Abstract
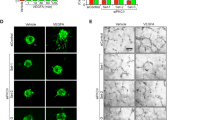
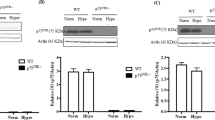
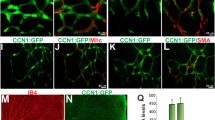
NADPH oxidase 4 (Nox4) is a major isoform of NADPH oxidases playing an important role in many biological processes. Previously we have shown that Nox4 is highly expressed in retinal blood vessels and is upregulated in oxygen-induced retinopathy (OIR). However, the exact role of endothelial Nox4 in retinal angiogenesis remains elusive. Herein, using endothelial cell (EC)-specific Nox4 knockout (Nox4EC−KO) mice, we investigated the impact of endothelial Nox4 deletion on retinal vascular development and pathological angiogenesis during OIR. Our results show that deletion of Nox4 in ECs led to retarded retinal vasculature development with fewer, blunted-end tip cells and sparser, dysmorphic filopodia at vascular front, and reduced density of vascular network in superficial, deep, and intermediate layers in postnatal day 7 (P7), P12, and P17 retinas, respectively. In OIR, loss of endothelial Nox4 had no effect on hyperoxia-induced retinal vaso-obliteration at P9 but significantly reduced aberrant retinal neovascularization at P17 and decreased the deep layer capillary density at P25. Ex vivo study confirmed that lack of Nox4 in ECs impaired vascular sprouting. Mechanistically, loss of Nox4 significantly reduced expression of VEGF, p-VEGFR2, integrin αV, angiopoietin-2, and p-ERK1/2, attenuating EC migration and proliferation. Taken together, our results indicate that endothelial Nox4 is important for retinal vascular development and contributes to pathological angiogenesis, likely through regulation of VEGF/VEGFR2 and angiopoietin-2/integrin αV/ERK pathways. In addition, our study suggests that endothelial Nox4 appears to be essential for intraretinal revascularization after hypoxia. These findings call for caution on targeting endothelial Nox4 in ischemic/hypoxic retinal diseases.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Carmeliet P, Jain RK (2011) Molecular mechanisms and clinical applications of angiogenesis. Nature 473(7347):298–307. https://doi.org/10.1038/nature10144
Potente M, Carmeliet P (2017) The link between angiogenesis and endothelial metabolism. Annu Rev Physiol 79:43–66. https://doi.org/10.1146/annurev-physiol-021115-105134
Gerhardt H, Golding M, Fruttiger M, Ruhrberg C, Lundkvist A, Abramsson A, Jeltsch M, Mitchell C, Alitalo K, Shima D, Betsholtz C (2003) VEGF guides angiogenic sprouting utilizing endothelial tip cell filopodia. J Cell Biol 161(6):1163–1177. https://doi.org/10.1083/jcb.200302047
Geudens I, Gerhardt H (2011) Coordinating cell behaviour during blood vessel formation. Development 138(21):4569–4583. https://doi.org/10.1242/dev.062323
Jakobsson L, Franco CA, Bentley K, Collins RT, Ponsioen B, Aspalter IM, Rosewell I, Busse M, Thurston G, Medvinsky A, Schulte-Merker S, Gerhardt H (2010) Endothelial cells dynamically compete for the tip cell position during angiogenic sprouting. Nat Cell Biol 12(10):943–953. https://doi.org/10.1038/ncb2103
Blanco R, Gerhardt H (2013) VEGF and Notch in tip and stalk cell selection. Cold Spring Harbor Perspect Med 3(1):a006569. https://doi.org/10.1101/cshperspect.a006569
Kim YM, Kim KE, Koh GY, Ho YS, Lee KJ (2006) Hydrogen peroxide produced by angiopoietin-1 mediates angiogenesis. Can Res 66(12):6167–6174. https://doi.org/10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-05-3640
Parfenova H, Basuroy S, Bhattacharya S, Tcheranova D, Qu Y, Regan RF, Leffler CW (2006) Glutamate induces oxidative stress and apoptosis in cerebral vascular endothelial cells: contributions of HO-1 and HO-2 to cytoprotection. Am J Physiol Cell Physiol 290(5):C1399-1410. https://doi.org/10.1152/ajpcell.00386.2005
Drummond GR, Sobey CG (2014) Endothelial NADPH oxidases: which NOX to target in vascular disease? TEM 25(9):452–463. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tem.2014.06.012
Wang H, Yang Z, Jiang Y, Hartnett ME (2014) Endothelial NADPH oxidase 4 mediates vascular endothelial growth factor receptor 2-induced intravitreal neovascularization in a rat model of retinopathy of prematurity. Mol Vis 20:231–241
Nisimoto Y, Diebold BA, Cosentino-Gomes D, Constentino-Gomes D, Lambeth JD (2014) Nox4: a hydrogen peroxide-generating oxygen sensor. Biochemistry 53(31):5111–5120. https://doi.org/10.1021/bi500331y
Li J, Wang JJ, Yu Q, Chen K, Mahadev K, Zhang SX (2010) Inhibition of reactive oxygen species by Lovastatin downregulates vascular endothelial growth factor expression and ameliorates blood-retinal barrier breakdown in db/db mice: role of NADPH oxidase 4. Diabetes 59(6):1528–1538
Li J, Wang JJ, Zhang SX (2015) NADPH oxidase 4-derived H2O2 promotes aberrant retinal neovascularization via activation of VEGF receptor 2 pathway in oxygen-induced retinopathy. J Diabetes Res 2015:963289. https://doi.org/10.1155/2015/963289
Vogel J, Kruse C, Zhang M, Schroder K (2015) Nox4 supports proper capillary growth in exercise and retina neo-vascularization. J Physiol 593(9):2145–2154. https://doi.org/10.1113/jphysiol.2014.284901
Stahl A, Connor KM, Sapieha P, Chen J, Dennison RJ, Krah NM, Seaward MR, Willett KL, Aderman CM, Guerin KI, Hua J, Lofqvist C, Hellstrom A, Smith LE (2010) The mouse retina as an angiogenesis model. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci 51(6):2813–2826. https://doi.org/10.1167/iovs.10-5176
Welser-Alves JV, Boroujerdi A, Milner R (2014) Isolation and culture of primary mouse brain endothelial cells. Methods Mol Biol 1135:345–356. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-1-4939-0320-7_28
Ruck T, Bittner S, Epping L, Herrmann AM, Meuth SG (2014) Isolation of primary murine brain microvascular endothelial cells. JoVE 93:e52204. https://doi.org/10.3791/52204
Reed MJ, Karres N, Eyman D, Vernon RB (2007) Culture of murine aortic explants in 3-dimensional extracellular matrix: a novel, miniaturized assay of angiogenesis in vitro. Microvasc Res 73(3):248–252. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.mvr.2007.02.002
Zudaire E, Gambardella L, Kurcz C, Vermeren S (2011) A computational tool for quantitative analysis of vascular networks. PLoS ONE 6(11):e27385. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0027385
Hackett SF, Wiegand S, Yancopoulos G, Campochiaro PA (2002) Angiopoietin-2 plays an important role in retinal angiogenesis. J Cell Physiol 192(2):182–187
Felcht M, Luck R, Schering A, Seidel P, Srivastava K, Hu J, Bartol A, Kienast Y, Vettel C, Loos EK, Kutschera S, Bartels S, Appak S, Besemfelder E, Terhardt D, Chavakis E, Wieland T, Klein C, Thomas M, Uemura A, Goerdt S, Augustin HG (2012) Angiopoietin-2 differentially regulates angiogenesis through TIE2 and integrin signaling. J Clin Invest 122(6):1991–2005. https://doi.org/10.1172/JCI58832
Fu S, Fan L, Pan X, Sun Y, Zhao H (2015) Integrin alphav promotes proliferation by activating ERK 1/2 in the human lung cancer cell line A549. Mol Med Rep 11(2):1266–1271. https://doi.org/10.3892/mmr.2014.2860
Kobayashi-Sakamoto M, Isogai E, Hirose K, Chiba I (2008) Role of alphav integrin in osteoprotegerin-induced endothelial cell migration and proliferation. Microvasc Res 76(3):139–144. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.mvr.2008.06.004
Rikitake Y, Kawashima S, Yamashita T, Ueyama T, Ishido S, Hotta H, Hirata K, Yokoyama M (2000) Lysophosphatidylcholine inhibits endothelial cell migration and proliferation via inhibition of the extracellular signal-regulated kinase pathway. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol 20(4):1006–1012
Ushio-Fukai M, Nakamura Y (2008) Reactive oxygen species and angiogenesis: NADPH oxidase as target for cancer therapy. Cancer Lett 266(1):37–52. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.canlet.2008.02.044
Peshavariya H, Dusting GJ, Jiang F, Halmos LR, Sobey CG, Drummond GR, Selemidis S (2009) NADPH oxidase isoform selective regulation of endothelial cell proliferation and survival. Naunyn-Schmiedeberg’s Arch Pharmacol 380(2):193–204. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00210-009-0413-0
Tojo T, Ushio-Fukai M, Yamaoka-Tojo M, Ikeda S, Patrushev N, Alexander RW (2005) Role of gp91phox (Nox2)-containing NAD(P)H oxidase in angiogenesis in response to hindlimb ischemia. Circulation 111(18):2347–2355. https://doi.org/10.1161/01.CIR.0000164261.62586.14
Al-Shabrawey M, Bartoli M, El-Remessy AB, Platt DH, Matragoon S, Behzadian MA, Caldwell RW, Caldwell RB (2005) Inhibition of NAD(P)H oxidase activity blocks vascular endothelial growth factor overexpression and neovascularization during ischemic retinopathy. Am J Pathol 167(2):599–607
Pendyala S, Gorshkova IA, Usatyuk PV, He D, Pennathur A, Lambeth JD, Thannickal VJ, Natarajan V (2009) Role of Nox4 and Nox2 in hyperoxia-induced reactive oxygen species generation and migration of human lung endothelial cells. Antioxid Redox Signal 11(4):747–764. https://doi.org/10.1089/ARS.2008.2203
Sharma PS, Sharma R, Tyagi T (2011) VEGF/VEGFR pathway inhibitors as anti-angiogenic agents: present and future. Curr Cancer Drug Targets 11(5):624–653. https://doi.org/10.2174/156800911795655985
Augustin HG, Koh GY, Thurston G, Alitalo K (2009) Control of vascular morphogenesis and homeostasis through the angiopoietin-Tie system. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol 10(3):165–177. https://doi.org/10.1038/nrm2639
Reiss Y, Droste J, Heil M, Tribulova S, Schmidt MH, Schaper W, Dumont DJ, Plate KH (2007) Angiopoietin-2 impairs revascularization after limb ischemia. Circ Res 101(1):88–96. https://doi.org/10.1161/CIRCRESAHA.106.143594
Hakanpaa L, Sipila T, Leppanen VM, Gautam P, Nurmi H, Jacquemet G, Eklund L, Ivaska J, Alitalo K, Saharinen P (2015) Endothelial destabilization by angiopoietin-2 via integrin beta1 activation. Nat Commun 6:5962. https://doi.org/10.1038/ncomms6962
Carlson TR, Feng Y, Maisonpierre PC, Mrksich M, Morla AO (2001) Direct cell adhesion to the angiopoietins mediated by integrins. J Biol Chem 276(28):26516–26525. https://doi.org/10.1074/jbc.M100282200
Yun JH, Park SW, Kim JH, Park YJ, Cho CH, Kim JH (2016) Angiopoietin 2 induces astrocyte apoptosis via alphavbeta5-integrin signaling in diabetic retinopathy. Cell Death Dis 7:e2101. https://doi.org/10.1038/cddis.2015.347
Lee HS, Oh SJ, Lee KH, Lee YS, Ko E, Kim KE, Kim HC, Kim S, Song PH, Kim YI, Kim C, Han S (2014) Gln-362 of angiopoietin-2 mediates migration of tumor and endothelial cells through association with alpha5beta1 integrin. J Biol Chem 289(45):31330–31340. https://doi.org/10.1074/jbc.M114.572594
Bhandarkar SS, Jaconi M, Fried LE, Bonner MY, Lefkove B, Govindarajan B, Perry BN, Parhar R, Mackelfresh J, Sohn A, Stouffs M, Knaus U, Yancopoulos G, Reiss Y, Benest AV, Augustin HG, Arbiser JL (2009) Fulvene-5 potently inhibits NADPH oxidase 4 and blocks the growth of endothelial tumors in mice. J Clin Invest 119(8):2359–2365. https://doi.org/10.1172/JCI33877
Menden H, Welak S, Cossette S, Ramchandran R, Sampath V (2015) Lipopolysaccharide (LPS)-mediated angiopoietin-2-dependent autocrine angiogenesis is regulated by NADPH oxidase 2 (Nox2) in human pulmonary microvascular endothelial cells. J Biol Chem 290(9):5449–5461. https://doi.org/10.1074/jbc.M114.600692
Singh A, Koduru B, Carlisle C, Akhter H, Liu R-M, Schroder K, Brandes RP, Ojcius DM (2017) NADPH oxidase 4 modulates hepatic responses to lipopolysaccharide mediated by Toll-like receptor-4. Sci Rep 7(1):14346. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-017-14574-8
Zhao W, Feng H, Guo S, Han Y, Chen X (2017) Danshenol A inhibits TNF-α-induced expression of intercellular adhesion molecule-1 (ICAM-1) mediated by NOX4 in endothelial cells. Sci Rep 7(1):12953. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-017-13072-1
Turner CJ, Badu-Nkansah K, Hynes RO (2017) Endothelium-derived fibronectin regulates neonatal vascular morphogenesis in an autocrine fashion. Angiogenesis 20(4):519–531. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10456-017-9563-8
Gorin Y, Block K, Hernandez J, Bhandari B, Wagner B, Barnes JL, Abboud HE (2005) Nox4 NAD(P)H oxidase mediates hypertrophy and fibronectin expression in the diabetic kidney. J Biol Chem 280(47):39616–39626. https://doi.org/10.1074/jbc.M502412200
Deliyanti D, Alrashdi SF, Touyz RM, Kennedy CR, Jha JC, Cooper ME, Jandeleit-Dahm KA, Wilkinson-Berka JL (2020) Nox (NADPH oxidase) 1, Nox4, and Nox5 promote vascular permeability and neovascularization in retinopathy. Hypertension (Dallas, TX, 1979) 75(4):1091–1101. https://doi.org/10.1161/hypertensionaha.119.14100
Acknowledgements
This study was supported, in part, by NIH/NEI Grants EY019949, EY025061, EY030970, a research grant NGR G2019302 from the Brightfocus Foundation, and an Unrestricted Grant to the Department of Ophthalmology, the State University of New York at Buffalo, from Research to Prevent Blindness.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interests
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interests.
Ethical Approval
All animal procedures were approved by the Institutional Animal Care and Use Committees at the University at Buffalo, State University of New York, and in accordance with the guidelines of the ARVO statements for the “Use of Animals in Ophthalmic and Vision Research.”
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Tang, X., Wang, J.J., Wang, J. et al. Endothelium-specific deletion of Nox4 delays retinal vascular development and mitigates pathological angiogenesis. Angiogenesis 24, 363–377 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10456-020-09757-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10456-020-09757-3