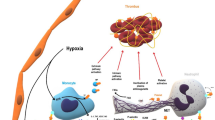
Abstract
Embolization has tremendously evolved in recent years and has expanded to treatment of a variety of pathologic processes. There has been emerging evidence that the level of arterial occlusion and the distribution of embolic particles may play an important role in the clinical outcome. This is a comprehensive literature review to identify variables that play important role in determination of level of occlusion of blood vessels and distribution of embolic particles. The literature searches between 1996 to 2020 through PubMed and Ovid-MEDLINE yielded over 1030 articles of which 30 studies providing details on the level of occlusion are reviewed here. We divided the playing factors into characteristics of the particles, solution/injection and vascular bed. Accordingly, particle size, type and aggregation, compressibility/deformability, and biodegradability are categorized as the factors involving particles’ behavioral nature. Infusion rate and concentration/dilution of the medium are related to the carrying solution. Hemodynamics and the arterial resistance are characteristics of the vascular bed that also play an important role in the distribution of embolic particles. Understanding and predicting the level of embolization is a complex multi-factor problem that requires more evidence, warranting further randomized controlled trials, and powered human and animal studies.


Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- PVA:
-
Polyvinyl alcohol
- TGMS:
-
Trisacryl gelatin microspheres
- PVAMSs:
-
PVA microspheres
- AVMs:
-
Arteriovenous Malformations
- UAE:
-
Uterine Artery Embolization
References
Amili, O., J. Golzarian, and F. Coletti. in vitro study of particle transport in successively bifurcating vessels. Ann. Biomed. Eng. 47(11):2271–2283, 2019.
Andrews, R. T., and C. A. Binkert. Relative rates of blood flow reduction during transcatheter arterial embolization with tris-acryl gelatin microspheres or polyvinyl alcohol: quantitative comparison in a swine model. J. Vasc. Interv. Radiol. 14(10):1311–1316, 2003.
Aramburu, J., R. Antón, A. Rivas, J. C. Ramos, B. Sangro, and J. I. Bilbao. Numerical investigation of liver radioembolization via computational particle–hemodynamics: the role of the microcatheter distal direction and microsphere injection point and velocity. J. Biomech. 49(15):3714–3721, 2016.
Aramburu, J., R. Antón, A. Rivas, J. C. Ramos, B. Sangro, and J. I. Bilbao. Computational assessment of the effects of the catheter type on particle–hemodynamics during liver radioembolization. J. Biomech. 49(15):3705–3713, 2016.
Arnold, M. J., J. J Keung, and B. McCarragher. Interventional Radiology: Indications and Best Practices: American Academy of Family Physicians; 2019 [Available from: https://www.aafp.org/afp/2019/0501/p547.html.
Beaujeux, R., A. Laurent, J. Hodes, M. Wassef, and J. J. Merland. Calibrated sphere embolization of craniofacial tumors and arteriovenous malformations. Neuroradiology. 16:562–564, 1991.
Bendszus, M., R. Klein, R. Burger, M. Warmuth-Metz, E. Hofmann, and L. Solymosi. Efficacy of trisacryl gelatin microspheres versus polyvinyl alcohol particles in the preoperative embolization of meningiomas. AJNR. 21(2):255–261, 2000.
Bilbao, J. I., E. de Luis, J. A. G. de Jalón, A. de Martino, M. D. Lozano, A. M. de la Cuesta, et al. Comparative study of four different spherical embolic particles in an animal model: a morphologic and histologic evaluation. J. Vasc. Intervent. Radiol. 19(11):1625–1638, 2008.
Brown, A. C., and C. E. Ray. Anterior spinal cord infarction following bronchial artery embolization. Semin. Interv. Radiol. 29(3):241–244, 2012.
Burns, P. B., R. J. Rohrich, and K. C. Chung. The levels of evidence and their role in evidence-based medicine. Plastic Reconstr. Surg. 128(1):305–310, 2011.
Bushi, D., Y. Grad, S. Einav, O. Yodfat, B. Nishri, and D. Tanne. Hemodynamic evaluation of embolic trajectory in an arterial bifurcation: an in-vitro experimental model. Stroke. 36(12):2696–2700, 2005.
Caine, M., M. S. McCafferty, S. McGhee, P. Garcia, W. M. Mullett, X. Zhang, et al. Impact of Yttrium-90 microsphere density, flow dynamics, and administration technique on spatial distribution: analysis using an in vitro model. J. Vasc. Interv. Radiol. 28(2):260–8.e2, 2017.
Childress, E. M., and C. Kleinstreuer. Impact of fluid-structure interaction on direct tumor-targeting in a representative hepatic artery system. Ann. Biomed. Eng. 42(3):461–474, 2014.
Choe, D. H., M. H. Han, G. H. Kang, K. M. Yeon, and M. C. Han. An experimental study of embolic effect according to infusion rate and concentration of suspension in transarterial particulate embolization. Invest. Radiol. 32(5):260–267, 1997.
Chua, G. C., M. Wilsher, M. P. Young, I. Manyonda, R. Morgan, and A. M. Belli. Comparison of particle penetration with non-spherical polyvinyl alcohol versus trisacryl gelatin microspheres in women undergoing premyomectomy uterine artery embolization. Clin. Radiol. 60(1):116–122, 2005.
Chung, E. M., J. P. Hague, M. A. Chanrion, K. V. Ramnarine, E. Katsogridakis, and D. H. Evans. Embolus trajectory through a physical replica of the major cerebral arteries. Stroke. 41(4):647–652, 2010.
Das, R., A. Wale, S. A. Renani, L. Ratnam, L. Mailli, J. Y. Chun, et al. Randomised controlled trial of particles used in uterine fibRoid Embolisation (PURE): non-spherical polyvinyl alcohol versus calibrated microspheres. Cardiovasc. Interv. Radiol. 45(2):207–215, 2022.
Derdeyn, C. P., V. B. Graves, M. S. Salamat, and A. Rappe. Collagen-coated acrylic microspheres for embolotherapy: in vivo and in vitro characteristics. AJNR Am. J. Neuroradiol. 18(4):647–653, 1997.
Golzarian, J., E. Lang, D. Hovsepian, T. Kroncke, L. Lampmann, P. Lohle, et al. Higher Rate of partial devascularization and clinical failure after uterine artery embolization for fibroids with spherical polyvinyl alcohol. Cardiovasc. Interv. Radiol. 29(1):1–3, 2006.
Golzarian, J., and L. Weng. Particle embolization: factors affecting arterial distribution. J. Vasc. Interv. Radiol. 25(11):1773–1774, 2014.
Hidaka, K., L. Moine, G. Collin, D. Labarre, J. L. Grossiord, N. Huang, et al. Elasticity and viscoelasticity of embolization microspheres. J. Mech. Behav. Biomed. Mater. 4(8):2161–2167, 2011.
Hu, J., H. Albadawi, B. W. Chong, A. R. Deipolyi, R. A. Sheth, A. Khademhosseini, et al. Advances in biomaterials and technologies for vascular embolization. Adv. Mater. 31(33):1901071, 2019.
Hwang, J. H., S. W. Park, I. S. Chang, S. I. Jung, H. J. Jeon, Y. S. Lho, et al. Comparison of nonspherical polyvinyl alcohol particles and microspheres for prostatic arterial embolization in patients with benign prostatic hyperplasia. BioMed Res. Int. 2017:8732351, 2017.
Jiang, W., Z. Shen, H. Luo, X. Hu, and X. Zhu. Comparison of polyvinyl alcohol and tris-acryl gelatin microsphere materials in embolization for symptomatic leiomyomas: a systematic review. Minim. Invasive Therapy Allied Technol. 25(6):289–300, 2016.
Kennedy, A. S., C. Kleinstreuer, C. A. Basciano, and W. A. Dezarn. Computer modeling of yttrium-90-microsphere transport in the hepatic arterial tree to improve clinical outcomes. Int J. Radiat. Oncol. Biol. Phys. 76(2):631–637, 2010.
Keussen, I., J. Bengtsson, D. Gavier-Widén, and E. Karlstam. Uterine artery embolization in a sheep model: biodegradable versus non-degradable microspheres. Acta radiologica. 59(10):1210–1217, 2018.
Kishimoto, K., K. Osuga, N. Maeda, Y. Higashi, A. Hayashi, Y. Hori, et al. Embolic effects of transcatheter mesenteric arterial embolization with microspheres on the small bowel in a dog model. J. Vasc. Interv. Radiol. 25(11):1767–1773, 2014.
Laurent, A., M. Wassef, R. Chapot, Y. Wang, E. Houdart, L. Feng, et al. Partition of calibrated tris-acryl gelatin microspheres in the arterial vasculature of embolized nasopharyngeal angiofibromas and paragangliomas. Journal of Vascular and Interventional Radiology 16(4):507–513, 2005.
Laurent, A., M. Wassef, J. Namur, J. Martal, D. Labarre, and J. P. Pelage. Recanalization and particle exclusion after embolization of uterine arteries in sheep: a long-term study. Fertil. Steril. 91(3):884–892, 2009.
Laurent, A., M. Wassef, J. P. Saint Maurice, J. Namur, J. P. Pelage, A. Seron, et al. Arterial distribution of calibrated tris-acryl gelatin and polyvinyl alcohol microspheres in a sheep kidney model. Invest. Radiol. 41(1):8–14, 2006.
Lewis, A. L., C. Adams, W. Busby, S. A. Jones, L. C. Wolfenden, S. W. Leppard, et al. Comparative in vitro evaluation of microspherical embolisation agents. J. Mater. Sci. Mater. Med. 17(12):1193–1204, 2006.
Maluccio, M. A., A. M. Covey, L. B. Porat, J. Schubert, L. A. Brody, C. T. Sofocleous, et al. Transcatheter arterial embolization with only particles for the treatment of unresectable hepatocellular carcinoma. J. Vasc Interv. Radiol. 19(6):862–869, 2008.
McLucas, B., L. Adler, and R. Perrella. Uterine fibroid embolization: nonsurgical treatment for symptomatic fibroids11No competing interests declared. J. Am Coll. Surg. 192(1):95–105, 2001.
McWilliams, J. P., T. A. Bilhim, F. C. Carnevale, S. Bhatia, A. J. Isaacson, S. Bagla, et al. Society of Interventional Radiology Multisociety Consensus Position Statement on Prostatic Artery Embolization for Treatment of Lower Urinary Tract Symptoms Attributed to Benign Prostatic Hyperplasia: From the Society of Interventional Radiology, the Cardiovascular and Interventional Radiological Society of Europe, Société Française de Radiologie, and the British Society of Interventional Radiology: Endorsed by the Asia Pacific Society of Cardiovascular and Interventional Radiology, Canadian Association for Interventional Radiology, Chinese College of Interventionalists, Interventional Radiology Society of Australasia, Japanese Society of Interventional Radiology, and Korean Society of Interventional Radiology. J Vasc Interv. Radiol. 30(5):627–37.e1, 2019.
Moher, D., A. Liberati, J. Tetzlaff, and D. G. Altman. Preferred reporting items for systematic reviews and meta-analyses: the PRISMA statement. BMJ. 339:2535, 2009.
Morishita, A., J. Tani, T. Nomura, K. Takuma, M. Nakahara, K. Oura, et al. Efficacy of combined therapy with drug-eluting beads-transcatheter arterial chemoembolization followed by conventional transcatheter arterial chemoembolization for unresectable hepatocellular carcinoma: a multi-Center study. Cancer. 13(18):4605, 2021.
Patel, T. Y., D. M. Hovsepian, and J. R. Duncan. Measurement of blood flow before and after embolization with use of fluorescent microspheres in an animal model. J. Vasc. Interv. Radiol. 17(1):103–111, 2006.
Peixoto, L. S., F. M. Silva, M. A. L. Niemeyer, G. Espinosa, P. A. Melo, M. Nele, et al. Synthesis of Poly(Vinyl Alcohol) and/or Poly(Vinyl Acetate) Particles with Spherical Morphology and Core-Shell Structure and its Use in Vascular Embolization. Macromol. Symp. 243(1):190–199, 2006.
Pelage, J. P., A. Laurent, M. Wassef, M. Bonneau, D. Germain, R. Rymer, et al. Uterine artery embolization in sheep: comparison of acute effects with polyvinyl alcohol particles and calibrated microspheres. Radiology. 224(2):436–445, 2002.
Senturk, C., V. Cakir, K. Yorukoglu, O. Yilmaz, and A. Y. Goktay. Looking for the ideal particle: an experimental embolization study. Cardiovasc. Interv. Radiol. 33(2):336–345, 2010.
Sheth, R. A., S. Sabir, S. Krishnamurthy, R. K. Avery, Y. S. Zhang, A. Khademhosseini, et al. Endovascular embolization by transcatheter delivery of particles: past, present, and future. J. Funct. Biomater. 8(2):14, 2017.
Siskin, G. P., K. Dowling, R. Virmani, R. Jones, and D. Todd. Pathologic evaluation of a spherical polyvinyl alcohol embolic agent in a porcine renal model. J. Vasc. Interv. Radiol. 14(1):89–98, 2003.
Sommer, C. M., T. D. Do, C. L. Schlett, P. Flechsig, T. L. Gockner, A. Kuthning, et al. In vivo characterization of a new type of biodegradable starch microsphere for transarterial embolization. J. Biomater. Appl. 32(7):932–944, 2018.
Stampfl, S., N. Bellemann, U. Stampfl, C. M. Sommer, H. Thierjung, R. Lopez-Benitez, et al. Arterial distribution characteristics of Embozene particles and comparison with other spherical embolic agents in the porcine acute embolization model. J. Vasc. Interv. Radiol. 20(12):1597–1607, 2009.
Torres, D., N. V. Costa, J. Pisco, L. C. Pinheiro, A. G. Oliveira, and T. Bilhim. Prostatic artery embolization for benign prostatic hyperplasia: prospective randomized trial of 100–300 μm versus 300–500 μm versus 100- to 300-μm + 300- to 500-μm embospheres. J. Vasc. Interv. Radiol. 30(5):638–644, 2019.
van den Hoven, A. F., M. G. E. H. Lam, S. Jernigan, M. A. A. J. van den Bosch, and G. D. Buckner. Innovation in catheter design for intra-arterial liver cancer treatments results in favorable particle-fluid dynamics. J. Exp. Clin. Cancer Res. 34(1):74, 2015.
Verret, V., S. H. Ghegediban, M. Wassef, J. P. Pelage, J. Golzarian, and A. Laurent. The arterial distribution of Embozene and Embosphere microspheres in sheep kidney and uterus embolization models. J. Vasc. Interv. Radiol. 22(2):220–228, 2011.
Weiss, C. R., Y. Fu, C. Beh, C. Hu, D. Kedziorek, E.-J. Shin, et al. Bariatric arterial embolization with calibrated radiopaque microspheres and an Antireflux catheter suppresses weight gain and appetite-stimulating hormones in swine. J. Vasc. Interv. Radiol. 31(9):1483–1491, 2020.
Weng, L., M. Rusten, R. Talaie, M. Hairani, N. K. Rosener, and J. Golzarian. Calibrated bioresorbable microspheres: a preliminary study on the level of occlusion and arterial distribution in a rabbit kidney model. J. Vasc. Interv. Radiol. 24(10):1567–1575, 2013.
Wong, Y. S., A. V. Salvekar, K. D. Zhuang, H. Liu, W. R. Birch, K. H. Tay, et al. Bioabsorbable radiopaque water-responsive shape memory embolization plug for temporary vascular occlusion. Biomaterials. 102:98–106, 2016.
Young, S., N. Rostambeigi, and J. Golzarian. The common but complicated tool: review of embolic materials for the interventional radiologist. Semin. Intervent. Radiol. 38(5):535–541, 2021.
Yu, S. C., I. Lok, S. S. Ho, M. M. Tong, and J. W. Hui. Comparison of clinical outcomes of tris-acryl microspheres versus polyvinyl alcohol microspheres for uterine artery embolization for leiomyomas: results of a randomized trial. J. Vasc. Interv. Radiol. 22(9):1229–1235, 2011.
Funding
This study was not supported by any funding.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Ethical approval
This article does not contain any studies with human participants or animals performed by any of the authors.
Informed consent
For this type of study consent for publication is not required.
Additional information
Associate Editor Mona Kamal Marei oversaw the review of this article.
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Talaie, R., Torkian, P., Amili, O. et al. Particle Distribution in Embolotherapy, How Do They Get There? A Critical Review of the Factors Affecting Arterial Distribution of Embolic Particles. Ann Biomed Eng 50, 885–897 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10439-022-02965-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10439-022-02965-6