomide therapy in 18 patients with severe arteriovenous malformations. Nat Cardiovasc Res 1, 562–567. https://doi.org/10.1038/s44161-022-00080-2
Acknowledgements
We thank the lab members at Zhang and Hong lab and colleagues from China International Neuroscience Institute. This work is supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (No. 82220108010, 81971104, 82201439, 82122020, 82101369, 82102009 and 82330038). Beijing Municipal Commission of Education (BPHR20220113).
Funding
This work is supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (No. 82220108010, 81971104, 82201439, 82122020, 82101369, 82102009 and 82330038). Beijing Municipal Commission of Education (BPHR20220113).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
TT, JY and TH conceptualized the study and designed experiments; TT, JY and CJ conducted the majority of experiments with help from JL, JR, YZ, ZC, HL, XM, and ZW; CJ and DX performed the bioinformatic analysis; all authors acquired data; TT and JY analysed the data; TT, JY and TH wrote the original draft of the manuscript; JY, HZ and TH secured funding; all authors edited and approved the manuscript.
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Data sharing statement
The authors confirmed that all the data that supported the conclusions of this study have been included in the main article and its supplementary material. Additional data derived from this study, which also supported the presented findings, can be obtained by contacting the corresponding authors.
Consent to participate
Informed consent was obtained from all individual participants included in the study.
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Tu, T., Yu, J., Jiang, C. et al. Somatic BrafV600E mutation in the cerebral endothelium induces brain arteriovenous malformations. Angiogenesis (2024). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10456-024-09918-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10456-024-09918-8