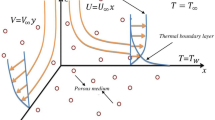
Abstract
The effect of local thermal non-equilibrium on the onset of double-diffusive convection in a porous medium consisting of two horizontal layers, each internally heated, is studied analytically. Linear stability theory is applied. Variations of permeability, fluid thermal conductivity, solid thermal conductivity, heat source strength in the solid and fluid phases, concentration source strength, interphase heat transfer coefficient and porosity are considered. In addition to the major effects from heterogeneity of permeability, fluid thermal conductivity and heat source strength in the fluid phase as with single-diffusive convection, it is now found that major effects arise from heterogeneity of solutal source strength and porosity. We used two different methods to obtain our results. Analytical results that readily show the effects of parameter variations were obtained by using a low-term Galerkin approximation, which was validated by using a highly accurate numerical solver. Since for a problem with large number of parameters simple analytical results are highly desirable, the quantification of the accuracy of a low-term Galerkin approximation presented in our paper is quite important.


Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- a :
-
Dimensionless horizontal wavenumber
- C :
-
Dimensionless concentration, \(\frac{(\rho c)_\mathrm{f} \rho _0 g\beta _\mathrm{C} K_1 H}{\mu k_\mathrm{f1} }(C^{*} -C_0)\)
- \(C^{*}\) :
-
Solute concentration
- \(C_{0}\) :
-
Solute concentration at each of the upper and lower boundaries
- D :
-
d/dz
- \(D_\mathrm{C}\) :
-
Solutal diffusivity
- h :
-
Interface heat transfer coefficient (incorporating the specific surface area) between the fluid and solid particles
- \(\hat{{h}}\) :
-
Parameter defined in Eq. (18)
- \(h_\mathrm{r}\) :
-
Interface heat transfer coefficient ratio, \(h_{2}/h_{1}\)
- g :
-
Gravitational acceleration
- g :
-
Gravitational acceleration vector
- H :
-
Dimensional layer depth
- k :
-
Thermal conductivity
- \(k_\mathrm{f}\) :
-
Thermal conductivity of the fluid phase
- \(\hat{{k}}_\mathrm{f}\) :
-
Parameter defined in Eq. (18)
- \(k_\mathrm{fr}\) :
-
Fluid thermal conductivity ratio, \(k_\mathrm{f2}/k_\mathrm{f1}\)
- \(k_\mathrm{s}\) :
-
Thermal conductivity of the solid phase
- \(\hat{{k}}_\mathrm{s}\) :
-
Parameter defined in Eq. (18)
- \(k_\mathrm{sr}\) :
-
Solid thermal conductivity ratio, \(k_\mathrm{s2}/k_\mathrm{s1}\)
- K :
-
Permeability of the porous medium
- \(K_\mathrm{r}\) :
-
Permeability ratio, \(K_{2}/K_{1}\)
- \(\hat{{K}}\) :
-
Parameter defined in Eq. (18)
- Le :
-
Lewis number, \(\frac{k_\mathrm{f1} }{(\rho c)_\mathrm{f} D_\mathrm{C}}\)
- N :
-
Interface heat transfer parameter, \(\frac{h_1 H^{2}}{\phi _1 k_\mathrm{f1}}\)
- P :
-
Dimensionless pressure, \(\frac{(\rho c)_\mathrm{f} K_1 }{\mu k_\mathrm{f1} }P^{*}\)
- \(P^{*}\) :
-
Pressure, excess over hydrostatic
- Q :
-
Volumetric heat source strength
- \(Q_\mathrm{C}\) :
-
Volumetric solute source strength
- \(\hat{{Q}}_\mathrm{C}\) :
-
Parameter defined in Eq. (18)
- \(Q_\mathrm{Cr}\) :
-
Solute source ratio, \(Q_\mathrm{C2}/Q_\mathrm{C1}\)
- \(\hat{{Q}}_\mathrm{f}\) :
-
Parameter defined in Eq. (18)
- \(Q_\mathrm{fr}\) :
-
Heat source ratio in the fluid phase, \(Q_\mathrm{f2}/Q_\mathrm{f1}\)
- \(\hat{{Q}}_\mathrm{s}\) :
-
Parameter defined in Eq. (18)
- \(Q_\mathrm{sr}\) :
-
Heat source ratio in the solid phase, \(Q_\mathrm{s2}/Q_\mathrm{s1}\)
- Ra :
-
Internal thermal Rayleigh number, \(\frac{(\rho c)_\mathrm{f} \rho _0 g\beta K_1 H^{3}Q_\mathrm{f1} }{2\mu k_\mathrm{f1}^{2}}\)
- \(Ra_\mathrm{C}\) :
-
Internal solutal Rayleigh number, \(\frac{(\rho c)_\mathrm{f} \rho _0 g\beta _\mathrm{C} K_1 H^{3}Q_\mathrm{C1} }{2\mu k_\mathrm{f1} D_\mathrm{C}}\)
- \({Ra}_\mathrm{eff}\) :
-
Effective combined Rayleigh number defined in Eq. (63)
- t :
-
Dimensionless time,\(\frac{k_\mathrm{f1} }{(\rho c)_\mathrm{f} H^{2}}t^{*}\)
- \(t^{*}\) :
-
Time
- T :
-
Dimensionless temperature, \(\frac{(\rho c)_\mathrm{f} \rho _0 g\beta K_1 H}{\mu k_\mathrm{f1} }(T^{*} -T_0)\)
- \(T^{*}\) :
-
Temperature
- \(T_{0}\) :
-
Temperature at each of the upper and lower boundaries
- (u, v, w):
-
Dimensionless velocity components, \(\frac{(\rho c)_\mathrm{f} H}{k_\mathrm{f1} }(u^{*},v^{*},w^{*})\)
- \(\mathbf{u}^{*}\) :
-
Darcy velocity, \((u^{*},v^{*},w^{*})\)
- (x, y, z):
-
Dimensionless Cartesian coordinates, \((x^{*},y^{*},z^{*})/H\); z is the vertically upward coordinate
- \((x^{*},y^{*},z^{*})\) :
-
Cartesian coordinates; \(z^{*}\) is the vertically upward coordinate
- \(\alpha \) :
-
Modified thermal diffusivity ratio, \(\frac{(\rho c)_\mathrm{s1} }{(\rho c)_\mathrm{f1} }\frac{k_\mathrm{f1} }{k_\mathrm{s1}}\)
- \(\beta \) :
-
Thermal expansion coefficient of the fluid
- \(\beta _\mathrm{C}\) :
-
Solutal expansion coefficient of the fluid
- \(\gamma \) :
-
Modified thermal conductivity ratio, \(\frac{\phi _1 k_\mathrm{f1} }{(1-\phi _1)k_\mathrm{s1}}\)
- \(\delta \) :
-
Dimensionless layer depth ratio (interface position)
- \(\hat{{\delta }}\) :
-
Parameter defined in Eq. (18)
- \(\delta _\mathrm{r}\) :
-
Inverse solid fraction ratio, \(\frac{1-\phi _1 }{1-\phi _2}\)
- \(\hat{{\varepsilon }}\) :
-
Parameter defined in Eq. (18)
- \(\varepsilon _\mathrm{r}\) :
-
Solid heat capacity ratio, \(\frac{(\rho c)_\mathrm{s2} }{(\rho c)_\mathrm{s1}}\)
- \(\mu \) :
-
Viscosity of the fluid
- \(\rho _{0}\) :
-
Fluid density at temperature \(T_{0}\)
- \(\rho _\mathrm{f}\) :
-
Fluid density
- \((\rho c)_\mathrm{f}\) :
-
Heat capacity of the fluid
- \((\rho c)_\mathrm{s}\) :
-
Heat capacity of the solid
- \(\phi \) :
-
Porosity
- \(\hat{{\phi }}\) :
-
Parameter defined in Eq. (18)
- \(\phi _\mathrm{r}\) :
-
Porosity ratio, \(\phi _{2}/\phi _{1}\)
- \(\mathrm{B}\) :
-
Basic state
- \(\mathrm{f}\) :
-
Fluid phase
- \(\mathrm{r}\) :
-
Relative quantity
- \(\mathrm{s}\) :
-
Solid phase
- 1:
-
The region \(0\le z^{*}<\delta H\)
- 2:
-
The region \(\delta H\le z^{*}\le H\)
- \('\) :
-
Perturbation variable
- *:
-
Dimensional variable
References
Barletta, A., Storesletten, L.: Thermoconvective instabilities in an inclined porous channel heated from below. Int. J. Heat Mass Transf. 54, 2724–2733 (2011)
Kulacki, F., Ramchandani, R.: Hydrodynamic instability in a porous layer saturated with a heat generating fluid. Thermo Fluid Dyn. 8, 179–185 (1975)
Kuznetsov, A.V., Nield, D.A.: The effect of strong heterogeneity on the onset of convection induced by internal heating in a porous medium: a layered model. Transp. Porous Media 99, 85–100 (2013)
Kuznetsov, A.V., Nield, D.A.: Local thermal non-equilibrium and heterogeneity effects on the onset of convection in an internally heated porous medium. Transp. Porous Media 102, 15–30 (2014)
Kuznetsov, A.V., Nield, D.A.: Local thermal non-equilibrium effects on the onset of convection in an internally heated layered porous medium with vertical throughflow. Int. J. Therm. Sci. 92, 97–105 (2015)
Nield, D.A.: Effects of local thermal nonequilibrium in steady convective processes in a saturated porous medium: forced convection in a channel. J. Porous Media 1, 181–186 (1998)
Nield, D.A.: A note on local thermal non-equilibrium in porous media near boundaries and interfaces. Transp. Porous Media 95, 581–584 (2012)
Nield, D.A., Bejan, A.: Convection in Porous Media, 4th edn. Springer, New York (2013)
Nield, D.A., Kuznetsov, A.V.: The effect of heterogeneity on the onset of convection induced by internal heating in a porous medium: a layered model. Transp. Porous Media 100, 83–99 (2013)
Nield, D.A., Kuznetsov, A.V.: Local thermal non-equilibrium and heterogeneity effects on the onset of convection in a layered porous medium. Transp. Porous Media 102, 1–13 (2014)
Nield, D.A., Kuznetsov, A.V.: Local thermal non-equilibrium and heterogeneity effects on the onset of convection in a layered porous medium with vertical throughflow. J. Porous Media 18, 125–136 (2015)
Nield, D.A., Kuznetsov, A.V., Barletta, A., Celli, M.: The effects of double diffusion and local thermal non-equilibrium on the onset of convection in a layered porous medium: non-oscillatory instability. Transp. Porous Media 107, 261–279 (2015)
Patil, P.M., Rees, D.A.S.: Linear instability of a horizontal thermal boundary layer formed by vertical throughflow in a porous medium: the effect of local thermal nonequilibrium. Transp. Porous Media 99, 207–227 (2013)
Rees, D.A.S., Bassom, A.P.: The onset of Darcy-Bénard convection in an inclined layer heated from below. Acta Mech. 144, 103–118 (2000)
Straughan, B.: Stability and Wave Motion in Porous Media. Springer, New York (2008)
Vadász, P.: Heat conduction in nanofluid suspensions. ASME J. Heat Transf. 128, 465–477 (2006)
Acknowledgments
A.V.K. gratefully acknowledges the support of the Alexander von Humboldt Foundation through the Humboldt Research Award.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kuznetsov, A.V., Nield, D.A., Barletta, A. et al. Local Thermal Non-equilibrium and Heterogeneity Effects on the Onset of Double-Diffusive Convection in an Internally Heated and Soluted Porous Medium. Transp Porous Med 109, 393–409 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11242-015-0525-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11242-015-0525-6