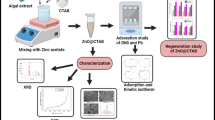
Abstract
The nano-Sulphonated Poly (glycidyl methacrylate)-Hexamethyl Pararosaniline Chloride (Crystal Violet; CV) composite (CV-SPGMA) has been developed as a novel adsorbent for treatment of Dichromate and Permanganate Contaminated Waste Water for the first time. The innovative adsorbent has been developed by adsorption of CV dye from wastewater using nano-Sulphonated Poly (glycidyl methacrylate) (SPGMA) particles. The study investigated the impact of various adsorption parameters. The CV content was observed to be linearly increased by variations in the concentration of CV up to 200 mg/L where maximum content obtained; 174.6 mg/g. The equilibrium almost reached after 90 min. An endothermic nature of the CV adsorption process has been noticed where 178 mg/g CV content obtained at 80 °C. The CV content decreased from 240 mg/g to 46 mg/g with the SPGMA adsorbent dose increment from 5 to 40 mg. The pH of adsorption exhibited the most pronounced impact, with the highest CV content achieved at a pH of 10.0 corresponding to 190.4 mg/g. The reusability of the produced CV-SPGMA adsorbent was examined for consecutive adsorption–desorption cycles, revealing a loss of just 13% in its initial adsorption efficiency after 10 cycles. In addition, the alterations in the chemical structure and morphology caused by the development of CV-SPGMA composite were observed through the utilization of characterization techniques including Fourier-transform infrared spectroscopy (FTIR), scanning electron microscopy (SEM), and energy-dispersive X-ray spectroscopy (EDAX). Finally, the developed CV-SPGMA composite adsorbent, for the first time, tested for the removal of Cr (VI) and Mn (VII) metal ions from dichromate and permanganate contaminated waters under mild adsorption conditions where shows seven folds affinity towards removal of the Cr (VI), 84.6 mg/g, than Mn (VII), 11.66 mg/g.











Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
No datasets were generated or analysed during the current study.
References
Noreen, S., Bhatti, H.N., Zuber, M., Zahid, M., Asgher, M.: Removal of actacid orange-RL dye using biocomposites: modeling studies. Pol. J. Environ. Stud. 26(5), 1–10 (2017)
Bhatti, H.N., Safa, Y., Yakout, S.M., Shair, O.H., Iqbal, M., Nazir, A.: Efficient removal of dyes using carboxymethyl cellulose/alginate/polyvinyl alcohol/rice husk composite: adsorption/desorption, kinetics and recycling studies. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 150(1), 861–870 (2020)
Noreen, S., Bhatti, H.N., Iqbal, M., Hussain, F., Sarim, F.M.: Chitosan, starch, polyaniline and polypyrrole biocomposite with sugarcane bagasse for the efficient removal of Acid Black dye. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 147(15), 439–452 (2020)
Mahmoodi, N.M., Arami, M.: Numerical finite volume modeling of dye decolorization using immobilized Titania nanophotocatalysis. Chem. Eng. J. 146(2), 189–193 (2009)
Ngo, A.C.R., Tischler, D.: Microbial degradation of azo dyes: approaches and prospects for a hazard-free conversion by microorganisms. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 19, 4740 (2022)
Pirkaramia, A., Olya, M.E., Limaee, N.Y.: Decolorization of azo dyes by photo electro adsorption process using polyaniline coated electrode. Prog. Org. Coat. 76, 682–688 (2013)
Umar, K., Mfarrej, M.F.B., Rahman, Q.I., Zuhaib, M., Khan, A., Zia, Q., Banawas, S., Nadeem, H., Khan, M.F., Ahmad, F.: ZnO Nano-swirlings forAzo Dye AR183 photocatalytic degradation and antimycotic activity. Sci. Rep. 2, 14023 (2022)
Maqbool, M., Bhatti, H.N., Sadaf, S., AL-Anazy, M.M., Iqbal, M.: Biocomposite of polyaniline and sodium alginate with Oscillatoria biomass: a potential adsorbent for the removal of basic blue 41. J. Mater. Res. Technol. 9(6), 14729–14741 (2020)
Maqbool, M., Sadaf, S., Bhatti, H.N., Rehmat, S., Kausar, A., Alissa, S.A., Iqbal, M.: Sodium alginate and polypyrrole composites with algal dead biomass for the adsorption of Congo red dye: kinetics, thermodynamics and desorption studies. Surf. Interfaces 25, 101183 (2021)
Foroutan, R., Mohammadi, R., MousaKhanloo, F., Sahebi, S., Ramavandi, B., Kumar, P.S., Vardhan, K.H.: Performance of montmorillonite/graphene oxide/CoFe2O4 as a magnetic and recyclable nanocomposite for cleaning methyl violet dye-laden wastewater. Adv. Powder Technol. 31, 3993–4004 (2020)
Bonyadi, Z., Kumar, P.S., Foroutan, R., Kafaei, R., Arfaeinia, H., Farjadfard, S., Ramavandi, B.: Ultrasonic-assisted synthesis of Populus alba activated carbon for water defluorination: application for real wastewater. Korean J. Chem. Eng. 36, 1595–1603 (2019)
Peighambardoust, S.J., A-Bavil, O., Foroutan, R., Arsalani, N.: Removal of malachite green using carboxymethyl cellulosegpolyacrylamide/montmorillonite nanocomposite hydroge. Int. J. Bio. Macromo. 159, 1122–1131 (2020)
Esvandi, Z., Foroutan, R., Peighambardoust, S.J., Akbari, A., Ramavandi, B.: Uptake of anionic and cationic dyes from water using natural clay and clay/starch/MnFe2O4 magnetic nanocomposite. Surf. Interfaces 21, 100754 (2020)
Foroutan, R., Peighambardoust, S.J., Esvandi, Z., Khatooni, H., Ramavandi, B.: Evaluation of two cationic dyes removal from aqueous environments using CNT/MgO/CuFe2O4 magnetic composite powder: a comparative study. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 9(2), 104752 (2021)
Shah, V., Madamwar, D.: Community genomics: Isolation, characterization and expression of gene coding for azoreductase. Int. Biodeter. Biodegrad. 79(4), 1–8 (2013)
Shertate, R.S., Thorat, P., Department of microbiology & Research center.: Biotransformation of textile dyes, a bioremedial aspect of marine environment. Am. J. Environ. Mental (2014)
Balamurugan, B., Thirumarimurugan, M., Kannadasan, T.: Anaerobic degradation of textile dye bath effluent using Halomonas sp. Bioresour. (2011)
Sharma, G., Kumar, A., Sharma, S., Al-Muhtaseb, A.H., Naushad, Mu., Ghfar, A.A., Ahamad, T., Stadler, F.J.: Fabrication and characterization of novel Fe0@Guar gumcrosslinked-soya lecithin nanocomposite hydrogel for photocatalytic degradation of methyl violet dye. Sep. Purif. Technol. 211, 895–908 (2019)
Sharma, G., Naushad, M., Pathania, D., Mittal, A., El-desoky, G.E.: Modification of Hibiscus cannabinus fiber by graft copolymerization: application for dye removal. Desalin. Water Treat. 54(11), 3114–3121 (2015)
Sharma, G., Dionysiou, D.D., Sharma, S., Kumar, A., Al-Muhtaseb, A.H., Naushad, M., Stadler, F.J.: Highly efficient Sr/Ce/activated carbon bimetallic nanocomposite for photoinduced degradation of rhodamine B. Catal. Today 335, 437–451 (2019)
Sharma, G., Pathania, D., Naushad, M., Kothiyal, N.C.: Fabrication, characterization and antimicrobial activity of polyaniline Th(IV) tungstomolybdophosphate nanocomposite material: efficient removal of toxic metal ions from water. Chem. Eng. J. 251, 413–421 (2014)
Worch, E.: Adsorption technology in water treatment: fundamentals, processes, and modeling. De Gruyter, Berlin, Boston (2012). https://doi.org/10.1515/9783110240238
Foroutan, R., Peighambardoust, S.J., Peighambardoust, S.H., Pateiro, M., Lorenzo, J.M.: Adsorption of crystal violet dye using activated carbon of lemon wood and activated carbon/Fe3O4 magnetic nanocomposite from aqueous solutions: a kinetic equilibrium thermodynamic study. Molecules 26, 2241 (2021)
Song, Y., Tan, J., Wang, G., Zhou, Li.: Superior amine-rich gel adsorbent from peach gum polysaccharide for highly efficient removal of anionic dyes. Carbohyd. Polym. 199, 178–185 (2018)
Pandey, V., Singh, S.B., Gupta, M.K., Afroz, M., Agrahari, S., Singh, H., Tandon, P.K.: Removal of the cationic dyes with activated carbon obtained from low-cost ginger waste. Mater Today: Proc. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.matpr.2023.12.056.
Mladenovic, N., Makreski, P., Tarbuk, A., Grgic, K., Boev, B., Mirakovski, D., Toshikj, E., Dimova, V., Dimitrovski, D., Jordanov, I.: Improved dye removal ability of modified rice husk with effluent from alkaline scouring based on the circular economy concept. Processes 8, 653 (2020)
El Khomri, M., El Messaoudi, N., Dbik, A., Bentahar, S., Lacherai, A., Chegini, Z.G., Iqbal, M.: Organic Dyes Adsorption on the Almond Shell (Prunus dulcis) as Agricultural Solid Waste from Aqueous Solution in Single and Binary Mixture Systems. Biointerface Res. Appl. Chem. 12, 2022–2040 (2022)
Saini, B., Dey, A.: Synthesis and characterization of copolymer adsorbent for crystal violet dye removal from water. Mater. Today: Proc. 61, 342–350 (2022)
Li, S.: Removal of crystal violet from aqueous solution by sorption into semi-interpenetrated networks hydrogels constituted of poly(acrylic acid-acrylamide-methacrylate) and amylase. Biores. Technol. 101, 2197–2202 (2010)
Mohamed, R.R., Abu Elella, M.H., Sabaa, M.W., Saad, G.R.: Synthesis of an efficient adsorbent hydrogel based on biodegradable polymers for removing crystal violet dye from aqueous solution. Cellulose 25, 6513–6529 (2018)
Jana, S., Ray, J., Mondal, B., Tripathy, T.: Efficient and selective removal of cationic organic dyes from their aqueous solutions by a nanocomposite hydrogel, katira gum-cl-poly(acrylic acid-co-N, N-dimethylacrylamide)@bentonite. Appl. Clay Sci. 173, 46–64 (2019)
Abu Elella, M.H., Sabaa, M.W., AbdElHafeez, E., Mohamed, R.R.: Crystal violet dye removal using crosslinked grafted xanthan gum. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 137, 1086–1101 (2019)
Mohy Eldin, M.S., Gouda, M.H., Abu-Saied, M.A., El-Shazly, Y.M.S., Farag, H.A.: Development of grafted cotton fabrics ions exchanger for dye removal applications: methylene blue model. Desalin. Water Treat. 57, 22049–22060 (2016)
MohyEldin, M.S., Elkady, M.F., Abdel Rahman, A.M., Soliman, E.A., Elzatahry, A.A., Youssef, M.E., Eweida, B.Y.: Preparation and characterization of imino diacetic acid functionalized alginate beads for removal of contaminates from waste water: I. methylene blue cationic dye model. Desalin. Water Treat. 40, 15–23 (2012)
MohyEldin, M.S., Aly, K., Khan, Z.A., Meky, A.E., Saleh, T.S., Elbogamy, A.S.: Development of novel acid-base ions exchanger for basic dye removal: phosphoric acid doped pyrazole-g-polyglycidyl methacrylate. Desalin. Water Treat. 57, 24047–24055 (2016)
Aksu, Z., In, Y.-S., Wong, N.F.Y., Tam: Algae for wastewater treatment. Springer-Verlag and Landes Bioscience, Germany, Biosorption of heavy metals by microalgae in batch and continuous systems pp. 37–53. (1998)
Van Nguyen, P., Thi Hong Truong, H., Pham, T.A., Le Cong, T., Le, T., Thi Nguyen, K.C.: Removal of manganese and copper from aqueous solution by yeast Papiliotrema huenov. Mycobiology 49, 507–520 (2021)
Ahmaruzzaman, Md.: Adsorption of phenolic compounds on low-cost adsorbents: a review. Adv. Coll. Interf. Sci. 143, 48–67 (2008)
Qian, Y., Gao, P., Xue, G., Liu, Z., Chen, J.: Oxidation of cefalexin by permanganate: reaction kinetics. Mech. Residual Antibacterial Act. Mol. 23, 2015 (2018)
Gupta, V., Kumari, S., Virvadiya, C.: Adsorption analysis of Mn(VII) from aqueous medium by activated orange peels powder. Int. Res. J. Pure Appl. Chem. 9, 1–8 (2015)
Ezeugo, J., Anadebe, C.V.: Removal of potassium permanganate from aqueous solution by adsorption onto activated carbon prepared from animal bone and corn cob. Equatorial J. Eng. 14-21 (2018)
Mahmoud, M.E., Yakout, A.A., Saad, S.R., Osman, M.M.: Removal of potassium permanganate from water by modified carbonaceous materials. Desalin. Water Treat. 57, 15559–15569 (2016)
Virvadiya, C., Kumari, S., Choudhary, V., Gupta, V.: Combined bio- and chemosorption of Mn(VII) from aqueous solution by PROSOPIS CINERARIA leaf powder. Eur. Chem. Bull. 3, 315–318 (2014)
Chaudhary, M.: Use of millet husk as a biosorbent for the removal of chromium and manganese ions from the aqueous solutions. Int. J. Chem. Environ. Pharm. Res. 2, 30–33 (2011)
Wan Ngah, W.S., Hanafiah, M.A.K.M.: Removal of heavy metal ions from wastewater by chemically modified plant wastes as adsorbents: a review. Bioresour. Technol. 99, 3935–3948 (2007)
Waranusantigula, P., Pokethitiyook, P., Kruatrachue, M., Upatham, E.S.: Kinetics of cbasic dye (methylene blue) biosorption by giant duckweed (Spirodela polyrrhiza). Environ. Pollut. 125, 385–392 (2003)
Vo, A.T., Nguyen, V.P., Ouakouak, A., Nieva, A., Doma, B.T., Jr., Tran, H.N., Chao, H.-P.: Efficient removal of Cr(VI) from water by biochar and activated carbon prepared through hydrothermal carbonization and pyrolysis: adsorption-coupled reduction mechanism. Water 11, 1164 (2019)
Varga, M., Takács, M., Záray, G., Varga, I.: Comparative study of sorption kinetics and equilibrium of chromium (VI) on charcoals prepared from different low-cost materials. Microchem. J. 107, 25–30 (2013)
Srinivasan, K.: Evaluation of rice husk carbon for the removal of trace inorganic form water. Thesis Submitted to I.I.T Madras (1986)
Fawzy, M.A., Darwish, H., Alharthi, S., Zaban, M.I., Noureldeen, A., Hassan, S.H.A.: Process optimization and modeling of Cd2+ biosorption onto the free and immobilized Turbinaria ornata using Box-Behnken experimental design. Sci. Rep. 12, 3256 (2022)
Malathi, S., Srinivasan, K., Gomathi, M.: Studies on the removal of Cr (VI) from aqueous solution by activated carbon developed from cottonseed activated withsulphuric acid. Int. J. Chem. Tech. Res. 8, 795–802 (2015)
Samani, M.R., Toghraie, D.: Removal of hexavalent chromium from water using polyaniline/ wood sawdust/ poly ethylene glycol composite: an experimental study. J. Environ. Health Sci. Eng. 17, 53–62 (2019)
Jassal, P.S., Raut, V.P., Anand, N.: Removal of chromium (VI) ions from Aqueous solution onto Chitosan and cross-linked chitosan beads. Proc. Indian Natl. Sci. Acad. 76, 1-6 (2010)
Marin, N.M.: Natural and synthetic polymers modified with acid blue 113 for removal of Cr3+, Zn2+ and Mn2+. Polymers 14, 2139 (2022)
El-Aassar, M.R., Tamer, T.M., El-Sayed, M.Y., Omer, A.M., Althobaiti, I.O., Youssef, M.E., Alolaimi, R.F., El Agammy, E.F., Alruwaili, M.S., Mohy-Eldin, M.S.: Development of azo dye immobilized poly (Glycidyl methacrylate-co-Methyl Methacrylate) polymers composites as novel adsorbents for water treatment applications: methylene blue-polymers composites. Polymers 14(21), 4672 (2022)
El-Aassar, M.R., Tamer, T.M., El-Sayed, M.Y., Omer, A.M., Althobaiti, I.O., Youssef, M.E., Alolaimi, R.F., El Agammy, E.F., Alruwaili, M.S., Mohy-Eldin, M.S.: Development of azo dye immobilized sulfonated poly (Glycidyl methacrylate) polymers composites as novel adsorbents for water treatment applications: methylene blue adsorption isotherm, kinetic, thermodynamic, and simulations studies. Molecules 27(23), 8418 (2022)
Mohy Eldin, M.S., Elkady, M.F., Abu-Saied, M.A., Abdel Rahman, A.M., Soliman, E.A., Elzatahry, A.A., Youssef, M.E.: Removal of cadmium ions from synthetic aqueous solutions using a novel nano-sulphonated poly glycidylmethacrylate cation exchanger: kinetic and equilibrium studies. J. App. Poly. Sci. 118, 3111–3122 (2010)
Elkady, M.F., Abu-Saied, M.A., Abdel Rahman, A.M., Soliman, E.A., Elzatahry, A.A., Youssef, M.E., Mohy Eldin, M.S.: Novel nano-sulphonated polyglycidyl methacrylate cation exchanger for removal of heavy metals: optimization of the operational conditions. Desalination 279, 152–162 (2011)
MohyEldin, M.S., Al-Bogami, A.S., Aly, K.M., Khan, Z.A., Mekky, A.E.M., Saleh, T.S., HakamyA, A.-W.: Removal of chromium (VI) metal ions using amberlite IRA-420 anions exchanger. Desalin. Water Treat. 60, 335–342 (2017)
Mohy Eldin, M.S., Alamry, K.A., Al-Malki, M.A.: Kinetic and isothermal studies of manganese (VII) ions removal using amberlite IRA-420 anions exchanger. Desalin. Water Treat. 72, 30–40 (2017)
Eren, Z., Acar, F.N.: Adsorption of reactive black 5 from an aqueous solution: equilibrium and kinetic studies. Desalination 194, 1–10 (2006)
Kannan, N., Sundaram, M.M.: Kinetics and mechanism of removal of methylene blue by adsorption on various carbons: a comparative study. Dyes Pigm. 51, 25–40 (2001)
Bulut, Y., Aydin, A.: A kinetics and thermodynamics study of methylene blue adsorption on wheat shells. Desalination 194, 259–267 (2006)
Satapathy, M.K., Das, P.: Optimization of crystal violet dye removal using novel soil-silver nanocomposite as nanoadsorbent using response surface methodology. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2, 708–714 (2014)
Ali, H., Muhammad, S.K.: Biosorption of crystal violet from water on leaf biomass of Calotropis procera. J. Environ. Sci. Technol. 1, 143–150 (2008)
Kumari, J., Krishnamoorthy, H., Arumugam, P., Radhakrishnan, T.K., Vasudevan, S.D.: An efficient removal of crystal violet dye from waste water by adsorption onto TLAC/Chitosan composite: a novel low cost adsorbent. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 96, 324–333 (2017)
Hamidzadeh, S., Torabbeigi, M., Shahtaheri, S.J.: Removal of crystal violet from water by magnetically modified activated carbon and nanomagnetic iron oxide. J. Environ. Heal. Sci. Eng. 13, 8 (2015)
Abdolahi, G., Dargahi, M., Ghasemzadeh, H.: Synthesis of starch-g-poly (acrylic acid)/ZnSe quantum dot nanocomposite hydrogel, for effective dye adsorption and photocatalytic degradation: thermodynamic and kinetic studies. Cellulose 27, 6467–6483 (2020)
Zhou, Y., Zhang, M., Wang, X., Huang, Q., Min, Y., Ma, T., Niu, J.: Removal of crystal violet by a novel cellulose-based adsorbent: comparison with native cellulose. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 53, 5498–5506 (2014)
Qiao, H., Zhou, Y., Yu, F., Wang, E., Min, Y., Huang, Q., Pang, L., Ma, T.: Effective removal of cationic dyes using carboxylate-functionalized cellulose nanocrystals. Chemosphere 141, 297–303 (2015)
Abu Elella, M.H., Sabaa, M.W., AbdElHafeez, E., Mohamed, R.R.: Crystal violet dye removal using crosslinked grafted xanthan gum. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 137, 1086–1101 (2019)
Mohamed, R.R., Abu Elella, M.H., Sabaa, M.W., Saad, G.R.: Synthesis of an efficient adsorbent hydrogel based on biodegradable polymers for removing crystal violet dye from aqueous solution. Cellulose 25, 6513–6529 (2018)
Bajpai, S., Jain, A.: Equilibrium and thermodynamic studies for adsorption of crystal violet onto spent tea leaves (STL). Water 4, 52–71 (2012)
Cheriaa, J., Khaireddine, M., Rouabhia, M., Bakhrouf, A.: Removal of triphenylmethane dyes by bacterial consortium. Sci. World J. 2012, 1–9 (2012)
Funding
This work was supported and funded by the Deanship of Scientific Research at Imam Mohammad Ibn Saud Islamic University (IMSIU), (grant number IMSIU-RP23098).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
T.T. performed the investigation and wrote the first draft, M. A. requested the fund and project management, A. O. performed the investigation and wrote the first draft, A. A. helped in project management, M.Y. applied the models for results and wrote the first draft, T.Y. applied the models for results and wrote the first draft, R.K. applied the models for results and wrote the first draft, M.S. tabulated the results and produced the figures, M. M. design and supervise the work, reviewed & edited the final version and submitted the manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Ethical approval
Not applicable. The research did not involve human participants or animals.
Consent to participate
Not applicable.
Consent to publish
Not applicable.
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Tamer, T., Abou-Krisha, M., Omer, A. et al. Nano-Sulphonated Poly (glycidyl methacrylate)-Hexamethyl Pararosaniline chloride novel composite adsorbent development for treatment of dichromate and permanganate contaminated waste water. Adsorption (2024). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10450-024-00460-z
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10450-024-00460-z