Abstract
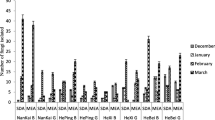
This study assessed the concentration characteristics of culturable airborne microbes in 60 family homes with children aged 1–15 years in Hangzhou, southeast China. The concentration of culturable airborne microbes ranged from 314 colony-forming units (CFU)/m3 to 2903 CFU/m3, with a mean value of 873 CFU/m3. The mean fungal concentration (653 CFU/m3) was significantly higher than the mean bacterial concentration of the atmosphere (220 CFU/m3), and the proportion of airborne fungi (73.9%) was significantly higher than that of airborne bacteria (26.1%). Microbial concentrations in family homes with a male child were significantly higher than those in homes with a female child, and there was a negative correlation between microbial concentration and living area per capita in family homes. The mean microbial concentration was highest in summer, followed by spring and autumn, and lowest in winter. This study provides an exposure database of airborne microbes in family homes in southeast China, suggesting that child gender and human occupancy in family homes significantly influence the microbial concentration in the air.









Similar content being viewed by others
Availability of data and materials
The datasets used and/or analyzed during the current study are available from the corresponding author on reasonable request.
References
Adams, R. I., Bhangar, S., Pasut, W., Arens, E. A., Taylor, J. W., Lindow, S. E., Nazaroff, W. W., & Bruns, T. D. (2015). Chamber bioaerosol study: outdoor air and human occupants as sources of indoor airborne microbes. PLoS ONE, 10(5), e0128022. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0128022
Adhikari, A., Reponen, T., Grinshpun, S. A., Martuzevicius, D., & LeMasters, G. (2006). Correlation of ambient inhalable bioaerosols with particulate matter and ozone: A two-year study. Environmental Pollution, 140, 16–28. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envpol.2005.07.004
Balasubramanian, R., Nainar, P., & Rajasekar, A. (2012). Airborne bacteria, fungi, and endotoxin levels in residential microenvironments: A case study. Aerobiologia, 28, 375–390. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10453-011-9242-y
Brągoszewska, E., & Biedroń, I. (2021). The efficiency of air purifiers at removing air pollutants in educational facilities-a preliminary study. Frontiers in Environmental Science, 709718(9), 1–7. https://doi.org/10.3389/fenvs.2021.70971
Bragoszewska, E., & Pawlak, M. (2021). Health risks associated with occupational exposure to biological air pollutants occurring during the processing of biomass for energy purposes: A case study. Energies, 14, 2086. https://doi.org/10.3390/en14082086
Chen, P. S., Tsai, F. T., Lin, C. K., Yang, C. Y., Chan, C. C., Young, C. Y., & Lee, C. H. (2010). Ambient influenza and avian influenza virus during dust storm days and background days. Environmental Health Perspectives., 118(9), 1211–1216. https://doi.org/10.1289/ehp.0901782
Fang, Z. G., Gong, C. J., Ouyang, Z. Y., Liu, P., Sun, L., & Wang, X. Y. (2014). Characteristic and concentration distribution of culturable airborne bacteria in residential environments in Beijing. China. Aerosol and Air Quality Research., 4, 943–953. https://doi.org/10.4209/aaqr.2013.04.0109
Fang, Z. G., Ouyang, Z. Y., Hu, L. F., Wang, X. K., Zheng, H., & Lin, X. Q. (2005). Culturable airborne fungi in outdoor environments in Beijing, China. Science of the Total Environment, 350, 47–58. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2005.01.032
Fang, Z. G., Ouyang, Z. Y., Liu, P., Sun, L., & Wang, X. Y. (2013). Airborne fungal community composition in indoor environments in Beijing. Huan Jing Ke Xue, 34, 2031–2037.
Fang, Z. G., Ouyang, Z. Y., Zheng, H., & Wang, X. K. (2008). Concentration and size distribution of culturable airborne microorganisms in outdoor environments in Beijing. China. Aerosol Science and Technology., 42, 325–334. https://doi.org/10.1080/02786820802068657
Fang, Z. G., Ouyang, Z. Y., Zheng, H., Wang, X. K., & Hu, L. F. (2007). Culturable airborne bacteria in outdoor environments in Beijing, China. Microbial Ecology., 54, 487–496. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00248-007-9216-3
Fang, Z. G., Tang, Q. Q., Gong, C. J., Ouyang, Z. Y., Liu, P., Sun, L., & Wang, X. Y. (2015). Profile and distribution characteristics of culturable airborne fungi in residential homes with children in Beijing. China. Indoor and Built Environment., 26, 1232–1242. https://doi.org/10.1177/1420326X15610178
Fang, Z. G., Yao, W. C., Lou, X. Q., Hao, C. M., Gong, C. J., & Ouyang, Z. Y. (2016). Profile and characteristics of culturable airborne bacteria in Hangzhou, Southeast of China. Aerosol and Air Quality Research., 16, 1690–1700. https://doi.org/10.4209/aaqr.2014.11.0274
Fang, Z. G., Zhang, J. W., Guo, W. J., & Lou, X. Q. (2019). Assemblages of culturable airborne fungi in a typical urban, tourism-driven center of southeast China. Aerosol and Air Quality Research., 19, 820–831. https://doi.org/10.4209/aaqr.2018.02.0042
Felgueiras, F., Mourão, Z., Fernandes, E. D. V., & Gabriel, M. F. (2022). Airborne bacterial and fungal concentrations and fungal diversity in bedrooms of infant twins under 1 year of age living in Porto. Environmental Research., 206, 112568. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envres.2021.112568
Fujiyoshi, S., Tanaka, D., & Maruyama, F. (2017). Transmission of airborne bacteria across built environments and its measurement standards: A review. Frontiers in Microbiology., 8, 2336. https://doi.org/10.3389/fmicb.2017.02336
Horner, W. E., Helbling, A., Salvaggio, J. E., & Lehrer, S. B. (1995). Fungal allergens. Clinical Microbiology Reviews., 8, 161–179. https://doi.org/10.1128/cmr.8.2.161
Hospodsky, D., Qian, J., Nazaroff, W. W., Yamamoto, N., Bibby, K., Rismani-Yazdi, H., & Peccia, J. (2012). Human occupancy as a source of indoor airborne bacteria. PLoS ONE, 7, e34867. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0034867
Hospodsky, D., Yamamoto, N., Nazaroff, W. W., Miller, D., Gorthala, S., & Peccia, J. (2015). Characterizing airborne fungal and bacterial concentrations and emission rates in six occupied children’s classrooms. Indoor Air, 25(6), 641–652. https://doi.org/10.1111/ina.12172
Hu, Q. X., Xu, X. Z., & Jiang, L. (1997). Effect of sampling time on sampling efficiency of airborne microbes. Shanghai Environmental Sciences., 16(5), 17–20.
Kim, K. Y., Kim, H. T., Kim, D., Nakajima, J., & Higuchi, T. (2009). Distribution characteristics of airborne bacteria and fungi in the feedstuff-manufacturing factories. Journal of Hazardous Materials., 169(1–3), 1054–1060. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2009.04.059
Kim, K. Y., Kim, Y. S., & Kim, D. (2010). Distribution characteristics of airborne bacteria and fungi in the general hospitals of Korea. Industrial Health., 48(2), 236–243. https://doi.org/10.2486/indhealth.48.236
Kumar, P., Singh, A. B., & Singh, R. (2022). Comprehensive health risk assessment of microbial indoor air quality in microenvironments. PLoS ONE, 17(2), e0264226. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0264226
Lee, B. G., Yang, J. L., Kim, E., Geum, S. W., Park, J. H., & Yeo, M. K. (2021). Investigation of bacterial and fungal communities in indoor and outdoor air of elementary school classrooms by 16S rRNA gene and ITS region sequencing. Indoorair., 31(5), 1553–1562. https://doi.org/10.1111/ina.12825
Madsen, A. M., Alwan, T., Ørberg, A., Uhrbrand, K., & Jørgensen, M. B. (2016). Waste workers’ exposure to airborne fungal and bacterial species in the truck cab and during waste collection. Annals of Occupational Hygiene., 60(6), 651–668. https://doi.org/10.1093/annhyg/mew021
Meadow, J. F., Altrichter, A. E., Kembel, S. W., Kline, J., Mhuireach, G., Moriyama, M., Northcutt, D., O’Connor, T. K., Womack, A. M., Brown, G. Z., Green, J. L., & Bohannan, B. J. (2012). Indoor airborne bacterial communities are influenced by ventilation, occupancy, and outdoor air source. Indoor Air, 24(1), 41–48. https://doi.org/10.1111/ina.12047
Polymenakou, P. N., Mandalakis, M., Stephanou, E. G., & Tselepides, A. (2008). Particle size distribution of airborne microorganisms and pathogens during an Intense African dust event in the eastern Mediterranean. Environmental Health Perspectives., 116, 292–296. https://doi.org/10.1289/ehp.10684
Prussin, A. J., & Marr, L. C. (2015). Sources of airborne microorganisms in the built environment. Microbiome., 3, 78. https://doi.org/10.1186/s40168-015-0144-z
Qian, J., Hospodsky, D., Yamamoto, N., Nazaroff, W. W., & Peccia, J. (2012). Size-resolved emission rates of airborne bacteria and fungi in an occupied classroom. Indoor Air, 22(4), 339–351. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1600-0668.2012.00769.x
Sadigh, A., Fataei, E., Arzanloo, M., & Imani, A. A. (2021). Bacteria bioaerosol in the indoor air of educational microenvironments: Measuring exposures and assessing health effects. Journal of Environmental Health Science and Engineering., 19(2), 1635–1642. https://doi.org/10.1007/s40201-021-00719-5
Sydonia, M., & Gediminas, M. (2022). Passive bioaerosol samplers: A complementary tool for bioaerosol research. A review. Journal of Aerosol Science., 163, 105992. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jaerosci.2022.105992
Täubel, M., Rintala, H., Pitkäranta, M., Paulin, L., Laitinen, S., Pekkanen, J., Hynärinen, A., & Nevalainen, A. (2009). The occupant as a source of house dust bacteria. Journal of Allergy and Clinical Immunology., 124(4), 834-840.e47. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jaci.2009.07.045
Vermeulen, L. C., Brandsema, P. S., Kassteele, J., Bom, B. C. J., Sterk, H. A. M., Sauter, F. J., Berg, H. H. J., & Husman, A. M. (2021). Atmospheric dispersion and transmission of Legionella from wastewater treatment plants: A 6-year case-control study. International Journal of Hygiene and Environmental Health., 237, 113811. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijheh.2021.113811
Wang, X. Y., Liu, W., Huang, C., Cai, J., Shen, L., Zou, Z. J., Lu, R. C., Chang, J., Wei, X. Y., & Sun, C. J. (2016). Associations of dwelling characteristics, home dampness, and lifestyle behaviors with indoor airborne culturable fungi: On-site inspection in 454 Shanghai residences. Building and Environment., 102, 159–166. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.buildenv.2016.03.010
Xie, H. L., Li, S. R., Yuan, X. Y., Liu, & G. W. (1999). Study on the disinfection of plant volatile secretion to the microorganism content in the air. Journal of Henan Agricultural University.
Yen, Y. C., Yang, C. Y., Mena, K. D., Cheng, Y. T., Yuan, C. S., & Chen, P. S. (2019). Jumping on the bed and associated increases of PM(10), PM(2.5), PM(1), airborne endotoxin, bacteria, and fungi concentrations. Environmental Pollution., 245, 799–809. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envpol.2018.11.053
Zhen, Q., Deng, Y., Wang, Y. Q., Wang, X. K., Zhang, H. X., Sun, X., & Ouyang, Z. Y. (2017). Meteorological factors had more impact on airborne bacterial communities than air pollutants. Science of the Total Environment., 601–602, 703–712. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2017.05.049
Zhou, Y., Lai, Y. H., Tong, X. Z., Leung, M. H. Y., Tong, J. C. K., Ridley, I. A., & Lee, P. K. H. (2020). Airborne bacteria in outdoor air and air of mechanically ventilated buildings at city scale in Hong Kong across seasons. Environmental Science & Technology., 54(19), 11732–11743. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.est.9b07623
Acknowledgements
The authors are grateful to the residents of the selected family homes for their cooperation. The authors also thank the teachers who provided valuable suggestions and the graduate students who performed the investigation.
Funding
This study was financially supported by the Project of Natural Science Foundation of Zhejiang Province, China (Grant number LY17D050006), and the Project of National Natural Science Foundation of China (Grant number 81402682).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Conceptualization was performed by Zhiguo Fang; methodology by Xiuyu Lou, Qing Tang, Junting Xie, Zhiguo Fang; formal analysis and investigation by Xiuyu Lou, Qing Tang, Junting Xie, Zhiguo Fang; writing—original draft preparation—by Xiuyu Lou, Zhiguo Fang; writing—review and editing—by Xiuyu Lou; funding acquisition—by Zhiguo Fang; resources by Zhiguo Fang; supervision by Zhiguo Fang.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Ethics approval
Not applicable.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Lou, X., Yang, Q., Xie, J. et al. Concentration characteristics of culturable airborne microbes in family homes in Hangzhou, China. Aerobiologia 39, 119–131 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10453-023-09779-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10453-023-09779-6