Abstract
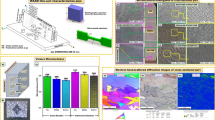
Compression molded polymer composites are generally produced with small dimensions for advanced engineering applications such as microelectronics. Among a broad range of polymers, ultra-high molecular weight polyethylene (UHMWPE) rises as an excellent matrix material due to its high impact absorbing, advanced wear resistive, low friction, self-lubricating, anti-corrosion and eco-friendly properties. Although UHMWPE based composites have been widely investigated in terms of tribology, impact behavior and mechanical properties, there is a big gap in literature regarding the micro-machinability of these advanced composites. In this work, polytetrafluoroethylene (PTFE) and aramid reinforced UHMWPE composites were produced in a compression molding chamber and these specimens were subjected to micro-milling operations by using a flat micro end cutter at three different spindle speeds. Micro-machining characteristics were evaluated in terms of surface roughness and cutting temperature. From the results, surface quality is heavily affected by spindle speed, which changes the material removal mechanism from tearing to shearing at higher rates. Molding pressure is also determinant on surface roughness by means of microstructural consolidation. Regarding the filler materials, it is possible to state that there are two different roughening mechanisms after milling. In the PTFE filled composites, machined surfaces include pitting topographies due to the detached particulate PTFE. However, fiber protrusions from the matrix enhance the roughness on the machined surfaces of the aramid reinforced composites. Furthermore, filler inclusions lead to a slight increase in the cutting temperatures during the milling operations.













Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ratchev, S., International Federation for Information Processing, Eds.: Precision assembly technologies and systems: 5th IFIP Wg 5.5 International Precision Assembly Seminar, IPAS 2010, Chamonix, France, February 14–17, 2010, proceedings. Berlin: Springer. (2010)
Chern, G.-L., Chuang, Y.: Study on vibration-EDM and mass punching of micro-holes. J. Mater. Process. Technol. 180(1–3), 151–160 (2006). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jmatprotec.2006.03.238
Qin, Y., et al.: Development of a new machine system for the forming of micro-sheet-products. Int. J. Mater. Form. 1(S1), 475–478 (2008). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12289-008-0098-9
Gara, S., Tsoumarev, O.: Effect of tool geometry on surface roughness in slotting of CFRP. Int. J. Adv. Manuf. Technol. 86(1–4), 451–461 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00170-015-8185-9
Gara, S., M’hamed, S., Tsoumarev, O.: Temperature measurement and machining damage in slotting of multidirectional CFRP laminate. Mach. Sci. Technol. 22(2), 320–337 (2018) https://doi.org/10.1080/10910344.2017.1365892
Sheikh-Ahmad, J., Twomey, J., Kalla, D., Lodhia, P.: Multiple Regression and Committee Neural Network Force Prediction Models in Milling FRP. Mach. Sci. Technol. 11(3), 391–412 (2007). https://doi.org/10.1080/10910340701554873
Pecat, O., Rentsch, R., Brinksmeier, E.: Influence of Milling Process Parameters on the Surface Integrity of CFRP. Procedia CIRP 1, 466–470 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.procir.2012.04.083
Azmi, A.I., Lin, R.J.T., Bhattacharyya, D.: Machinability study of glass fibre-reinforced polymer composites during end milling. Int. J. Adv. Manuf. Technol. 64(1–4), 247–261 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00170-012-4006-6
Hintze, W., Hartmann, D.: Modeling of Delamination During Milling of Unidirectional CFRP. Procedia CIRP 8, 444–449 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.procir.2013.06.131
Szallies, K., Siebert, N., Bergmann, J.P.: Low Frequency Oscillated Milling of Carbon Fiber-reinforced Plastics. Procedia CIRP 66, 153–158 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.procir.2017.03.298
Hocheng, H.: Machining technology for composite materials: principles and practice. Cambridge, UK ; Philadelphia, PA: Woodhead Pub (2012)
Iskandar, Y., Tendolkar, A., Attia, M.H., Hendrick, P., Damir, A., Diakodimitris, C.: Flow visualization and characterization for optimized MQL machining of composites. CIRP Ann. 63(1), 77–80 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cirp.2014.03.078
Agrawal, A., Satapathy, A.: Thermal and dielectric behaviour of polypropylene composites reinforced with ceramic fillers. J. Mater. Sci. Mater. Electron. 26(1), 103–112 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10854-014-2370-8
Sharma, S., Bijwe, J., Panier, S., Sharma, M.: Abrasive wear performance of SiC-UHMWPE nano-composites – Influence of amount and size. Wear 332–333, 863–871 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.wear.2015.01.012
Sharma, S., Bijwe, J., Panier, S.: Assessment of potential of nano and micro-sized boron carbide particles to enhance the abrasive wear resistance of UHMWPE. Compos. Part B Eng. 99, 312–320 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.compositesb.2016.06.003
Gürgen, S.: Low-velocity impact performance of UHMWPE composites consolidated with carbide particles. Arch. Civ. Mech. Eng. 20(2), 38 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s43452-020-00042-0
Senatov, F.S., Baranov, A.A., Muratov, D.S., Gorshenkov, M.V., Kaloshkin, S.D., Tcherdyntsev, V.V.: Microstructure and properties of composite materials based on UHMWPE after mechanical activation. J. Alloys Compd. 615, S573–S577 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jallcom.2013.12.175
Gao, P., Mackley, M.R.: The structure and rheology of molten ultra-high-molecular-mass polyethylene. Polymer 35(24), 5210–5216 (1994). https://doi.org/10.1016/0032-3861(94)90471-5
Chen, Y., Jiang, C., Cho, C.: An Investigation of the Compressive Behavior of Polymer Electrode Membrane Fuel Cell’s Gas Diffusion Layers under Different Temperatures. Polymers 10(9), 971 (2018). https://doi.org/10.3390/polym10090971
Chen, D., Chen, X.J., Gyimah, G.K.: Wear residues of aramid fibre formation in friction materials. Tribol. - Mater. Surf. Interfaces 2(3), 146–149 (2008). https://doi.org/10.1179/175158309X408306
Wang, S., Ge, S.: The mechanical property and tribological behavior of UHMWPE: Effect of molding pressure. Wear 263(7–12), 949–956 (2007). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.wear.2006.12.070
Panin, S.V., Kornienko, L.A., Alexenko, V.O., Ivanova, L.R., Shilko, S.V.: Influence of Nano- and Microfillers on the Mechanical and Tribotechnical Properties of ‘UHMWPE-PTFE’ Composites. Key Eng. Mater. 712, 161–165 (2016). https://doi.org/10.4028/www.scientific.net/KEM.712.161
Zhao, W., Xu, R., Ren, C., Wang, J., Yan, P.: Ion-Implantation Modification of Surface Flashover Properties in Vacuum of Polytetrafluoroethylene. IEEE Trans. Plasma Sci. 46(10), 3450–3456 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1109/TPS.2018.2819987
Iacovetta, D.J.: Synthesis of superhydrophobic nanocomposite coatings using electrodeposition. Master Thesis, University of Toronto (2014)
Rowland, H.D., King, W.P.: Micro and Nanomanufacturing via Molding. In BioNanoFluidic MEMS, P. J. Hesketh, Ed. Boston, MA: Springer US 131–151 (2008). https://doi.org/10.1007/978-0-387-46283-7_5
Gürgen, S., Çelik, O.N., Kuşhan, M.C.: Tribological behavior of UHMWPE matrix composites reinforced with PTFE particles and aramid fibers. Compos. Part B Eng. 173, 106949 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.compositesb.2019.106949
Gürgen, S.: Wear performance of UHMWPE based composites including nano-sized fumed silica. Compos. Part B Eng. 173, 106967 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.compositesb.2019.106967
Gürgen, S.: Wear behavior of UHMWPE composites under oxidative effect. Polym. Degrad. Stab. 199, 109912 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.polymdegradstab.2022.109912
Gürgen, S., Sert, A., Kuşhan, M.C.: An investigation on wear behavior of UHMWPE /carbide composites at elevated temperatures. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 138(16), 50245 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1002/app.50245
Kuram, E.: Micro-machinability of injection molded polyamide 6 polymer and glass-fiber reinforced polyamide 6 composite. Compos. Part B Eng. 88, 85–100 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.compositesb.2015.11.004
Campos Rubio, J.C., Panzera, T.H., Scarpa, F.: Machining behaviour of three high-performance engineering plastics. Proc. Inst. Mech. Eng. Part B J. Eng. Manuf. 229(1), 28–37 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1177/0954405414525142
Carr, J.W., Feger, C.: Ultraprecision machining of polymers. Precis. Eng. 15(4), 221–237 (1993). https://doi.org/10.1016/0141-6359(93)90105-J
Wu, J.J., Buckley, C.P., O’Connor, J.J.: Mechanical integrity of compression-moulded ultra-high molecular weight polyethylene: effects of varying process conditions. Biomaterials 23(17), 3773–3783 (2002). https://doi.org/10.1016/S0142-9612(02)00117-5
Parasnis, N.C., Ramani, K.: Analysis of the effect of pressure on compression moulding of UHMWPE. J. Mater. Sci. - Mater. Med. 9(3), 165–172 (1998). https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1008871720389
Sivasakthivel, P.S., Sudhakaran, R.: Optimization of machining parameters on temperature rise in end milling of Al 6063 using response surface methodology and genetic algorithm. Int. J. Adv. Manuf. Technol. 67(9–12), 2313–2323 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00170-012-4652-8
Price, D.M., Jarratt, M.: Thermal conductivity of PTFE and PTFE composites. Thermochim. Acta 392–393, 231–236 (2002). https://doi.org/10.1016/S0040-6031(02)00105-3
He, S., Sun, G., Cheng, X., Dai, H., Chen, X.: Nanoporous SiO 2 grafted aramid fibers with low thermal conductivity. Compos. Sci. Technol. 146, 91–98 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.compscitech.2017.04.021
Sofuoğlu, M.A., Gürgen, S.: Optimization of micromachining operation for particle reinforced UHMWPE composites. Arch. Civ. Mech. Eng. 22(3), 138 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s43452-022-00459-9
Gürgen, S., Sofuoğlu, M.A.: Micro-machining of UHMWPE composites reinforced with carbide fillers. Arch. Civ. Mech. Eng. 21(4), 146 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s43452-021-00299-z
Ge, S., et al.: Friction and wear behavior of nitrogen ion implanted UHMWPE against ZrO2 ceramic. Wear 255(7–12), 1069–1075 (2003). https://doi.org/10.1016/S0043-1648(03)00269-2
Xiong, D., Ge, S.: Friction and wear properties of UHMWPE/Al2O3 ceramic under different lubricating conditions. Wear 250(1–12), 242–245 (2001). https://doi.org/10.1016/S0043-1648(01)00647-0
Gürgen, S., Kuşhan, M.C.: The effect of silicon carbide additives on the stab resistance of shear thickening fluid treated fabrics. Mech. Adv. Mater. Struct. 24(16), 1381–1390 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1080/15376494.2016.1231355
Gürgen, S., Kuşhan, M.C.: The ballistic performance of aramid based fabrics impregnated with multi-phase shear thickening fluids. Polym. Test. 64, 296–306 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.polymertesting.2017.11.003
Gürgen, S., Kuşhan, M.C.: The stab resistance of fabrics impregnated with shear thickening fluids including various particle size of additives. Compos. Part Appl. Sci. Manuf. 94, 50–60 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.compositesa.2016.12.019
Kurtz, S.M.: The UHMWPE handbook: ultra-high molecular weight polyethylene in total joint replacement. Academic Press, Amsterdam; Boston (2004)
Baena, J., Wu, J., Peng, Z.: Wear Performance of UHMWPE and Reinforced UHMWPE Composites in Arthroplasty Applications: A Review. Lubricants 3(2), 413–436 (2015). https://doi.org/10.3390/lubricants3020413
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Sheikhi, M.R., Gürgen, S. Micro-milling Operation of UHMWPE Composites with PTFE and Aramid Reinforcements. Appl Compos Mater 30, 57–72 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10443-022-10073-w
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10443-022-10073-w