Abstract
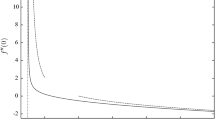
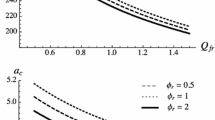
In this paper, we investigate the thermal convection flow which is driven by a heat-releasing concentration field. Different from our previous work on the internally heated double diffusive convection (IHDDC), in the current internally heated Rayleigh-Bénard convection (IHRBC), the fluid density depends solely on the temperature field and the concentration field only serves as the internal heat source. Linear stability analyses reveal that the most unstable mode is always the stationary one. The critical Rayleigh number, which measures the strength of the unstable driving force, decreases with the Schmidt number (the ratio between the viscosity and the molecular diffusivity of concentration field), but increases with the Prandtl number (the ratio between the viscosity and the thermal molecular diffusivity). Fully developed flows are then studied by three-dimensional direct numerical simulations. The unifying model developed for IHDDC can also be used to describe the transport properties for the current flow. The characteristic widths are smaller for the plumes descending from the top plate than those ascending from the bottom one.

摘要
本文研究了带放热效应的浓度场所引起的浮力对流现象, 与之前带放热效应的双扩散对流问题(IHDDC)不同, 本研究中流体 密度只依赖于温度场, 而浓度场只充当内热源, 即带放热效应的瑞利-伯纳德对流(IHRBC). 线性稳定性分析揭示出最不稳定模态总是 静态模态(相速度为零). 临界瑞利数(衡量不稳定驱动力的大小)随着施密特数(粘性与浓度扩散系数的比值)的增大而减小, 随普朗特数 (粘性与热扩散系数的比值)的增大而增大. 同时针对充分发展的流动开展非线性三维直接数值模拟研究. 结果表明适用于IHDDC的理 论模型也可以用来描述IHRBC的传输特性. 浓度场流动结构出现垂向的非对称性, 从顶部下降的羽状结构尺度要小于从底部上升的结 构尺度.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
D. J. Tritton, Internally heated convection in the atmosphere of Venus and in the laboratory, Nature 257, 110 (1975).
P. de Deckker, and W. D. Williams, Limnology in Australia (Springer Science & Business Media, Berlin, 2012).
G. Schubert, D. L. Turcotte, and P. Olson, Mantle Convection in the Earth and Planets (Cambridge University Press, Cambridge, 2001).
R. Krishnamurti, Convection induced by selective absorption of radiation: A laboratory model of conditional instability, Dyn. Atmos. Oceans 27, 367 (1998).
Y. Tasaka, and Y. Takeda, Effects of heat source distribution on natural convection induced by internal heating, Int. J. Heat Mass Transfer 48, 1164 (2005).
H. Wei, and Y. T. Chen, Numerical investigation of geometric size effect on the internal heated water pool natural convection behavior, Prog. Nucl. Energy 112, 34 (2019).
S. Verma, and R. Das, Effect of ground heat extraction on stability and thermal performance of solar ponds considering imperfect heat transfer, Sol. Energy 198, 596 (2020).
D. J. Tritton, and M. N. Zarraga, Convection in horizontal layers with internal heat generation. Experiments, J. Fluid Mech. 30, 21 (1967).
P. H. Roberts, Convection in horizontal layers with internal heat generation. Theory, J. Fluid Mech. 30, 33 (1967).
B. Travis, S. Weinstein, and P. Olson, Three-dimensional convection planforms with internal heat generation, Geophys. Res. Lett. 17, 243 (1990).
C. Sotin, and S. Labrosse, Three-dimensional thermal convection in an iso-viscous, infinite Prandtl number fluid heated from within and from below: Applications to the transfer of heat through planetary mantles, Phys. Earth Planet. Inter. 112, 171 (1999).
D. Goluskin, and E. P. van der Poel, Penetrative internally heated convection in two and three dimensions, J. Fluid Mech. 791, R6 (2016), arXiv: 1511.05966.
Z. Ding, and J. Wu, Coherent heat transport in two-dimensional penetrative Rayleigh-Bénard convection, J. Fluid Mech. 920, A48 (2021).
B. Straughan, Global stability for convection induced by absorption of radiation, Dyn. Atmos. Oceans 35, 351 (2002).
A. J. Harfash, Three dimensional simulation of radiation induced convection, Appl. Math. Comput. 227, 92 (2014).
A. J. Harfash, Three dimensional simulations and stability analysis for convection induced by absorption of radiation, Int. J. Numer. Methods Heat Fluid Flow 25, 810 (2015).
Y. Du, M. Zhang, and Y. Yang, Two-component convection flow driven by a heat-releasing concentration field, J. Fluid Mech. 929, A35 (2021).
S. Grossmann, and D. Lohse, Scaling in thermal convection: A unifying theory, J. Fluid Mech. 407, 27 (2000), arXiv: chao-dyn/9909032.
S. Grossmann, and D. Lohse, Thermal convection for large prandtl numbers, Phys. Rev. Lett. 86, 3316 (2001), arXiv: nlin/0011015.
S. Grossmann, and D. Lohse, Prandtl and Rayleigh number dependence of the Reynolds number in turbulent thermal convection, Phys. Rev. E 66, 016305 (2002).
S. Grossmann, and D. Lohse, Fluctuations in turbulent Rayleigh-Bénard convection: The role of plumes, Phys. Fluids 16, 4462 (2004).
L. Zhang, G. Y. Ding, and K. Q. Xia, On the effective horizontal buoyancy in turbulent thermal convection generated by cell tilting, J. Fluid Mech. 914, A15 (2021).
T. Zürner, Refined mean field model of heat and momentum transfer in magnetoconvection, Phys. Fluids 32, 107101 (2020), arXiv: 2005.10205.
Y. Yang, R. Verzicco, and D. Lohse, Two-scalar turbulent Rayleigh-Bénard convection: numerical simulations and unifying theory, J. Fluid Mech. 848, 648 (2018), arXiv: 1712.05519.
Q. Wang, D. Lohse, and O. Shishkina, Scaling in internally heated convection: A unifying theory, Geophys. Res. Lett. 48, e91198 (2021), arXiv: 2010.05789.
J. Z. Wu, B. F. Wang, and Q. Zhou, Massive heat transfer enhancement of Rayleigh-Bénard turbulence over rough surfaces and under horizontal vibration, Acta Mech. Sin. 38, 321319 (2022).
T. J. Wicks, and A. A. Hill, Stability of double-diffusive convection induced by selective absorption of radiation in a fluid layer, Continuum Mech. Thermodyn. 24, 229 (2012).
R. Ostilla-Monico, Y. Yang, E. P. van der Poel, D. Lohse, and R. Verzicco, A multiple-resolution strategy for direct numerical simulation of scalar turbulence, J. Comput. Phys. 301, 308 (2015), arXiv: 1502.01874.
G. Grötzbach, Spatial resolution requirements for direct numerical simulation of the Rayleigh-Bénard convection, J. Comput. Phys. 49, 241 (1983).
B. I. Shraiman, and E. D. Siggia, Heat transport in high-Rayleigh-number convection, Phys. Rev. A 42, 3650 (1990).
Funding
This work was supported by the Major Research Plan of National Natural Science Foundation of China (Grant Nos. 91852107 and 91752202). Mengqi Zhang acknowledges the financial support from the Ministry of Education, Singapore (MOE WBS No. R-265-000-689-114).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Du, Y., Zhang, M. & Yang, Y. Thermal convection driven by a heat-releasing scalar component. Acta Mech. Sin. 38, 321584 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10409-022-21584-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10409-022-21584-7